Fast detecting method of vitamin K1 used for preventing coupling hemorrhage after vaccine injection
A detection method and vitamin technology, applied in the field of electrochemical analysis, can solve the problems of poor enrichment and reproducibility of solid electrodes, poisonous mercury vapor, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing specific surface area and enhancing adsorption characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
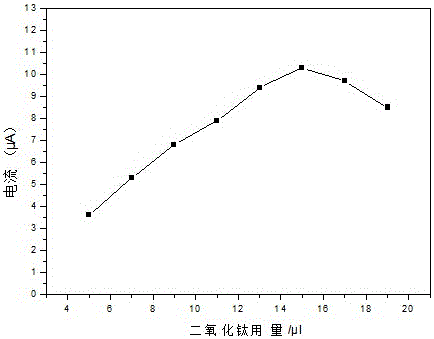
[0022] The glassy carbon electrode is polished with 0.1~0.2μm aluminum oxide powder, the nano-titanium dioxide is prepared according to the concentration of 12g / L, the particle size of the nano-titanium dioxide is between 15 and 17nm, and the ultrasonic method is used to disperse the titanium dioxide solution for 30 minutes. A milky white dispersion is formed. In the experiment, the thickness of the nano-titanium dioxide film has an impact on the peak current, such as figure 1 It can be seen that when the titania dispersion is gradually increased from 5 μl to 15 μl, the dissolution peak current gradually increases, but after 15 μl, the current decreases instead, so 15 μl dispersion is selected as the optimal coverage amount. The specific method is to drop 15 μl of the above-mentioned dispersion liquid on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, air-dry at room temperature, and repeat twice. The prepared titanium dioxide film modified glassy carbon electrode was used to det...
Embodiment 2
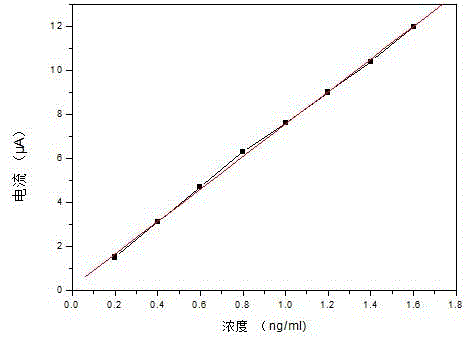
[0024] Establish a standard curve for the determination of vitamin K content and investigate the range of determination.
[0025] Take an appropriate amount of vitamin K1 standard stock solution, and use 5.0mol / L NaAc-HAc solution to prepare vitamin K1 content of 0.2ng / ml, 0.4ng / ml, 0.6ng / ml, 0.8ng / ml, 1.0ng / ml, 1.2ng / ml, 1.4ng / ml, 1.6ng / ml of a series of different vitamin K1 content standard solutions.
[0026] Take 5.0mol / L NaAc-HAc10~15ml of supporting electrolyte and add it into the measuring cup, blow high-purity nitrogen gas for 10min to remove oxygen, scan the blank supporting electrolyte in the potential range of -0.3V~-0.8V, and record the blank spectrum. Then add 2 ml of standard solutions with different concentrations to the supporting electrolyte, perform potential scanning and record the peak current value at -0.45V.
[0027] Correlate the peak currents produced by standard solutions with different vitamin K1 contents with the corresponding vitamin K1 contents t...
Embodiment 3
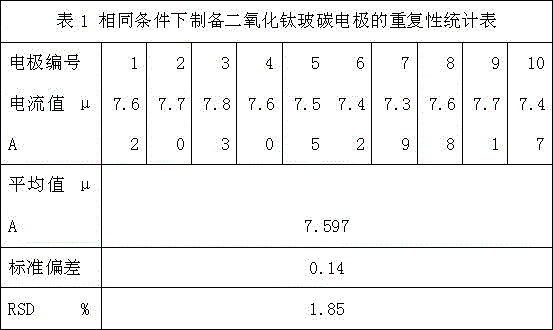
[0029] The repeatability of the electrode prepared by the method of the present invention for determining the content of vitamin K1 was investigated.
[0030] 10 titanium dioxide-modified glassy carbon electrodes were made by the method of Example 1, and the vitamin K1 current value of 1.0ng / ml was detected. The results are shown in Table 1, and the average value is 7.597±0.14μA (n=10, RSD=1.85%) , indicating that the titania-modified glassy carbon electrode prepared by this method has good preparation stability and repeatability.
[0031]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com