Extraction of polycosanol from cane vinasse
A technology of molasses alcohol waste liquid and pliol, which is applied in the field of extracting pliol from molasses alcohol waste liquid, and can solve problems such as soil and groundwater pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
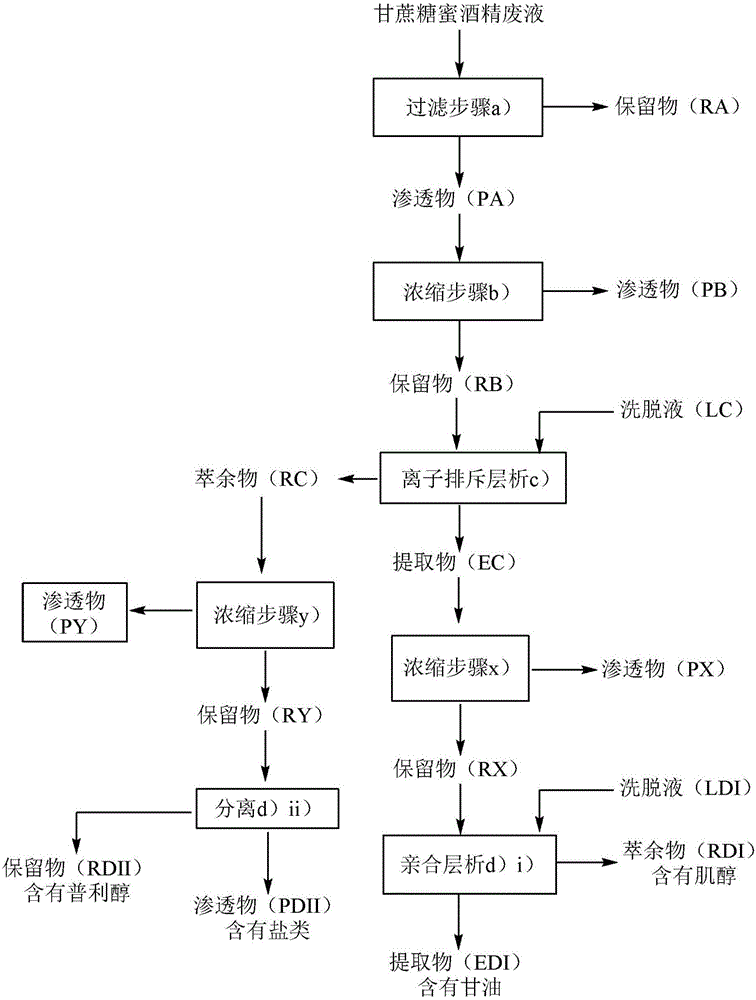
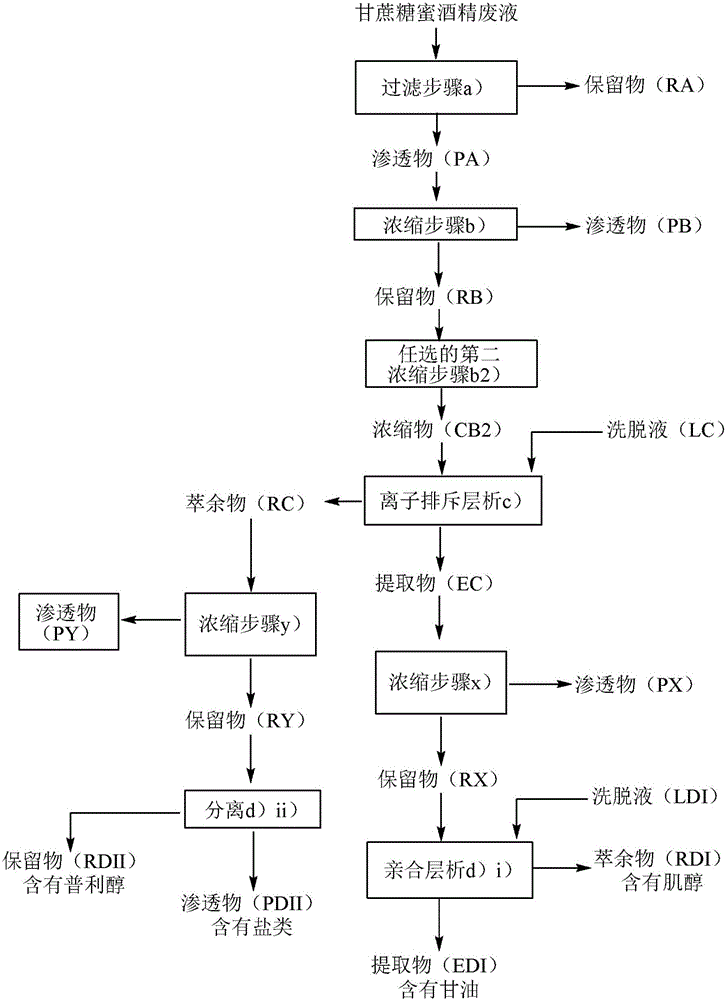
[0038] Example 1: Microfiltration of molasses alcohol waste (step a))
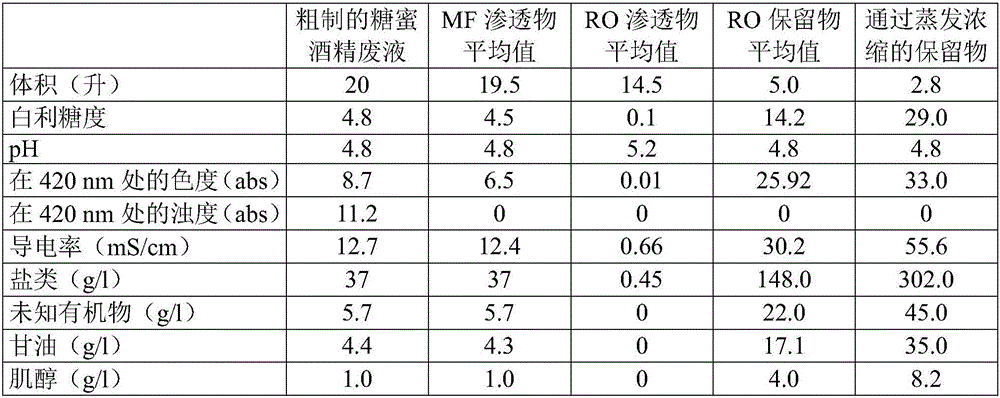
[0039] The feed is molasses alcohol waste liquid. Microfiltration was purchased from NovasepProcess KERASEP TM performed by a ceramic membrane. Using MicroKerasep TM Pilot plant to achieve a total filtration area of 0.023m 2 . The molasses alcohol spent liquor was loaded into the feed tank, pumped to circulate the liquor at 5 m / s with the transmembrane pressure set at 400 kPa (4 bar). Operate the system in batches. Permeate withdrawal was continued until no permeate flow was measured. The volumetric concentration factor [VCF=volume of feed / volume of retentate] was monitored. The permeate is collected to be fed to reverse osmosis.
[0040] Three membranes with cut-off sizes of 0.1 μm, 0.2 μm and 0.45 μm were tested. Membranes with a cutoff of 0.1 μm had the highest flow rates and the least tendency to become clogged. Perform microfiltration using a membrane with a particle cut-off of 0.1 μm unti...
example 2
[0042] Example 2: Reverse Osmosis (RO) (step b))
[0043] The feed was the permeate from Example 1. The pilot plant was equipped with a 4000 kPa (40 bar), 1250 l / h piston pump, RO / NF helical housing module. Pressure is set with a back pressure needle valve and flow rate is controlled with a flow meter. The