Preparation method for spirulina polymer composite tissue engineering scaffold
A composite tissue and polymer technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of hydrophilicity, limited degradability, low production efficiency, low content of spirulina, etc., and achieve the advantages of hydrophilicity and degradability, Improved hydrophilicity and good hydrophilicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
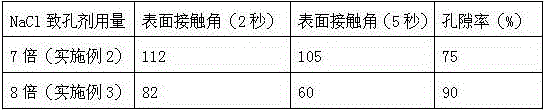
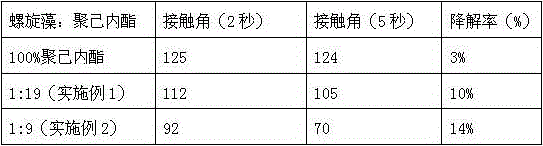
[0022] Add 0.1 g of the crude extract of spirulina and 1.9 g of polycaprolactone to acetic acid to prepare a solution with a concentration of 10%, mix it with 14 g of NaCl after stirring for 48 hours, and then pour it into a mold of the desired shape through After air-drying at room temperature for 24 hours, dry for 48 hours at a vacuum degree of 0.01MPa and a temperature of 50°C, take out the sample and immerse it in deionized water, and replace the deionized water for a total of 18 times every 4 hours. The obtained spirulina polymer tissue engineering porous scaffold material is 0.001 Under MPa, vacuum-dry at 50°C for 24h and store in a vacuum desiccator.
[0023] The crude extract of spirulina is prepared by the following method: the dry powder of spirulina that has been dried, crushed, and passed through an 80-mesh sieve is mixed with deionized water at a mass ratio of 10:90, dissolved at 55°C for 6 hours and cooled to room temperature. The solution was centrifuged at 5000...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Add 0.2g of the crude extract of spirulina and 1.8g of polycaprolactone to 11.3g of acetic acid, stir for 48 hours and mix with 14g of NaCl, then pour it into a mold of the desired shape and air-dry it at room temperature for 24 hours , and then dried for 48 hours at a vacuum degree of 0.01MPa and a temperature of 50°C, took out the sample and immersed it in deionized water, and replaced the deionized water every 4h for a total of 18 times. Store in a vacuum desiccator after vacuum drying for 24 h.
Embodiment 3
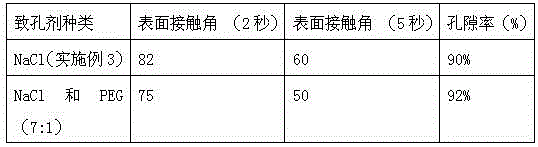
[0031] Dissolve 0.2g of spirulina crude extract and 1.8g of polycaprolactone in acetic acid to prepare a solution with a mass concentration of 15%, mix it with 16g of NaCl after stirring for 48 hours, and then pour it into a mold of the desired shape After air-drying at room temperature for 24 hours, dry for 48 hours at a vacuum degree of 0.01MPa and a temperature of 50°C, take out the sample and immerse it in deionized water, and replace the deionized water every 4 hours for a total of 18 times. The obtained spirulina polymer porous scaffold material is 0.001 Under MPa, vacuum-dry at 50°C for 24h and store in a vacuum desiccator.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com