Heavy metal collecting agent and thallium-removal method used for sintering desulfurization waste water
A heavy metal trapping agent and desulfurization wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of unstable removal efficiency, high treatment cost, long reaction time, etc., to achieve The effect of reducing the dosage of chemicals, good trapping effect and good removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Mix 15g of urea, 2g of diethylenetriamine, 0.4g of epichlorohydrin with water, control the reaction temperature at 25℃ and react for 1h, then add 2.5ml of carbon disulfide dropwise to keep the reaction temperature unchanged, continue stirring for 3h, and then heat up After reaching 55°C, the reaction was continued for 2 hours. After the temperature dropped to room temperature, 0.4 g of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate was added, and after stirring for 15 minutes, a new agent M1 was obtained.
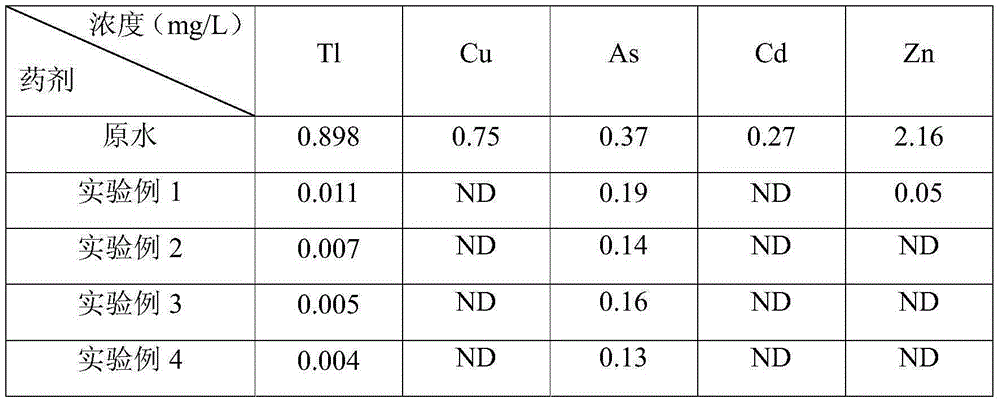
[0029] The experimental wastewater was taken from the sintering desulfurization wastewater of a steel plant, the pH of the water sample was 6.8, and the thallium concentration was 0.898 mg / L. Take 500ml waste water adjusted to pH=9 by CaO, add 1.5gPAC, stir for 10min and then stand still, take 400ml supernatant, add 1.4gM1 and 0.2gPAM and continue stirring for 10min, take the supernatant and measure the thallium concentration after standing.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Mix 15g of urea with 2g of diethylenetriamine, 0.4g of epichlorohydrin and water, control the reaction temperature at 25℃ and react for 1h, then add 2.5ml of carbon disulfide dropwise to keep the reaction temperature unchanged, continue stirring for 3h, and then heat up After reaching 55°C, the reaction was continued for 2 hours. After the temperature dropped to room temperature, 0.4 g of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate was added, and after stirring for 15 minutes, a new agent M1 was obtained.
[0031] The experimental wastewater was taken from the sintering desulfurization wastewater of a steel plant, the pH of the water sample was 6.8, and the thallium concentration was 0.898 mg / L. Take 500ml waste water adjusted by CaO to pH=9, add 1.8g PAC, stir for 10min and then stand still, take 400ml supernatant liquid and add 1.2gM1 and 0.3gPAM to continue stirring for 10min, take the supernatant liquid and measure the thallium concentration after standing.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Mix 20g of urea, 3g of diethylenetriamine, 0.6g of epichlorohydrin with water, control the reaction temperature at 25℃ and react for 1h, then add 3ml of carbon disulfide dropwise to keep the reaction temperature unchanged, continue stirring for 3.5h, and then heat up After reaching 60°C, the reaction was continued for 2 hours. After the temperature was lowered to room temperature, 0.6 g of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate was added, and after stirring for 15 minutes, a new agent M2 was obtained.
[0033] The experimental wastewater was taken from the sintering desulfurization wastewater of a steel plant, the pH of the water sample was 6.8, and the thallium concentration was 0.898 mg / L. Take 500ml waste water adjusted to pH=9 by CaO, add 1.6gPAC, stir for 10min and then stand still, take 400ml supernatant and add new medicine 1gM2 and 0.2gPAM and continue to stir for 10min, take the supernatant and measure thallium concentration after standing.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com