Living plant ascorbic acid detection method based on microelectrode biosensor
A biosensor, ascorbic acid technology, applied in the field of detection, can solve problems such as static detection only, irreversible damage to samples, complex sample processing, etc., and achieve the effect of simple detection conditions and portable detection equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
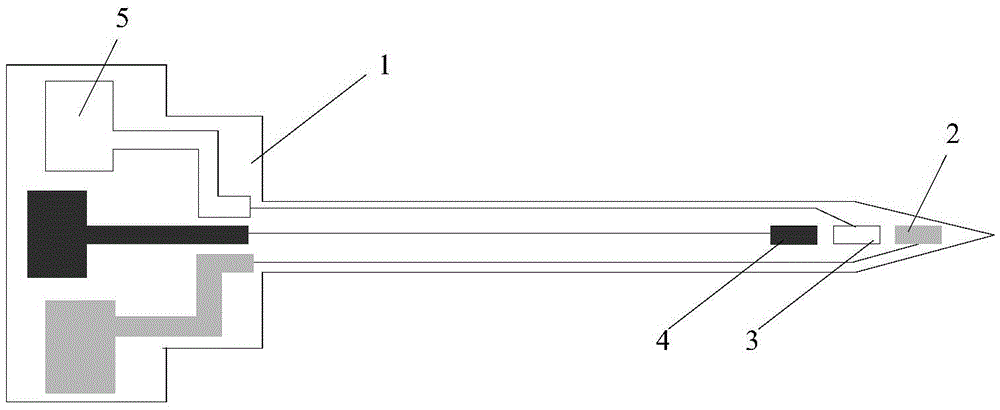
[0035] Such as figure 1 , the microelectrode array is prepared on the silicon wafer substrate 1 by etching technology and electrodeposition technology, with a length of 5 cm and a thickness of 1.5 mm. The electrode 4 has a sharp point facing outward from the silicon chip substrate 1, and the other end is wider, on which a connecting element 5 is arranged (one electrode is connected to a corresponding connecting element). Among them, Ag / AgCl is the reference electrode, platinum is the counter electrode, and the modified gold electrode is the working electrode. During detection, an electrochemical workstation is used to connect the connection element 5 in the microelectrode array, and the current is detected by cyclic voltammetry on the electrochemical workstation, and then the current data is converted into concentration data, and the data is collected by the signal acquisition module.
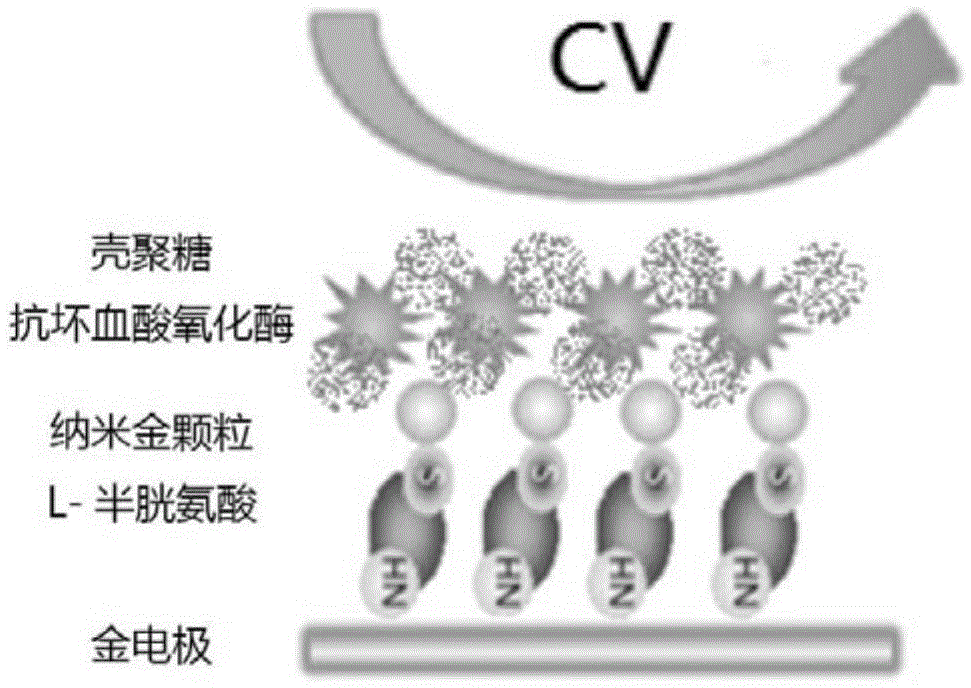
[0036] see figure 2 , the modification steps of the gold electrode are as follows:
[0...
