Method for Determining Content of Impurity Elements in Alloy and Preparation Method of Sample Solution
A technology of impurity elements and sample solutions, applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve problems such as inappropriateness, complicated and cumbersome operation, long inspection cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of ensuring reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
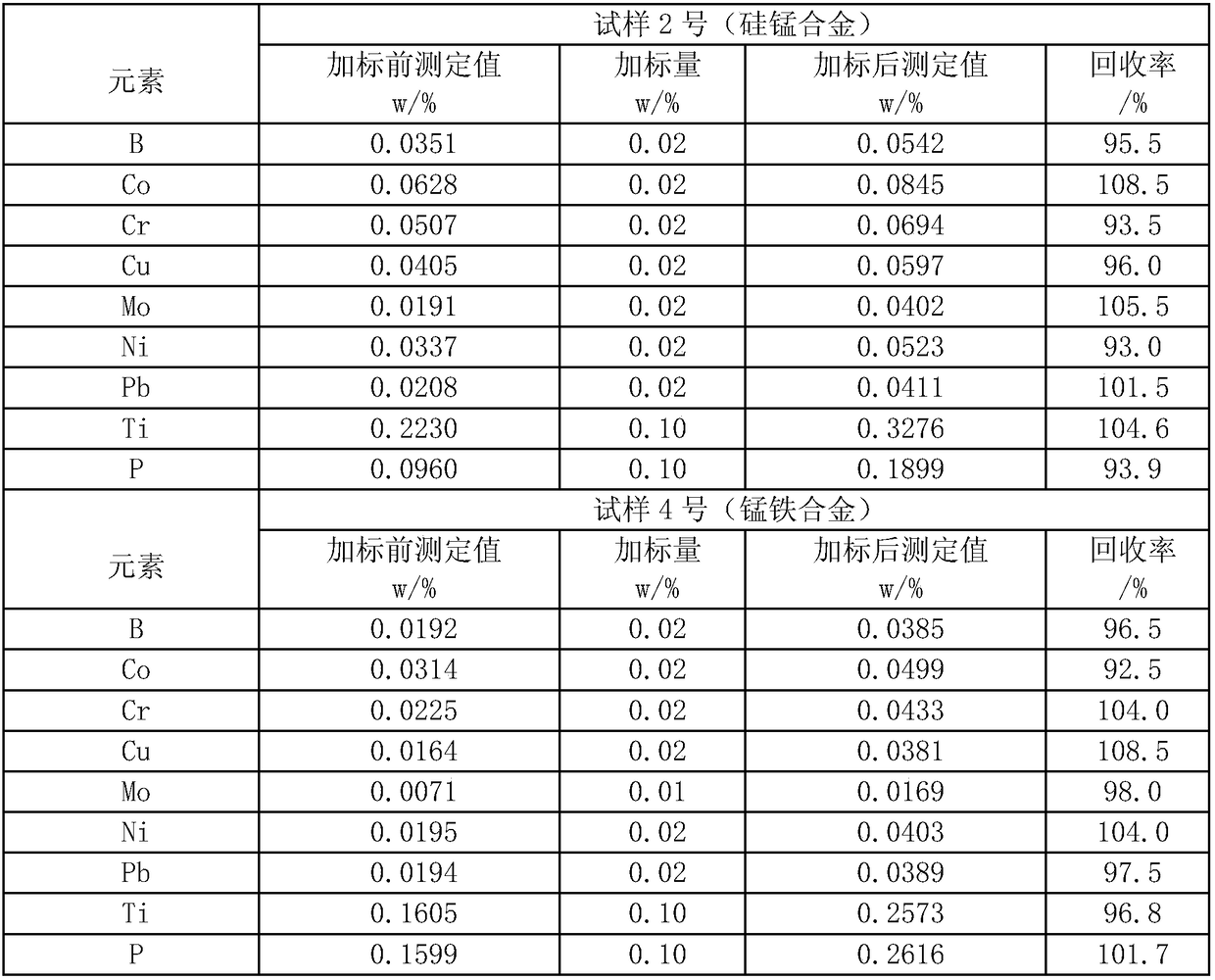
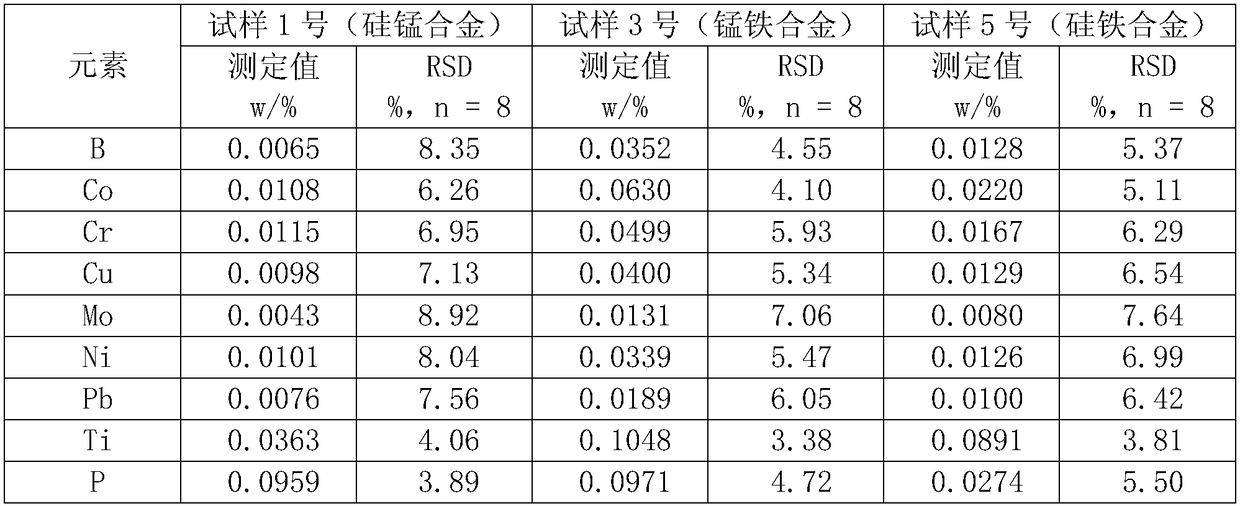
[0052] Digestion of silicon-manganese alloy samples
[0053] Weigh 0.2g of the silicon-manganese alloy sample (hereinafter referred to as sample No. 1), add 4mL of undiluted concentrated nitric acid and 2mL of hydrogen peroxide to the cup wall by washing the cup wall, heat the reaction at high temperature and keep it in a boiling state for 4min ;Add 2mL of hydrogen peroxide to carry out strong oxidation reaction when the solution is boiling, and keep the solution boiling for 3 minutes; Add 4mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid and continue to react under high temperature heating and boiling until there is no brown smoke in the solution. The color gradually changes Shallow; wash the container wall with about 3mL water, and continue to react for 5min under the boiling state of the solution; wash the container wall with about 3mL water and cool the solution to 55°C, and keep the solution at a temperature range of 55°C on a low-temperature electric heating plate Add a total of 1m...