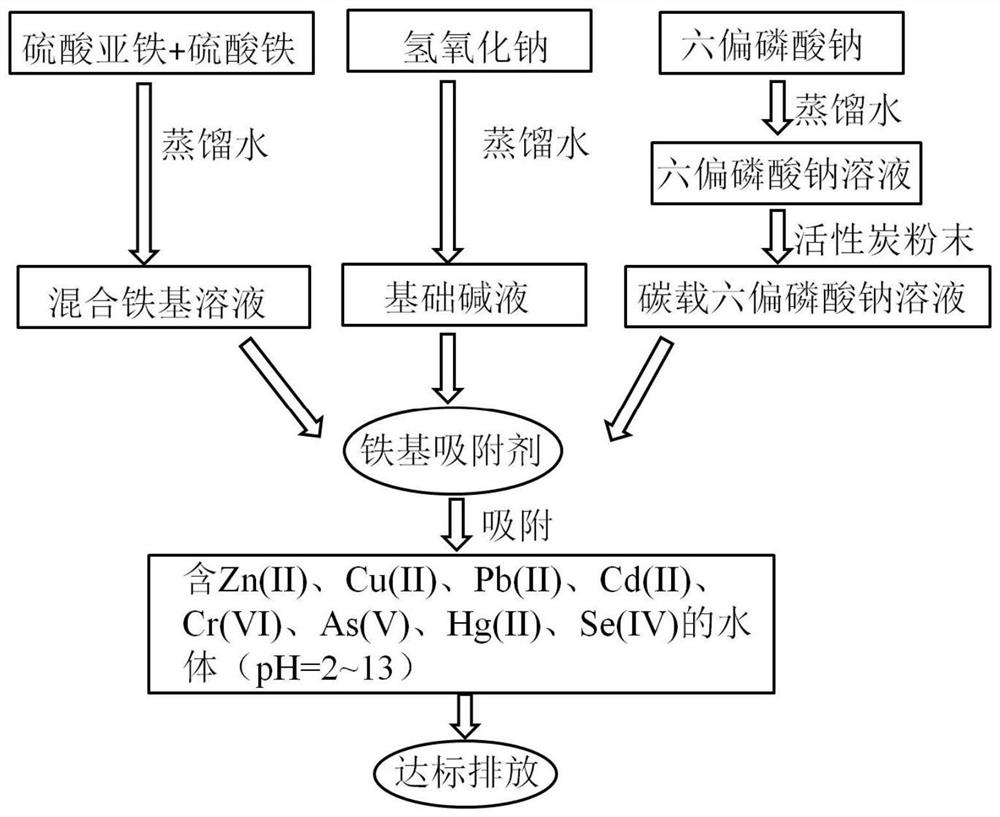
Iron-based adsorbent and preparation method thereof
An adsorbent, iron-based technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the number of active sites on the surface of the adsorption material, reducing the adsorption of heavy metal cations, unfavorable solid-liquid separation, etc. problems, achieve the effects of reducing loss, reducing oxidation rate, and enhancing stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The effect of different molar ratios of Fe(II) and Fe(III) on the removal of various heavy metal ions in water:
[0029] Preparation of mixed iron-based solution: according to the molar ratio of ferrous iron Fe(II) to ferric iron Fe(III) is 2:1, 2.5:1, 3:1, respectively weigh the corresponding mass of ferrous sulfate and ferric sulfate, Mix it into distilled water at the same time, stir until completely dissolved in a sealed state, prepare three mixed iron-based solutions with a concentration of 0.5moL / L respectively, and regard the volume of the mixed iron-based solution as 5 unit volumes.
[0030] Basic lye preparation: according to OH - The molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 2:1, weigh sodium hydroxide, mix it into distilled water, stir until completely dissolved in a sealed state, and prepare a base with a concentration of 2.0moL / L and a volume of 2.5 unit volumes lye.
[0031] Sodium hexametaphosphate solution preparation: according to [P 6 o 18 ] 6- Weigh sodiu...
Embodiment 2
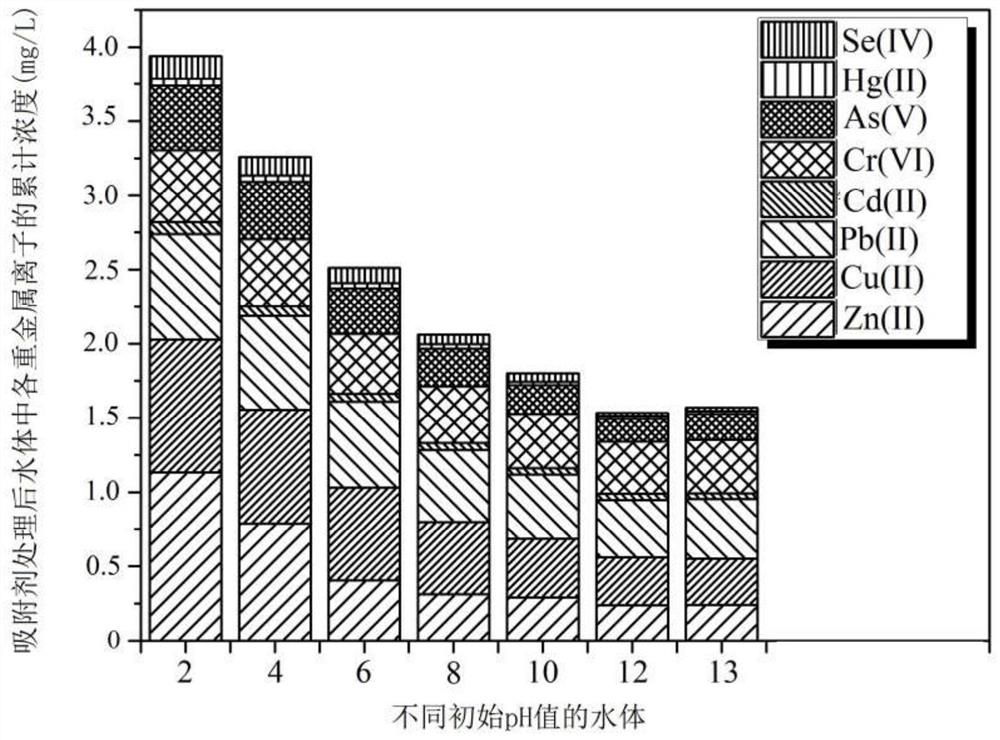
[0040] Different OH - The effect of the molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) on the removal of various heavy metal ions in water:
[0041] Preparation process is with embodiment 1, and embodiment 1 difference is:
[0042] Preparation of mixed iron-based solution: The molar ratio of Fe(II) to Fe(III) was 2.5:1, and three mixed iron-based solutions with a concentration of 0.75moL / L and a volume of 5 unit volumes were prepared.
