Method for producing fully water-soluble monoammonium phosphate and co-producing ammonium magnesium phosphate by wet process phosphoric acid
A technology of water-soluble monoammonium phosphate and wet-process phosphoric acid, which is applied in the fields of phosphate, phosphorus oxyacids, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of product impurity, filtration and impurity removal, etc., to improve production efficiency and benefit, Good filtration performance, enhanced purity and solubility effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
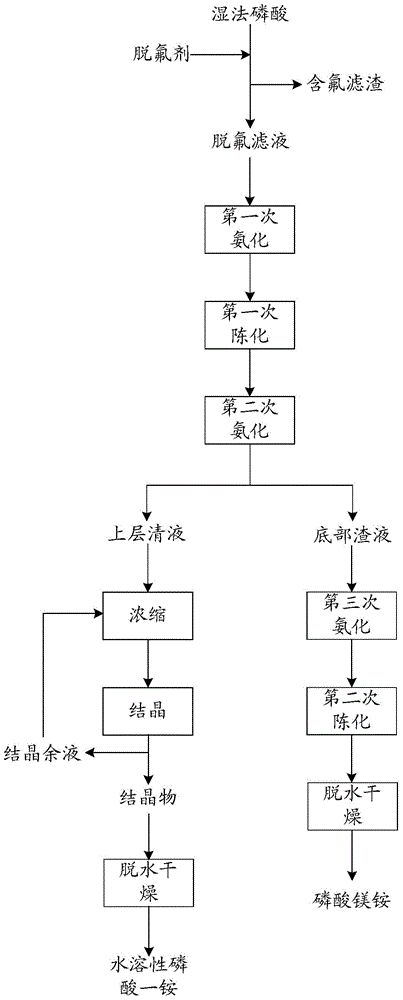
[0042] S10. Add 20 g of sodium sulfate to the raw material liquid of wet-process phosphoric acid, react at room temperature for 1-2 hours to perform pre-defluorination, remove 70% of fluorine in wet-process phosphoric acid, filter to obtain defluorinated filtrate and filter residue, and use 50 g of filter residue to deionize The water was washed several times until it was acid-free, and 23g of sodium fluorosilicate product was obtained after drying. Since the washing water contained the material components of wet-process phosphoric acid, it was returned to the defluorination filtrate during operation to avoid waste of raw materials, and 1040g of defluorination filtrate was obtained. Fluorine wet-process phosphoric acid.
[0043] S20, passing ammonia gas into 1040 g of defluorinated wet-process phosphoric acid obtained in the step S10 to carry out ammoniation once until the pH is 2.5, and aging for 20 minutes to obtain the first aging solution;
[0044] S30, feeding gaseous amm...
Embodiment 2
[0049] S10. Add 24g of sodium nitrate to the raw material liquid of wet-process phosphoric acid, react at room temperature for 1-2 hours for pre-defluorination, filter to obtain defluorination filtrate and filter residue, filter residue with 50g of deionized water until it is acid-free, and dry to obtain 24g sodium fluorosilicate product, washing water is returned in the defluorination filtrate, always gets 1045g of defluorination filtrate.
[0050] S20, pass gas ammonia into the 1045g defluorination filtrate obtained in step S10 to carry out ammoniation for the first time until the pH is 2.4, and age for 20min to obtain the first aging liquid;
[0051] S30, inject gaseous ammonia into the first aging liquid to carry out the second ammoniation to pH = 4.6, and centrifuge to obtain the supernatant liquid and the bottom slag liquid;
[0052] S40, 945g of the supernatant obtained in the S30 step is concentrated to 62%, after cooling and crystallization for 1h, centrifuged to obta...
Embodiment 3
[0056] S10. Add 20 g of sodium sulfate to the wet-process phosphoric acid raw material liquid, react at room temperature for 1 to 2 hours for pre-defluorination, filter to obtain the defluorination filtrate and filter residue, wash the filter residue with 50 g of deionized water until it is acid-free, and dry it to obtain 23g of sodium fluorosilicate product, because the washing water contains the material composition of wet-process phosphoric acid, so it is returned in the defluorination filtrate during operation, and a total of 1040g of defluorination filtrate is defluorinated wet-process phosphoric acid.
[0057] S20, passing ammonia gas into 1040 g of defluorinated wet-process phosphoric acid obtained in step S10 to carry out ammoniation once until the pH is 2.0, and aging for 10 minutes to obtain the first aging solution;
[0058] S30, feeding gaseous ammonia into the first aging liquid to carry out the second ammoniation until the pH is 4.0, and then obtaining the superna...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com