Optical wireless communication device and method applied to turbid media
A technology of optical wireless communication and medium, which is applied in the field of wireless optical communication, can solve the problems of unfavorable wireless communication practical application, optical wireless communication link interruption bit error rate, high implementation cost, etc., to achieve rapid deployment, low bit error rate, The effect of low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
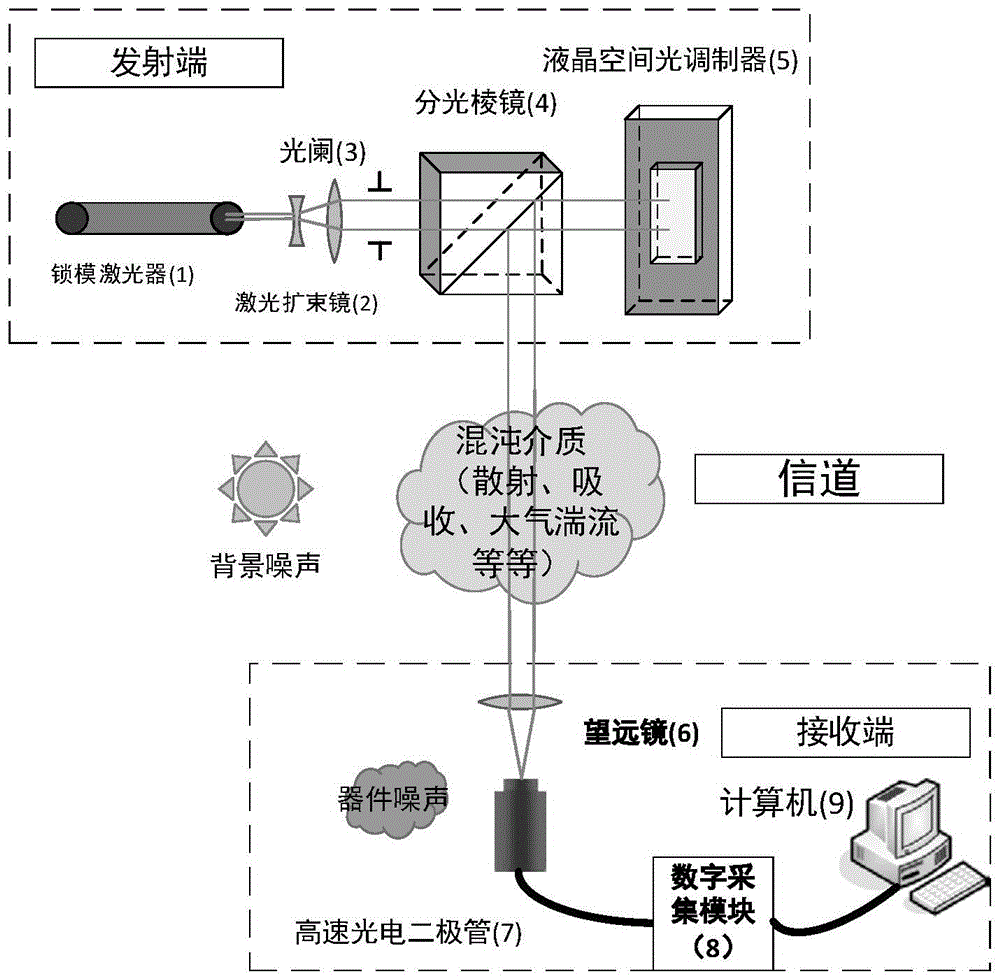
[0033] Combine figure 1 , The present invention is applied to the optical wireless communication method in the chaotic medium, the steps are as follows:
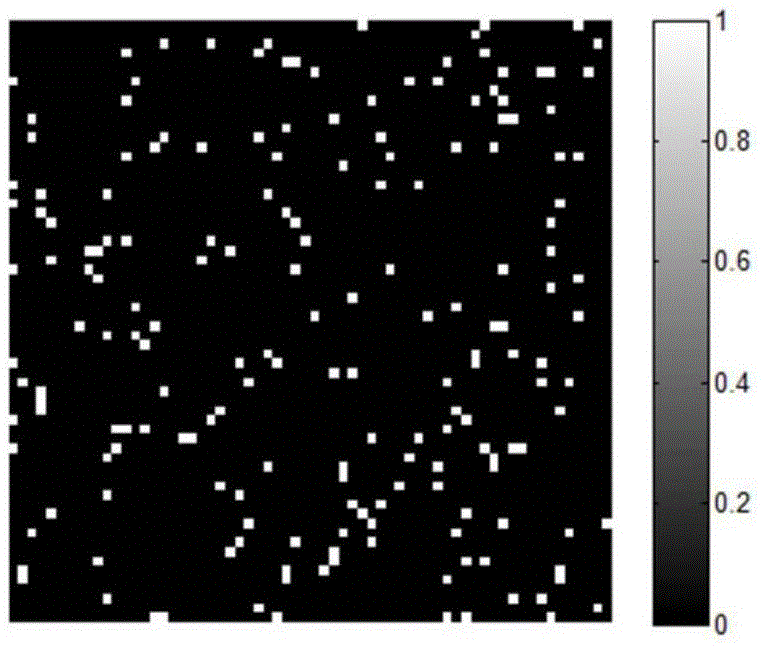
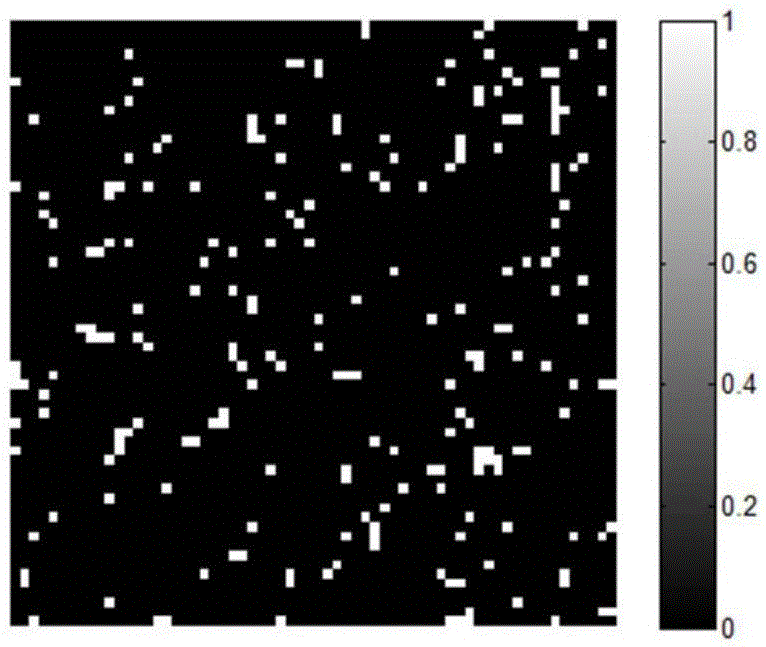
[0034] The first step, such as figure 1 As shown, for the 64×64 experimental signal to be transmitted, the sampling matrix of 1500×4096 is generated by C++ and imported into the memory of the digital micro-reflective array DMD. According to the coding rules, the signal to be transmitted is shown in Figure 2(a) and 2(c)) for encoding.
[0035] The second step is to process the disturbance of the chaotic medium to the signal, and obtain the expression of the relationship between the signal at the receiving end and the signal at the transmitting end
[0036] The third step is to construct the transmission equation y=λAx+e in the chaotic medium, and perform the spatial second-order correlation operation to obtain the signal transmission equation △=λΦx. Using convex optimization algorithm and CVX convex optimization toolkit, use Matla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com