[0043] Basic lye preparation: OH - The molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, and the three concentrations are 2.5moL / L, 3.75moL / L and 5moL / L respectively, and the volume is 3 units volume of base lye.
[0044] Sodium hexametaphosphate solution preparation: [P 6 o 18 ] 6- The molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 4:6, and a sodium hexametaphosphate solution with a concentration of 1.25moL / L and a volume of 2 unit volumes is prepared.
[0045] Preparation of carbon-supported sodium hexametaphosphate solution: The solid / liquid ratio of activated carbon...
Embodiment 3
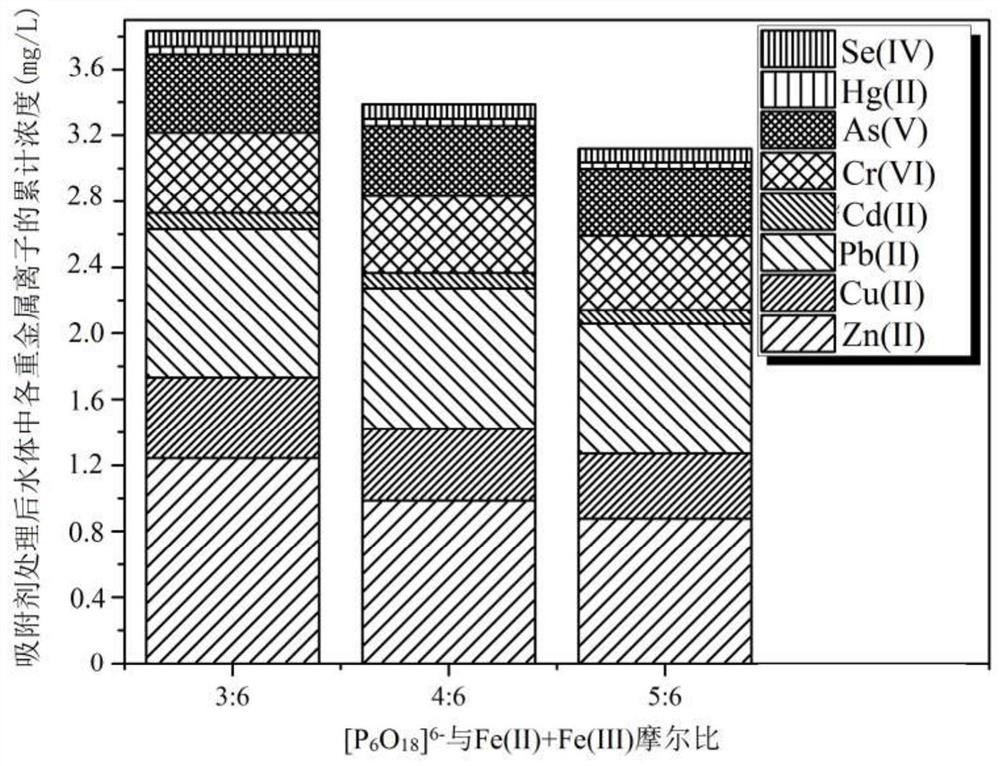
[0052] Different [P 6 o 18 ] 6- The effect of the molar ratio of Fe(II)+Fe(III) on the removal of various heavy metal ions in water:
[0053] Preparation process is with embodiment 1, and embodiment 1 difference is:
[0054] Preparation of mixed iron-based solution: The molar ratio of Fe(II) to Fe(III) was 2.5:1, and three mixed iron-based solutions with a concentration of 1moL / L and a volume of 5 unit volumes were prepared.
[0055] Basic lye preparation: OH - The molar ratio to Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 3:1, and the basic lye with a concentration of 4.29moL / L and a volume of 3.5 unit volumes is prepared.
[0056] Sodium hexametaphosphate solution preparation: [P 6 o 18 ] 6- The molar ratio to Fe(II)+Fe(III) is 3:6, 4:6, 5:6, and the prepared concentration is 1.67moL / L, 2.22moL / L, 2.78moL / L, and the volume is 1.5 unit volume of three parts sodium hexametaphosphate solution.
[0057] Preparation of carbon-supported sodium hexametaphosphate solution: The solid / liquid ratio of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com