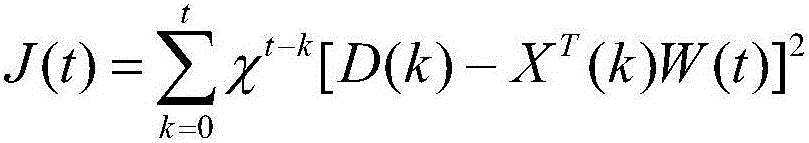Near-infrared brain function signal extracting method based on least square support vector machine
A technology of support vector machine and least squares, applied in diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, sensors, etc., can solve the problems of low detection accuracy of near-infrared brain function activity signal, error interference of brain function activity signal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
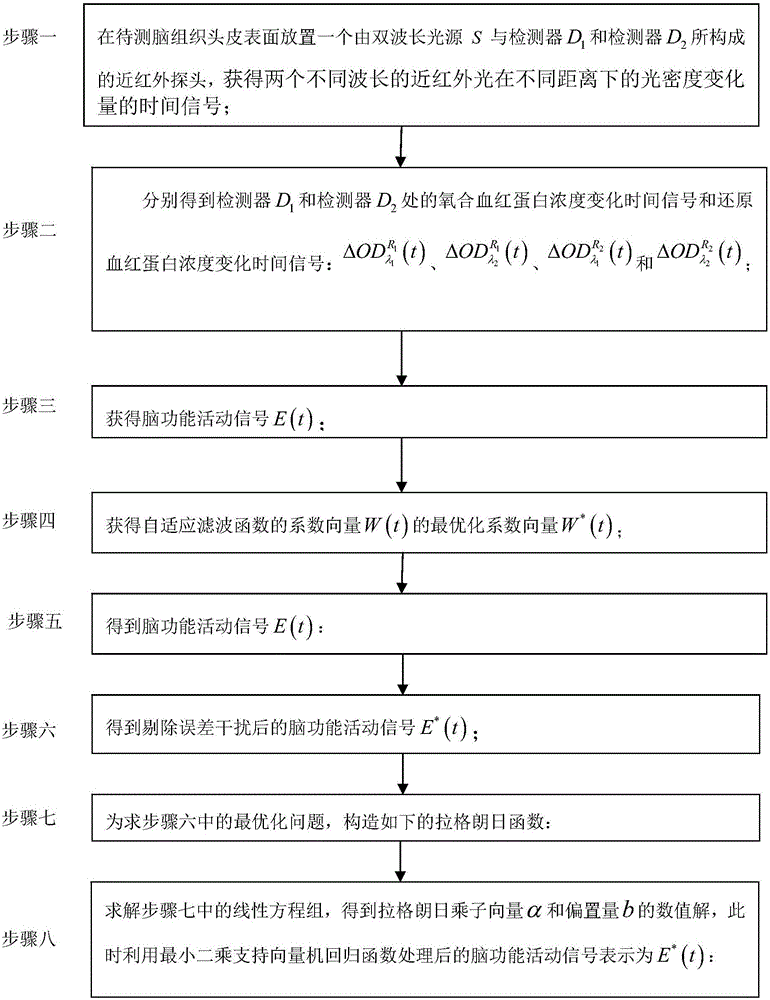
[0064] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 and figure 2 To illustrate this embodiment, the method for extracting near-infrared brain function signals based on the least squares support vector machine of this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
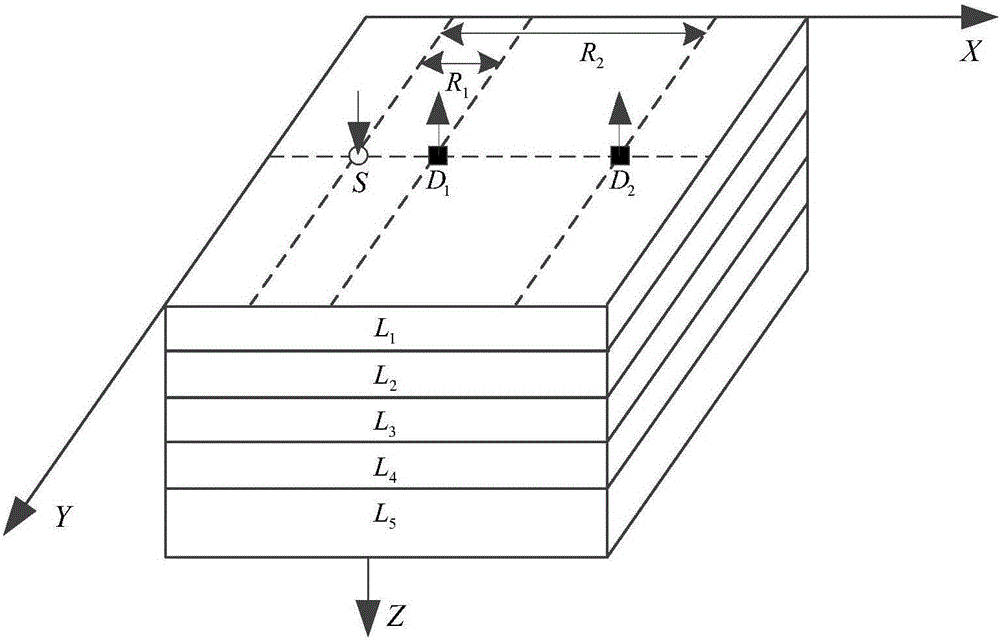
[0065] Step 1: Place a dual-wavelength light source S and detector D on the surface of the scalp of the brain tissue to be tested 1 and detector D 2 A near-infrared probe composed of a dual-wavelength light source S and a detector D 1 The straight-line distance between 1 , dual-wavelength light source S and detector D 2 The straight-line distance between 2 , the dual-wavelength light source S emits two kinds of near-infrared light with wavelengths λ 1 and lambda 2 , detector D 1 and detector D 2 It is used to obtain the diffuse reflection light intensity in the quiet state of the brain and the diffuse reflection light intensity in the brain-induced excitation state, so as to ob...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0135] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: 5mm1 2 <40mm;
[0136] Among them, R 1 For the dual-wavelength light source S and detector D 1 The straight-line distance between; R 2 For the dual-wavelength light source S and detector D 2 the distance between.
[0137] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0138] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the R 1 10mm, R 2 is 40mm. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com