Method for preparing porous carbon-loaded nano-material
A technology of porous carbon and nano-metal, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of high price and limited scale commercial application, achieve low cost and avoid synthesis difficulties , the effect of huge application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
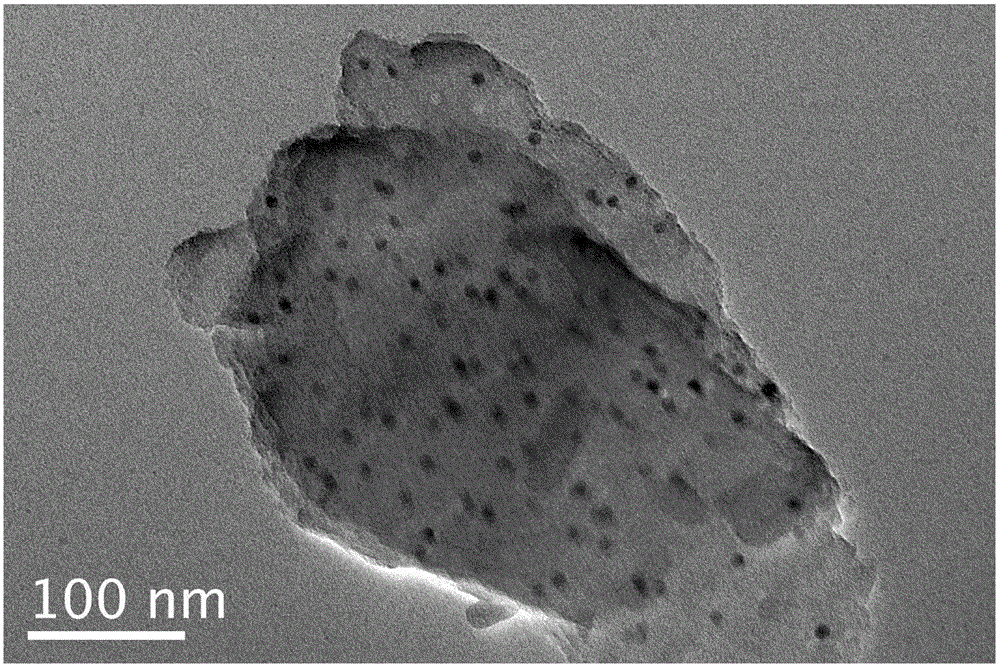
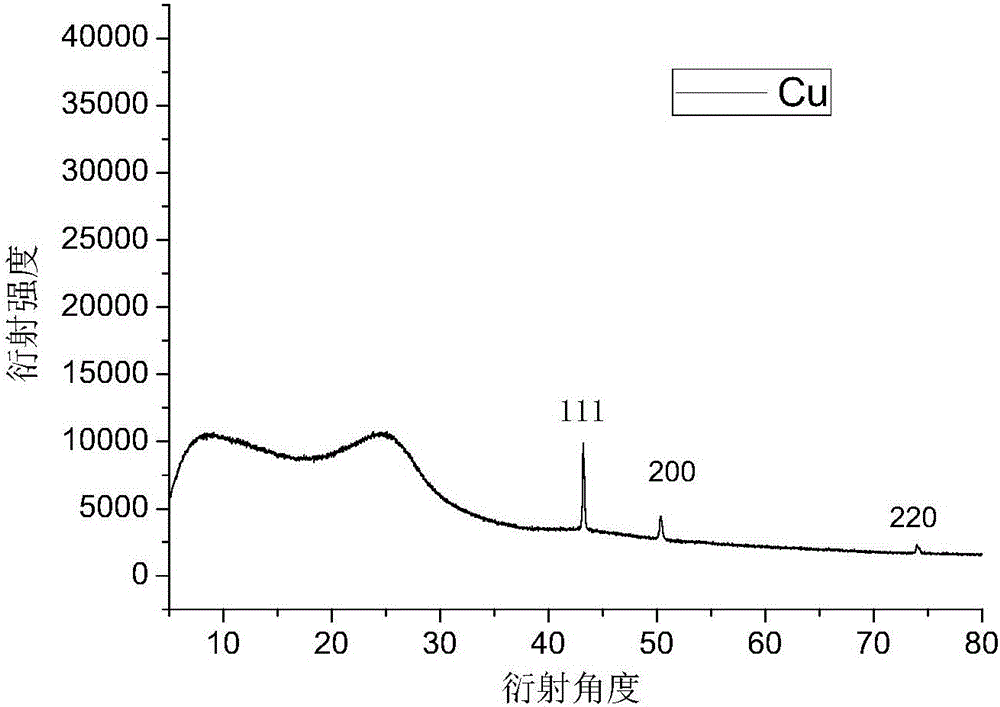
[0025] Example 1: Porous carbon supported nano-Cu
[0026] Synthetic raw materials: glucose, ethylenediamine, Cu(NO 3 ) 2? 3H 2 O (copper nitrate)
[0027] (1) Weigh 1g of glucose and 0.1g of Cu(NO 3 ) 2? 3H 2 O In a 100mL beaker, slowly add 10g of ethylenediamine dropwise and place the beaker in a heatable magnetic stirrer. The temperature of the magnetic stirrer was raised to 100° C., and the stirring was continued for 60 min until the medicine in the beaker was in a molten state.
