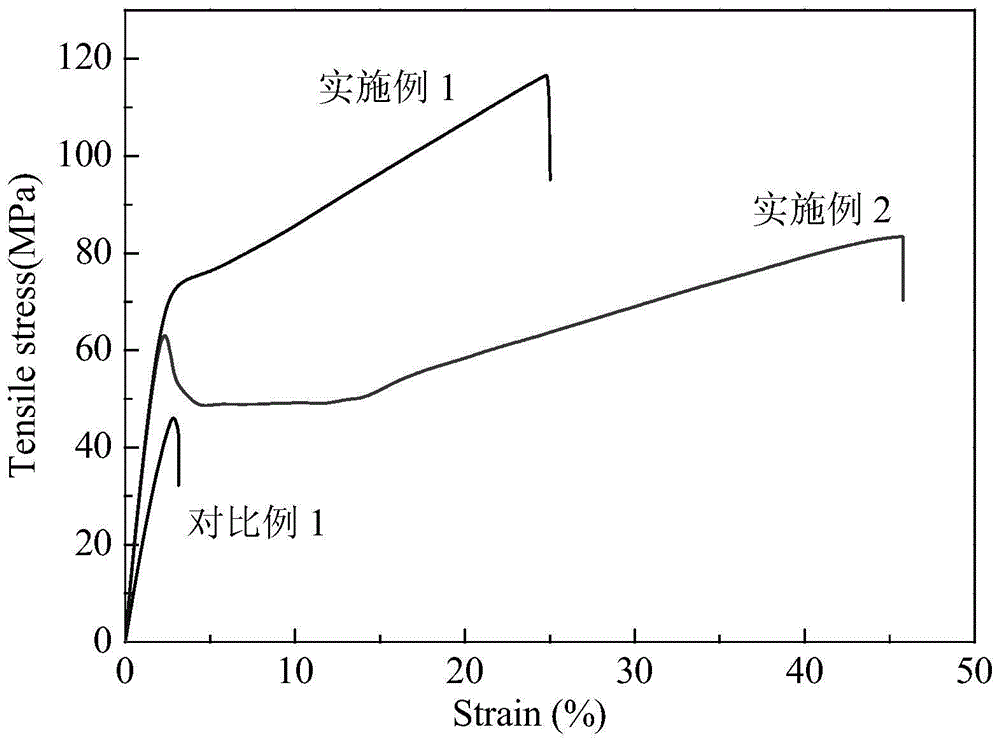
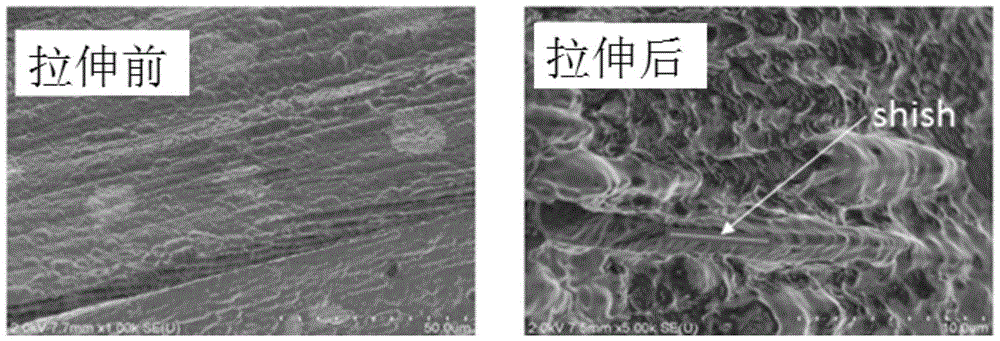
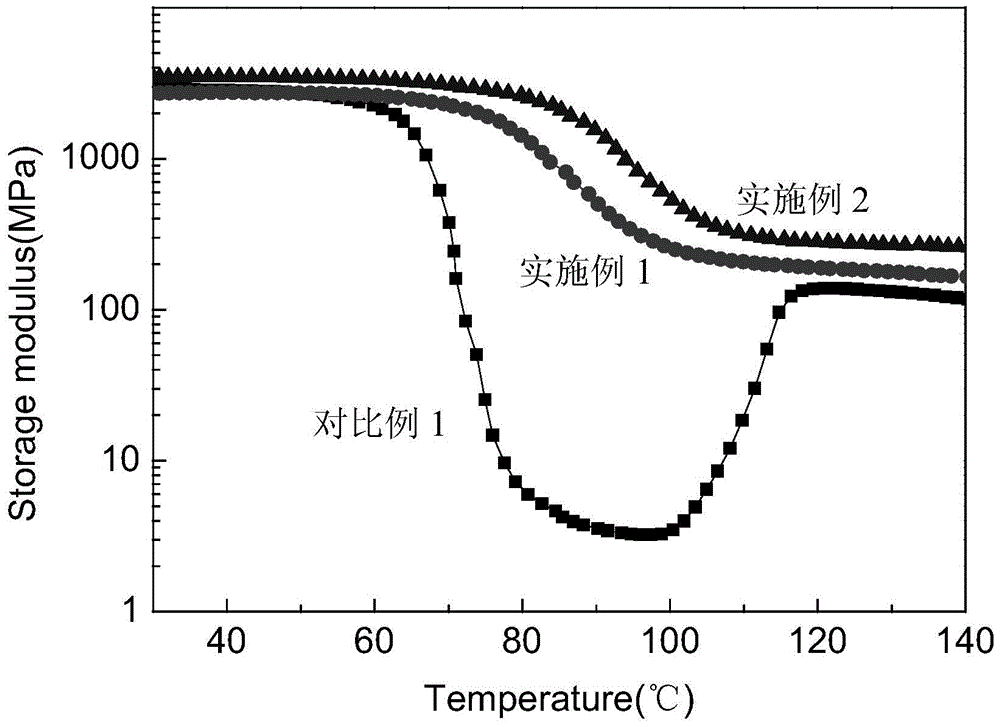
A kind of preparation method of high-strength and high-toughness heat-resistant polylactic acid base film material
A polylactic acid base film and polylactic acid technology, which is applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve the problems that the reinforcing effect of inorganic fillers cannot be fully exerted, the inorganic fillers cannot be completely compatible with polylactic acid, and the interface stress transfer efficiency is low. Achieve the effect of improving the interface stress transfer efficiency, low cost and easy industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033]Weigh the dried N,N'-1,2-bis(phenyloxalamide)-ethane and polylactic acid (4032D), add it to the torque rheometer according to the mass ratio of 0.5 / 99.5, and set it at 180°C After melt blending at 50rpm for 4min, the resulting composition was hot-pressed at 230°C by a flat vulcanizer to form a 1mm-thick sheet, then kept at 150°C for 2min, and then cooled to room temperature at a rate of 50°C / min. spare. The obtained sheet was stretched three times in hot air at 75°C, cooled to room temperature, and cut into standard specimens for mechanical property testing according to relevant standards. The test results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Weigh the dried N,N'-1,2-bis(phenyloxalamide)-ethane and polylactic acid (4032D), add it to the torque rheometer according to the mass ratio of 0.5 / 99.5, and set it at 180°C After melt blending at 50rpm for 4min, the resulting composition was hot-pressed at 230°C by a flat vulcanizer to form a 1mm-thick sheet, then kept at 150°C for 2min, and then cooled to room temperature at a rate of 50°C / min. spare. The resulting sheet was stretched 5 times in hot air at 75°C, cooled to room temperature, and cut into standard specimens for mechanical property testing according to relevant standards. The test results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Weigh the dried N,N'-ethyl-bis-(2-aza-ethyl acetate) bisoxamide and polylactic acid (4032D), and add them to the torque rheometer at a mass ratio of 1.0 / 99.0 , after melt blending at 180°C and 50rpm for 4min, the resulting composition was hot-pressed into a 1mm-thick sheet at 220°C by a flat vulcanizer, then kept at 140°C for 3min, and then heated at 50°C / min Speed down to room temperature and set aside. The resulting sheet was stretched 5 times in hot air at 75°C, cooled to room temperature, and cut into standard specimens for mechanical property testing according to relevant standards. The test results are listed in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com