Method for extracting water-soluble dietary fibers from honeysuckle stems
A technology of dietary fiber and honeysuckle, applied in food extraction, function of food ingredients, food science, etc., can solve the problem of low utilization rate of honeysuckle, achieve the effect of improving dietary fiber structure, good extraction rate, and increasing utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
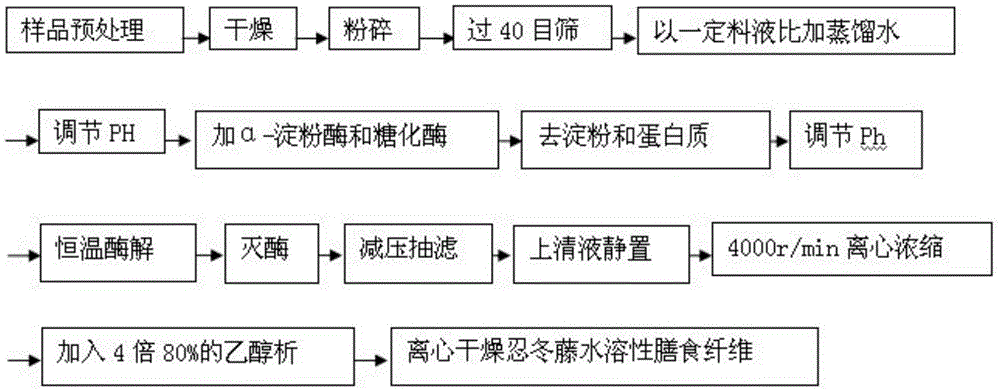
[0047] Wash and drain the honeysuckle vines, dry them in a constant temperature drying oven, crush them, and pass through a 40-mesh sieve [4] .
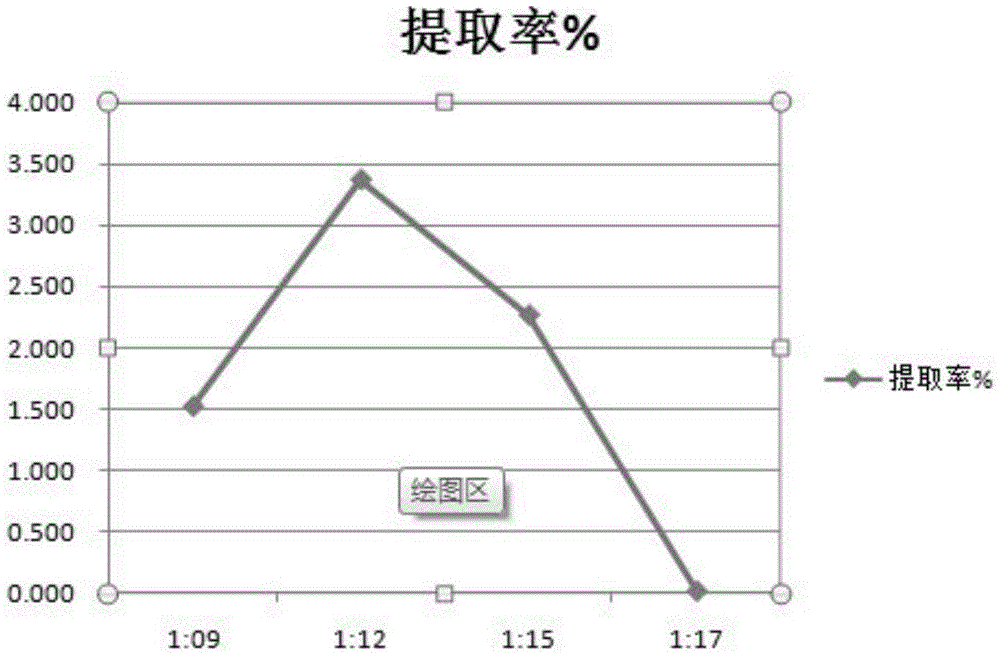
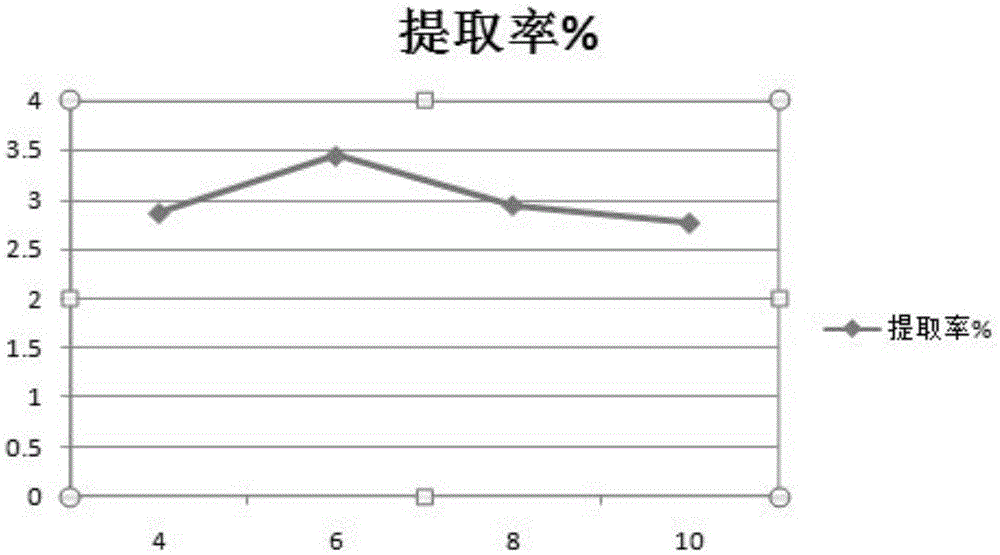
[0048] Accurately weigh 3.000g of 12 pretreated honeysuckle samples and place them in dry and clean conical flasks, add water to disperse, and set the mass ratio of solid to liquid as 1:9, 1:12, 1:15 and 1:17 respectively , each material-liquid ratio was parallelized three times, adjusted pH 6.0 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, added 3-5 drops of buffer solution, added α-amylase with a pipette gun, sealed, and enzymatically hydrolyzed for 45 minutes in a constant temperature water bath at 60°C ;Inactivate the enzyme by raising the temperature, adjust the pH to 4.5 with hydrochloric acid after cooling to room temperature, add buffer solution, add glucoamylase, re-seal, enzymatically hydrolyze for 1 hour at a constant temperature of 45°C, and inactivate the enzyme by heating [3]. After cooling to room temperature, adjust ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Wash and drain the honeysuckle vines, dry them in a constant temperature drying oven, crush them, and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0061] Accurately weigh 3.000g of 12 pretreated honeysuckle samples and place them in dry and clean conical flasks, add water to