[0028] (2) From the molten liquid mentioned in (1), take out a part of the solution and put it in a 120°C oven as sample A, and put the other part of the solution into a high-temperature reaction kettle and put it in a 120°C oven as sample B, and react for 48 hours. A dark brown bulky solid was obtained, and sample B was dark brown dense solid.
[0029] (3) Grind the sample A and sample B obtained in (2) with a mortar, and divide them into two crucibles, and then put them under N 2 Heat ...
experiment example 2
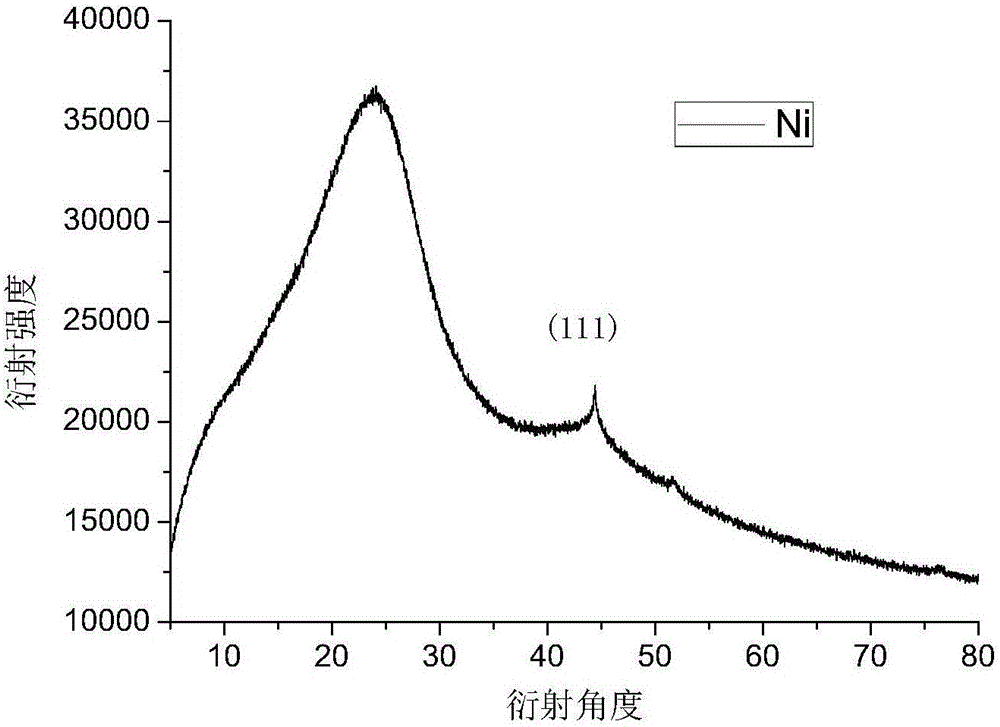
[0031] Experimental example 2: Porous carbon supported nano-Ni alloy
[0032] Synthetic raw materials: glucose, polyethyleneimine (PEI), Ni(NO 3 ) 2? 6H 2 o
[0033] (1) Weigh 10g glucose, 0.1gPEI, 0.1gNi(NO 3 ) 2? 6H 2 O in a 100mL beaker, then place the beaker in a heatable magnetic stirrer. The temperature of the magnetic stirrer was raised to 220° C., and the stirring was continued for 60 min until the medicine in the beaker was in a molten state.
[0034] (2) Afterwards, put the beaker into an oven at 250°C and react for 1 hour to obtain a dark brown puffy solid.
[0035] (3) Grind the product obtained in (2) with a mortar and put it in a crucible. The product obtained by the reaction was heated at 250°C in 5% H 2 / N 2 Under the condition of heat treatment for 24 hours, the porous carbon-supported nano-Ni particles are obtained.
experiment example 3
[0036] Experimental example 3: Porous carbon supported nano-TiO 2
[0037] Synthetic raw materials: sucrose, ethanolamine, TiOSO 4 (titanyl sulfate)
[0038] (1) Weigh 1g of sucrose and 5g of ethanolamine into a 100mL beaker, then place the beaker in a heatable magnetic stirrer. The temperature of the magnetic stirrer was raised to 100°C, and the stirring was continued until the medicine in the beaker was in a molten state.
[0039] (2) Weigh 10g TiOSO 4 Add it to the molten liquid described in (1), and continue to stir for 15 minutes until it reaches a molten state. Afterwards, the beaker was put into an oven at 160° C., and reacted for 40 hours to obtain a dark brown puffy solid.
[0040] (3) Grind the product obtained in (2) with a mortar and put it in a crucible. The product obtained by the reaction is in N 2 Heat treatment at 250°C for 24 hours under protection to obtain porous carbon-supported TiO 2 nanoparticles, XRD shows TiO 2 The particle size is 20nm, and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com