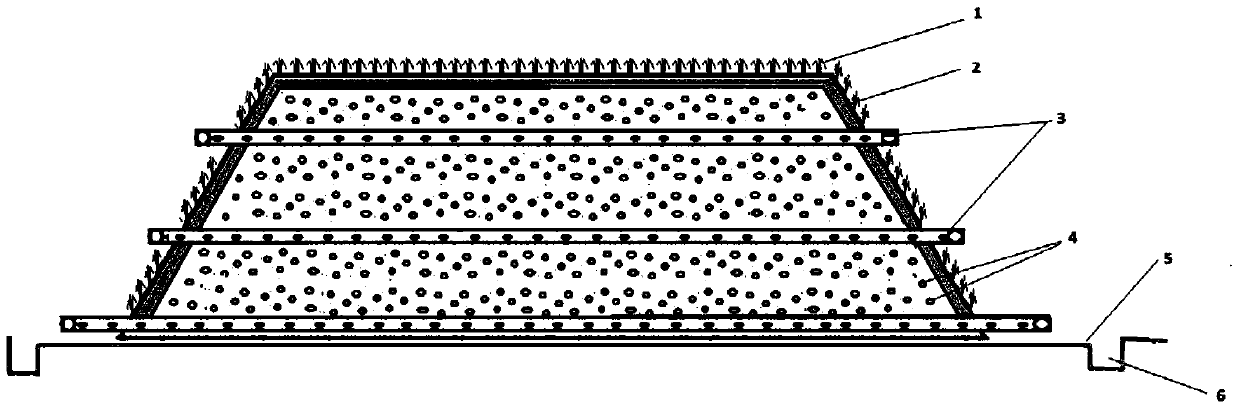
A method for remediating harmful organic and/or heavy metal contaminated substrates
A technology of organic matter and heavy metals, which is applied in the field of environmental bioremediation, can solve the problems that ecological piles cannot remove heavy metals, high cost investment, slow effect of phytoremediation, etc., and achieve the effect of resource reuse and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
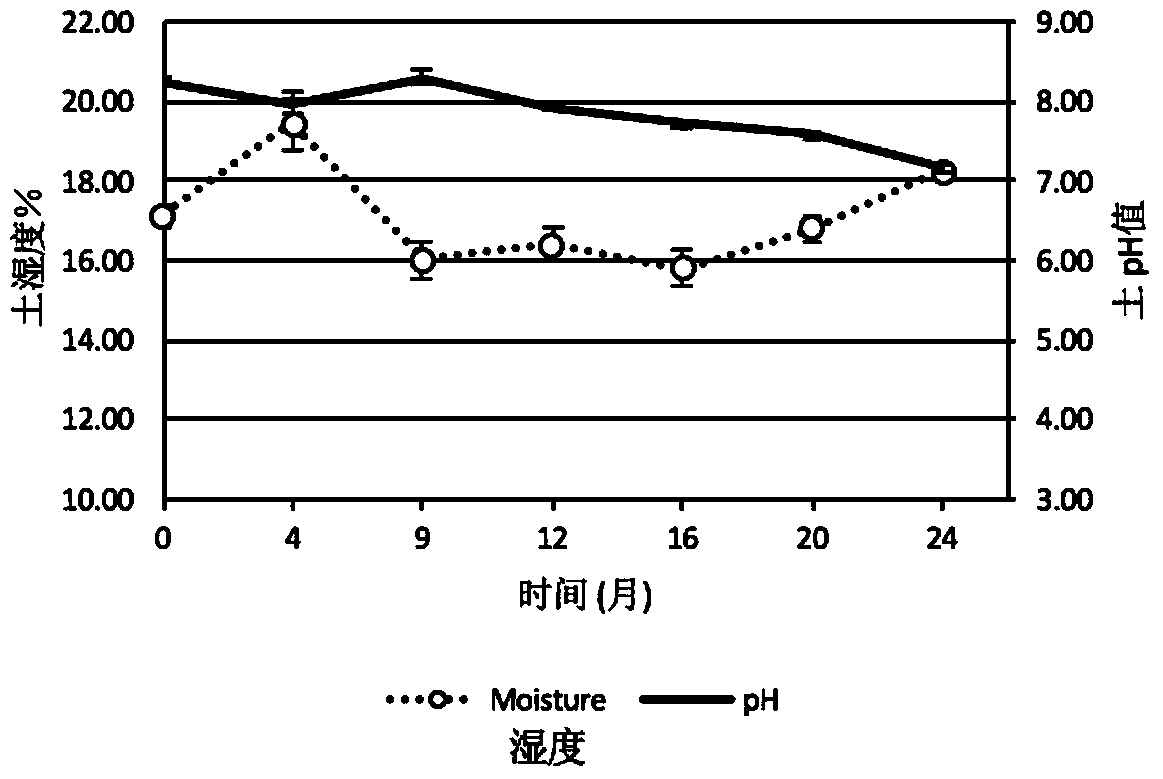
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Embodiment 1: Restoration of the ecological pile system of TPH polluted soil
[0073] The soil of the food processing site is contaminated by mineral oil in the deep layer (2-4m below the surface layer), and the oil-contaminated soil needs to be excavated from the site at first. A total of 4870m was excavated 3 The analysis showed that the average level of TPH reached 1613ppm. Contaminated soil was stored in an unused parking lot (concrete floor). Then mix the nutrient salt (nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of 25:4) with the polluted soil, the ratio of fertilizer to soil is 5kg / m 3 . The soil was also added with TPH-degrading bacteria Pseudomonas putida (strain preservation number: ATCC: PCA5581) and TPH-degrading bacteria flora isolated from the site-contaminated soil. The degrading bacteria were isolated by adding 10g of TPH-contaminated soil to 500ml of deficient medium, cultured at 100rpm for 2 weeks, and then transferred to the same medium supplemented with diesel ...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2: Remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated clay by ecological pile system
[0089] The PAH-contaminated soil came from a wood preservative processing plant. Analysis by a third-party laboratory shows that the level of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the pollution can reach 580ppm. The isolation method of PAH-degrading bacteria is as follows: add 10g of PAH-contaminated soil to 500ml of deficient medium, culture at 100rpm for 2 weeks, switch to a new deficient medium, and add a small amount of naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene, fluorene, and fluorescein every week. Anthracene as the sole carbon source. After cultivating for 5 weeks, the isolated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria group and the known plant growth-promoting bacteria Pseudomonas (strain preservation number ATCC: 55089) and the bacterial strain Bacillus (bacterial strain) that can produce biosurfactants No. DSM: 3258) mixed and embedded into spherical col...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Embodiment 3: The ecological stack system remediates the soil polluted by oil sludge containing crude oil and heavy metals
[0103] Sludge-contaminated soil comes from oilfield companies. The soil was polluted by petroleum hydrocarbons and Cd with concentrations of 30 000ppm and 10ppm, respectively (measured by a third-party laboratory).
[0104] The isolation method of total petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria is as follows: add 10 g of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil into 500 ml defect culture medium (Abraham et al. Diesel oil was added to the culture medium weekly for 3 months, and then the inoculum was embedded with alginate. The number of microorganisms contained in each pellet is 10 8 -10 9 CFU. At the same time, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria, plant growth-promoting bacteria and plant seeds are embedded in the colloid for plant coverage on the surface of the ecological pile.
[0105] The application ratio of embedded petroleu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com