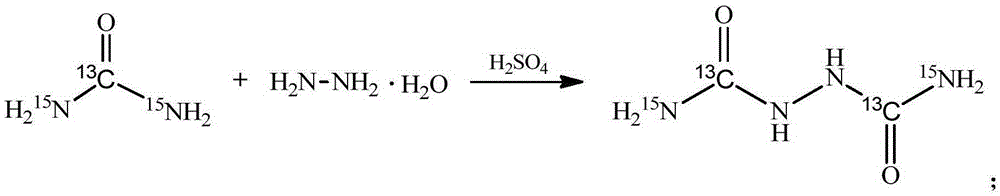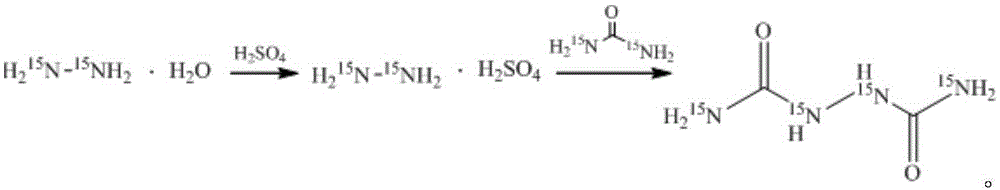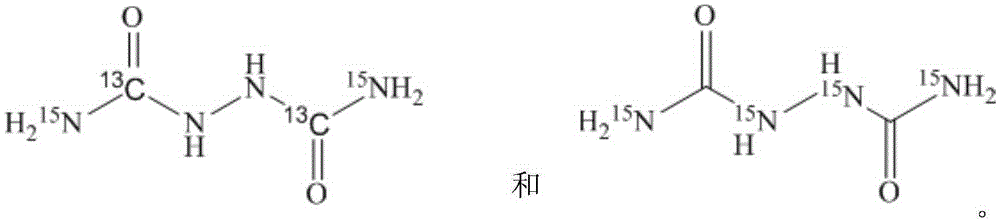Stable isotope 13C or 15N-labeled biurea synthesis method
A stable isotope and synthesis method technology, which is applied in the field of synthesis of stable isotope 13C or 15N labeled biurea, can solve the problems of difficult separation and recovery, lower isotope utilization rate, and difficult to meet the synthesis of stable isotope labeled biurea, and achieve the utilization The effect of high efficiency, simple operation, good practical value and economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Stable isotope labeled biurea-[ 13 C 2 , 15 N 2 ] The synthetic method, the concrete synthetic process of this method comprises the following steps:
[0030] In the reactor, add 12.5g (0.1mol) of 40wt% hydrazine hydrate N 2 h 4 ·H 2 O solution, be warmed up to 100 ℃, under stirring state, slowly add the sulfuric acid 98g (0.3mol) of the 30wt% freshly prepared dropwise, then add the urea-[ 13 C, 15 N 2 ], heat preservation reaction for 9 hours; after the reaction, cool to room temperature, suction filter, wash the product with warm water at 30°C, then filter with suction, and dry to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 50°C to obtain 8.7g of white powder with a yield of 71.2%, urea -[ 13 C, 15 N 2 ] has an isotope utilization rate of 71.2%, a chemical purity of 99.02%, and an isotope abundance of 99.02atom%. 15 N and 99.05atom% 13 c.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Stable isotope labeled biurea-[ 13 C 2 , 15 N 2 ] The synthetic method, the concrete synthetic process of this method comprises the following steps:
[0033] In the reactor, add 15g (0.15mol) of 50wt% hydrazine hydrate N 2 h 4 ·H 2 O solution, warming up to 120°C, under stirring, slowly add 514.5g (0.525mol) of freshly prepared 10wt% sulfuric acid, and then add 6.3g (0.1mol) of urea-[ 13 C, 15 N 2], heat preservation reaction for 7 hours; after the reaction, cool to room temperature, filter with suction, wash the product with warm water at 35°C, filter with suction again, and dry to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 50°C to obtain 10.7g of white powder with a yield of 87.6%, urea -[ 13 C, 15 N 2 ] has an isotope utilization rate of 87.6%, a chemical purity of 99.6%, and an isotope abundance of 99.35atom%. 15 N and 99.12atom% 13 c.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Stable isotope labeled biurea-[ 13 C 2 , 15 N 2 ] The synthetic method, the concrete synthetic process of this method comprises the following steps:
[0036] In the reactor, add 10g (0.12mol) of 60wt% hydrazine hydrate N 2 h 4 ·H 2 O solution, warming up to 120°C, under stirring, slowly add 47.04g (0.24mol) of freshly prepared 50wt% sulfuric acid, and then add 6.3g (0.1mol) of urea-[ 13 C, 15 N 2 ], heat preservation reaction for 5 hours; after the reaction, cool to room temperature, suction filter, wash the product with warm water at 40°C, then filter with suction, and dry to constant weight in a vacuum oven at 50°C to obtain 10.2g of white powder with a yield of 83.2%, urea -[ 13 C, 15 N 2 ] has an isotope utilization rate of 83.2%, a chemical purity of 99.45%, and an isotope abundance of 99.22atom%. 15 N and 99.15atom% 13 c.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com