disperse, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:12, adjust the pH to 6.0 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, add 3- 5 drops of buffer solution, add α-amylase with a pipette gun, seal, and enzymolyze in a constant temperature water bath at 60°C for 45 minutes; heat up to inactivate the enzyme, cool to room temperature, adjust the pH to 4.5 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, and add buffer solution , add glucoamylase, re-seal, enzymatically hydrolyze at 45°C for 1 hour, heat up to inactivate the enzyme [4] . After cooling to room temperature, adjust Ph4.8, add a buffer solution, add respectively a concentration of 1.0% (ie 0.01g / ml) cellulase 40ul, a concentration of 0.3% (ie 0.003g / ml) xylana...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Wash and drain the honeysuckle vines, dry them in a constant temperature drying oven, crush them, and pass through a 40-mesh sieve.
[0067] Accurately weigh 3.000 g of 15 pretreated honeysuckle samples and place them in dry and clean conical flasks, add water to disperse, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:12, adjust the pH to 6.0 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, add 3- 5 drops of buffer solution, add α-amylase with a pipette gun, seal, and enzymolyze in a constant temperature water bath at 60°C for 45 minutes; heat up to inactivate the enzyme, cool to room temperature and adjust the pH to 4.5 with hydrochloric acid, add buffer solution, and add glucoamylase , re-sealed, enzymatically hydrolyzed for 1 hour at a constant temperature of 45°C, and inactivated by heating [4] . After cooling to room temperature, adjust Ph4.8, add buffer solution, and add 40ul concentrations of 0.5%, 0.8%, 1.0%, 1.2%, 1.5% respectively (0.005g / ml, 0.008g / ml, 0.010g / ml, 0.012...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com