feed was loaded into the feed tank and then concentrated until 4000 kPa (40 bar) was reached. Operating system in batch mode. The pressure was adjusted to keep the permeate flow rate below 100 liters / hour to prevent bursting of the element. Registered (registered) VCF, until the maximum operating pressure is reached. The operation was carried out at a constant pressure of 3000 kPa (30 bar). Membrane is FILMTEC purchased from Filmtec Corporation TM BW30-2540 film.
[0044] The flow rate decreased continuously with the concentration increasing, and the maximum VCF reached was 3.9. The average flow rate at this concentration is about 10l / h.m 2 . After the concentratio...
example 3
[0055] Example 3: Ion exclusion chromatography (step c)).
[0056] The chromatography column is a 25 mm x 1000 mm glass column with adjustable plunger and sleeve for temperature control, distributed with 25 μm PTFE frit. The total resin exchange capacity is about 460ml. A circulating water bath was used at 60 °C, along with a peristaltic pump and an autosampler.
[0057]Resin is Dowex TM 99320 Resin and Amberlite TM CR1310 resin (both available from Dow Chemical Co.).
[0058] resin filled
[0059] Resin loading was performed in a column half filled with degassed demineralized water. After heating to the proper temperature by recirculating hot water (flow rate = 4BV / h) during at least 30 minutes, the resin level was adjusted.
[0060] Before any separation, the resin was compacted by performing a double pulse test, but without any sampling and data recording (flow rate = 4BV / h). Compaction is due to the expansion and contraction of the resin, after which the product is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com