Embodiment 2
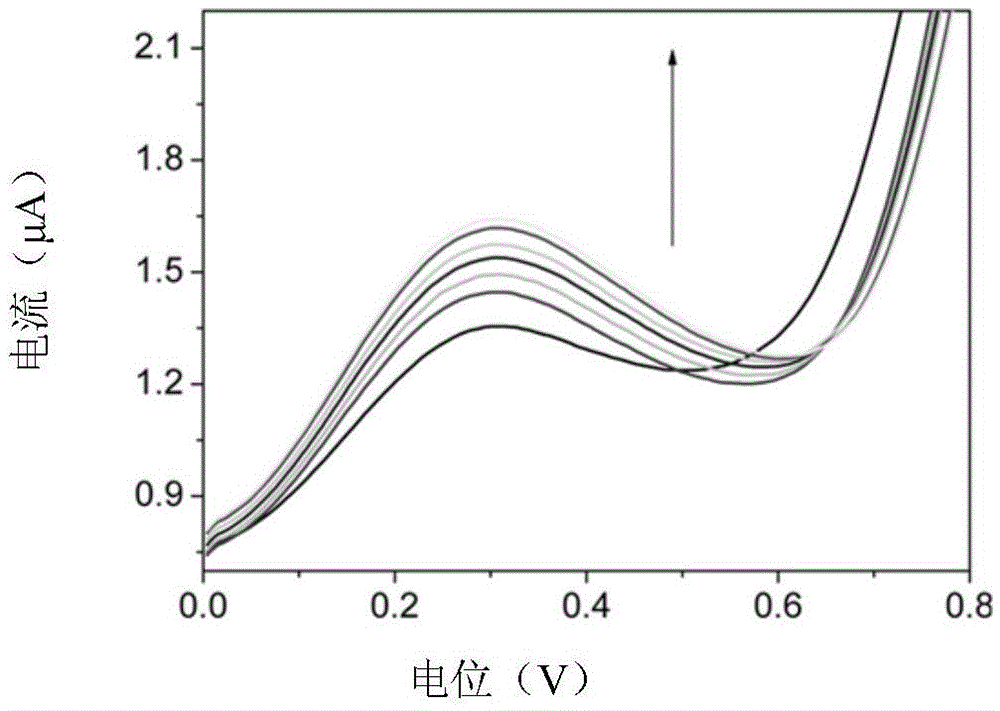
[0042] Glucose-phosphate buffer (pH=7.4) solutions with concentrations of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 mmol / L were prepared respectively, and the prepared microelectrodes were used for cyclic voltammetry detection (voltage -0.2 to 1.0V, scanning Speed 100mV / s), obtain the curve ( image 3 ), make the microelectrode working curve, the linear equation is i=1.308+0.0515c (the unit of current i is μA, the unit of concentration c is mmol / L), and the linear range can reach 1-10mmol / L.
[0043] After cleaning the microelectrode prepared in Example 1, first detect three parts of standard concentration (2, 5, 8mmol / L) ascorbic acid solution for electrochemical calibration, and the biosensor system will automatically adjust the deviation to meet the working curve and slope deviation through calculation. Within 15%, the microelectrodes were determined to be functioning properly.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com