Promoter for regulating and controlling expression of genes in non-secretory type glandular hairs and application of promoter
A non-secretory glandular hair, gene regulation technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve the problems of time and space regulation of target genes, excessive consumption of cell material and energy, harm and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Cloning of the Genome Sequence of the Promoter from the Artemisia annua Genome
[0031] 1. Cultivate aseptic vaccines of Artemisia annua:
[0032] Artemisia annua seeds were soaked in ethanol with a volume fraction of 75% for 1 min, then soaked in 20% (w / v) NaClO for 20 min, rinsed with sterile water for 3 to 4 times, blotted the surface moisture with sterile absorbent paper, and inoculated Cultivate on hormone-free MS solid medium at 25°C and 16h / 8h (sunlight / darkness) under light, after 14 days you can obtain sterile A. annua seedlings;
[0033] 2. Genomic DNA extraction
[0034] Put a leaf of Artemisia annua (1cm 2 About the size, take it in an ice box), add 2 steel balls. Add 300 μL TPS buffer (operate in a fume hood, TPS contains mercaptoethanol), shake at 55-60 Hz for 100 seconds. Then add 300 μL TPSbuffer (fume hood). Water bath at 65°C for 1h (shake every 20min), and the time can be extended appropriately, up to 1.5h. Cool to room temperature and centrifug...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Analyze the cis-acting elements of the AaTPS7 gene promoter to determine the type of AaTPS7 gene promoter
[0051] The length of the AaTPS7 gene promoter sequence obtained in the present invention is 1167bp. In order to find the cis-acting elements on the promoter, the promoter of AaTPS7 gene was analyzed with Plantcare (http: / / bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be / webtools / plantcare / html / ). The analysis found that in addition to TATAbox and CAATbox, there are many cis-acting elements on the promoter of polycloning: CGTCA-motif, HSE, MBS, MRE, TC-richrepeats, WUN-motif, etc.
[0052] The cis-acting elements in the promoter sequence are shown in Table 4:
[0053] Table 4: Analysis of regulatory elements in the promoter sequence
[0054]
[0055] In Table 4, the positions of -980, -907, -678 and -130 refer to the corresponding positions in the sequence listed in Example 1.
[0056] CGTCA-motif is a methyl jasmonate response element; HES responds to heat stress; MBS and MRE ar...
Embodiment 3
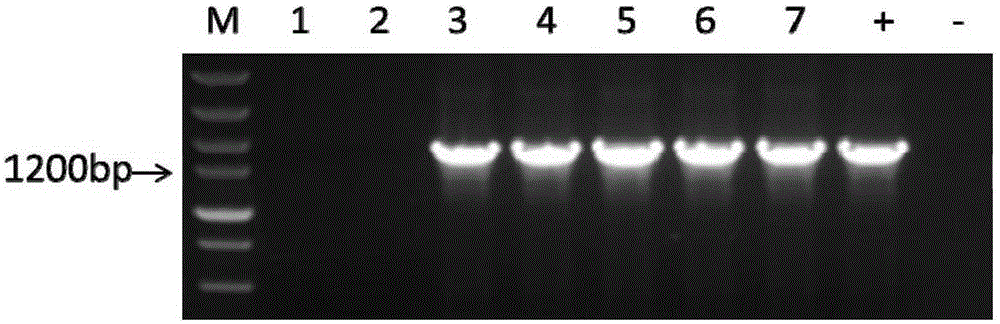
[0058] Connect the obtained promoter into the pCAMBIA-1391z vector and fuse the GUS reporter gene
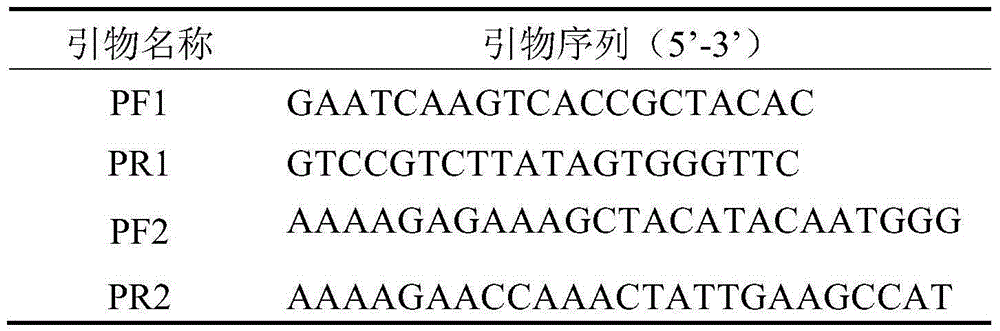
[0059] In order to study the expression of the gene promoter in different plant parts, the promoter proTPS7 of the AaTPS7 gene was connected to the pCAMBIA-1391z vector and fused with the GUS reporter gene. site, the NcoI restriction site was introduced into the reverse primer, and the primer sequence is shown in the table below:
[0060] Table 5 pCAMBIA1391z-proTPS7 vector constructs PCR primers
[0061]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com