Mineral separation technology for recycling graphite and mica in graphite tailings
A technology for graphite tailings and medium graphite is applied in the field of beneficiation technology for recovering graphite and mica in graphite tailings, and can solve the problems of low grade recovery rate of graphite and mica concentrate, unsatisfactory separation and recovery effect of graphite and mica, etc. , to achieve the effect of improving resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The graphite content in the tailings pond of the graphite mining area in Luobei County, Heilongjiang is 4.98%, the mica content is 5.45%, the feldsparized mica accounts for 19.22%, the quartz accounts for 21.35%, the feldspar accounts for 19.65%, the garnet accounts for 7.0%, and the anorthite Accounting for 5.73%, pyroxene 3.83%, tremolite 3.88%, other non-metallic gangue minerals 8.91%. The sieving analysis of graphite tailings shows that -0.074mm accounts for 89.90%, the particle size is relatively fine, and the gangue minerals are complex.
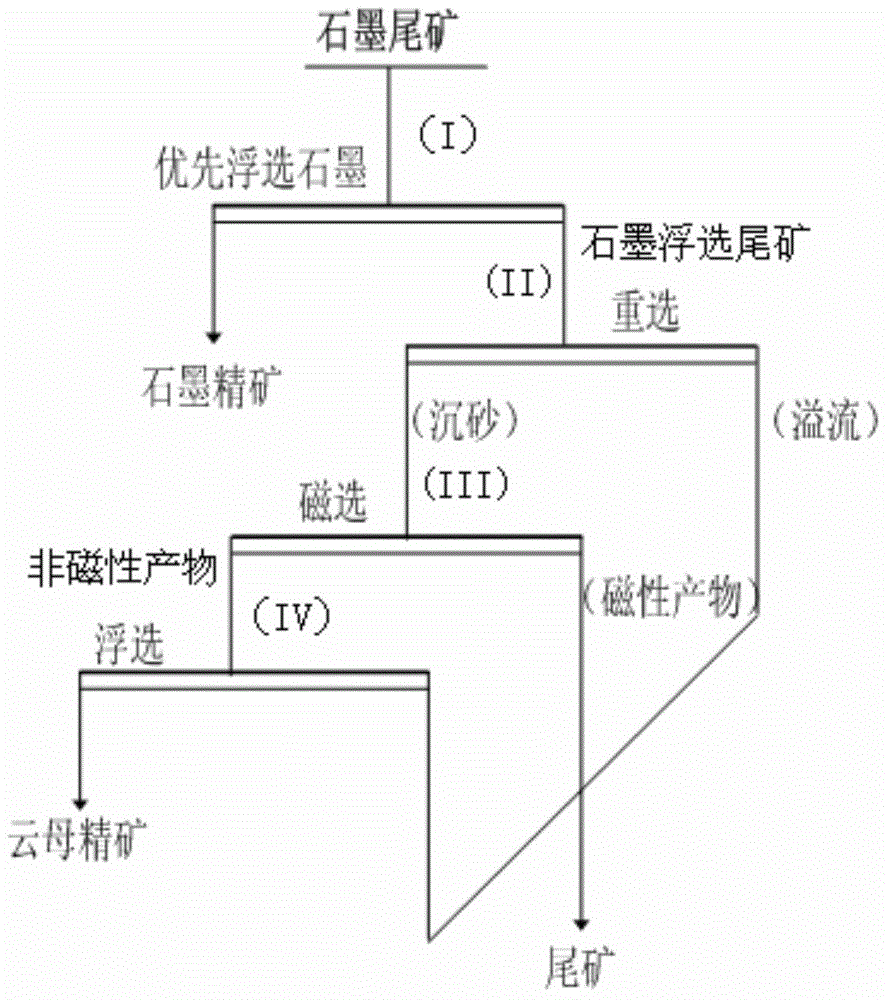
[0034] process such as figure 1 shown. The add-on of depressant, collector, foaming agent in step I is in every ton of graphite tailings, and the add-on of inhibitor, collector, foaming agent in step IV is in per ton of non-magnetic minerals.
[0035] Step I: The above-mentioned graphite tailings are not ground and directly enter the flotation machine to preferentially recover graphite, the mass concentration of the pulp is 3...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Graphite tailings are taken from a graphite tailings pool in Hubei Province, which contains 3.85% amorphous carbon, 13.16% mica, 43.15% quartz, 20.81% feldspar, 11.88% montmorillonite, and epidote 2.05%, magnetite content 1.07%, other mineral content 4.03%. The mineral particle size is relatively coarse, -0.074mm accounts for 60.84%, and the mineral composition is complex. This process is suitable for the graphite tailings.
[0041] process such as figure 1 shown. The add-on of depressant, collector, foaming agent in step I is in every ton of graphite tailings, and the add-on of inhibitor, collector, foaming agent in step IV is in per ton of non-magnetic minerals.
[0042] Step I: Since the particle size of the graphite tailings taken from the tailings pond is relatively coarse, the graphite tailings are firstly ground, and the grinding fineness is -0.074mm, accounting for 90.00%, and then the ground tailings are subjected to flotation. The mass concentration of ore...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com