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The sample to be digested is 0.5000g silico-manganese sample (hereinafter referred to as No. 2 sample), add 10mL concentrated nitric acid and 5mL hydrogen peroxide, react at high temperature and keep it in boiling state for 8min; add 5mL hydrogen peroxide again for strong oxidation and keep Boil for 5 minutes; add 10 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid and boil at high temperature until no nitrogen dioxide brown smoke is generated; rinse the container with about 5 mL of water and evaporate the concentrated solution volume to about 5 mL; rinse the container with 5 mL of water and cool the solution to 57 ° C, and dissolve the solution Place it in a 57°C water bath to keep warm, and add a total of 2.5mL of hydrofluoric acid twice for reaction.
[0058] In addition, the silicon-manganese alloy sample was digested in the same manner as in Example 1, and the content of impurity elements was determined by ICP-OES.
Embodiment 3
[0060] The sample to be digested is 0.3000g ferromanganese alloy sample (hereinafter referred to as No. 3 sample), add 6mL concentrated nitric acid and 3mL hydrogen peroxide, react at high temperature and keep boiling for 5min; add 3mL hydrogen peroxide again for strong oxidation and keep boiling for 4min ;Add 6mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid and boil at high temperature until no brown smoke of nitrogen dioxide is produced; Rinse the container with about 4mL of water and evaporate the concentrated solution volume to about 5mL; Rinse the container with 5mL of water and cool the solution to 58°C, place the solution in Keep it warm in a water bath at 58°C, and add a total of 1.5mL of hydrofluoric acid twice for reaction.
[0061] Besides, the ferromanganese sample was digested according to the same method as in Example 1 and the content of impurity elements was determined by ICP-OES.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com