HPPD inhibitor-resistant gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
An inhibitor and gene technology, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering and plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems affecting the biosynthesis of carotenoids and the obstruction of phytoene desaturase catalysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1 Isolation, Purification and Identification of HPPD Inhibitor-Resistant Bacterial Strain-Human Paleobacterium OchrobactrumanthropiH-2
[0063] 1. Source of soil samples
[0064] Soil samples were collected from 5 cm below the soil layer of the experimental fields sprayed with HPPD inhibitors.
[0065] 2. Isolation and purification of HPPD inhibitor-resistant strains
[0066] Enrichment of bacterial strains: Weigh 20 grams of soil samples respectively, one of which is added to 1 / 10LB liquid medium containing 0.3mM HPPD inhibitor (filling volume is 50ml / 300ml Erlenmeyer flask), the other soil sample Add to the 1780 modified liquid culture medium containing 0.3mM HPPD inhibitor (75% isoxaflutole water dispersible granule) (filling volume is 50ml / 300ml Erlenmeyer flask), set 30 o The enrichment culture was carried out in a C shaker at 200 rpm.
[0067] Acclimatization and purification of strains: Each time of enrichment culture for 7 days, the culture was centri...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Cloning of DNA fragments of embodiment 2 highly resistant to HPPD inhibitors
[0074] Partial DNA Fragments Highly Tolerant to HPPD Inhibitors Obtained by PCR Method
[0075] Designed according to the OchrobactrumanthropiHPPD inhibitor resistance gene sequence published in NCBI
[0076] Primer 1-F: 5′-ATGAAGACTTCGATAGCAACCGT-3′
[0077] Primer 1-R: 5′-TCAGAGTGCCACAGCACTTTTTG-3′
[0078] Using high-fidelity Taq enzyme KOD-FX to amplify the partial sequence of the anti-HPPD inhibitor gene from the Ochrobacttrumanthropi genome, PCR program: 98 o C10sec, 60 o C30sec, 68 o C2min, a total of 30 cycles.
[0079] The PCR product of primer 1-F (shown in SEQIDNo: 3) and primer 1-R (shown in SEQIDNo: 4) is a 1902bp DNA fragment, which is a DNA fragment for obtaining high tolerance to HPPD inhibitors.
[0080] From Ochrobacttrumanthropi genomic DNA, the complete sequence of a DNA fragment highly resistant to HPPD inhibitors was amplified by Taq enzyme KOD-FX high-fidelity enz...
Embodiment 3
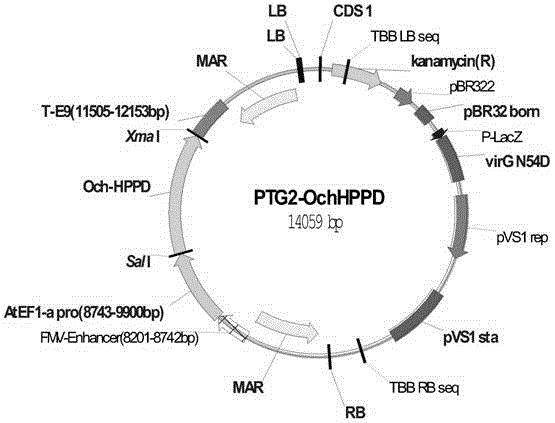
[0081] The construction of embodiment 3 plant expression vector PTG2-OchHPPD
[0082] According to the Och-HPPD gene sequence, design primers 2-F and 2-R
[0083] Primer 2-F: 5′-GTCGACATGAAGACTTCGATAGCAACCGT-3′
[0084] Primer 2-R: 5′-CCCGGGTCAGAGTGCCACAGCACTTTTTG-3′
[0085] The Och-HPPD gene sequence was amplified by PCR with primers 2-F (shown in SEQIDNo: 5) and 2-R (shown in SEQIDNo: 6), and then digested with SalI and XmaI to obtain an insert fragment; it was taken from the company and kept The PTG1 vector was digested with SalI and XmaI, and then the above-mentioned insert fragment and the vector were connected with ligase, and the ligation product was transformed into E. coli DH5α strain, and the positive selection was selected after culturing and screening in 2×YT medium containing 50 mg / L kanamycin Cloning, after extracting the plasmid, the clone with the correct sequence was selected by sequencing, and the plasmid with the target gene was obtained, named PTG2-OchHP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com