Method for selectively leaching rhenium from copper sulfide arsenic residues under normal pressure
A copper sulfide and selective technology, applied in the field of selective leaching of rhenium at atmospheric pressure, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of rhenium recovery, high content of copper and arsenic, increasing the cost of purification, etc., and achieves the effect of easy industrial application and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
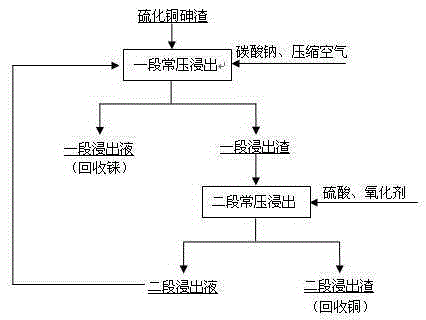
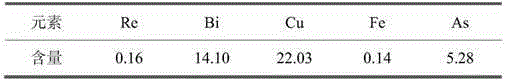
[0018] Example 1: (1) Weigh 500 g of the copper sulfide arsenic slag in Table 1, add the second-stage atmospheric pressure leaching solution, heat on a hot plate and start stirring at the same time. Raise the temperature to 75°C, pass in compressed air, adjust the pH value to 2, control the leaching time for 2 hours, filter after the reaction is completed, sample and analyze the filtrate, and sample and analyze the slag after drying. (2) Weigh 200g of a section of normal-pressure leaching residue, add tap water to adjust the liquid-solid ratio to 3:1, adjust the pH value to 2, heat it on a heating plate while stirring, and raise the temperature to 75°C. At this point, slowly add an appropriate amount of oxidizing agent (hydrogen peroxide) dropwise, and control the leaching time for 2 hours. After the reaction was completed, filter and sample the residue. Example 1 sample analysis results are shown in Table 2:
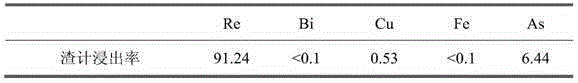
[0019] Each element leaching rate (%) in the test of table 2 emb...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: (1) Weigh 500 g of the copper sulfide arsenic slag material in Table 1, add the second-stage atmospheric pressure leaching solution, heat on an electric heating plate and start stirring at the same time. Raise the temperature to 75°C, feed compressed air, adjust the pH value to 3, control the leaching time for 2 hours, filter after the reaction,
[0022] The filtrate was sampled and analyzed, and the slag was dried and sampled for analysis. (2) Weigh 200g of a section of normal-pressure leaching residue, add tap water to adjust the liquid-solid ratio to 3:1, adjust the pH value to 3, heat it on a heating plate while stirring, and raise the temperature to 75°C. At this point, slowly add an appropriate amount of oxidizing agent dropwise, and control the leaching time for 2 hours. After the reaction was completed, filter and sample the residue. Example 2 sample analysis results are shown in Table 3:
[0023] Each element leaching rate (%) in the test of table...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3: (1) Weigh 500 g of the copper sulfide arsenic slag material in Table 1, add the second-stage atmospheric pressure leaching solution, heat on an electric heating plate and start stirring at the same time. Raise the temperature to 75°C, feed compressed air, adjust the pH value to 4, control the leaching time for 2 hours, filter after the reaction,
[0026] The filtrate was sampled and analyzed, and the slag was dried and sampled for analysis. (2) Weigh 200g of a section of normal-pressure leaching residue, add tap water to adjust the liquid-solid ratio to 3:1, adjust the pH value to 4, heat it on a heating plate while stirring, and raise the temperature to 75°C. At this point, slowly add an appropriate amount of oxidizing agent (hydrogen peroxide) dropwise, and control the leaching time for 2 hours. After the reaction was completed, filter and sample the residue. Example 3 sample analysis results are shown in Table 4:
[0027] Each element leaching rate (%) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com