Phellinus linteus strain and breeding method thereof
A technology of Phellinus linteus and strains, which is applied in the fields of biotechnology and microbial mutation breeding, can solve problems such as no Phellinus linteus strains and the like, and achieve the effect of increasing the yield of biomass and metabolic active substances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: Preparation and mutagenesis of protoplasts
[0031] (1) Activation and cultivation of strains Transfer the slant strain SH1 to a PDA plate, and culture in a 26°C incubator for 8-10 days. Pick the plate mycelium into a homogenizer, add a small amount of liquid culture medium, homogenize and crush it, inoculate it in 100mL liquid culture medium, keep the temperature at 26°C, and culture it statically for 10 days, during which the mycelia are slightly shaken 2-3 times a day.
[0032] (2) Preparation of protoplasts The hyphae were collected by filtration and cultured statically, rinsed with sterile water for 1-2 times, and the water on the surface of the mycelia was blotted dry with sterile absorbent paper. Add 1mL enzyme solution (0.12g wall-lyzing enzyme (purchased from Guangdong Institute of Microbiology), 0.03g disintegrating enzyme (purchased from Sigma) to 12mL 0.6mol / L mannitol solution according to every 0.3g mycelium, and after 0.2 μm bacteria filter...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Screening of mutagenic strains
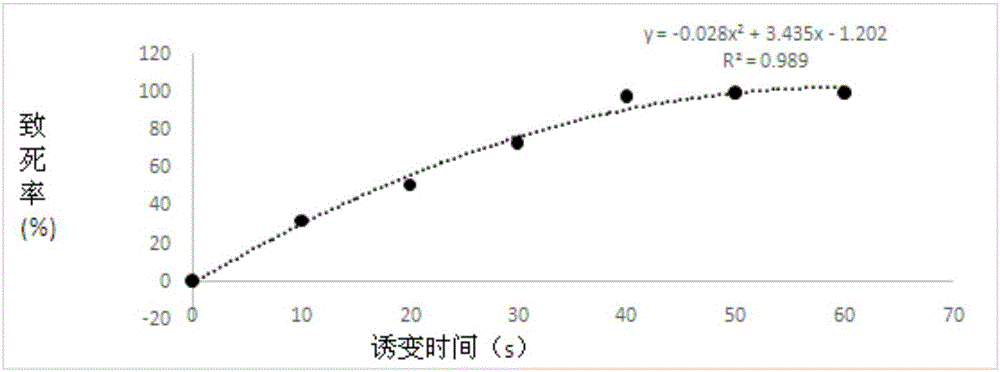
[0035] (1) Preliminary screening of mutagenized strains Take 100 μL of the bacterial solution after mutagenesis and evenly spread it on the regeneration medium. After culturing in a 26°C incubator for 7-10 days, the mutagenized strains will be regenerated. Densely mutated strains were quantitatively inoculated on a new PDA plate with a hole puncher with a diameter of 0.6 cm. After culturing for 10 days, the mycelium growth rate was counted. Taking the average growth rate of 30 non-mutated protoplast regenerated strains as a control, select the mutagenized strain whose mycelial growth rate is greater than that of the starting strain, and carry out the subculture experiment. The growth rate of mycelium was measured in each generation, passed down for 5 times, and 10 excellent strains with fast mycelial growth rate and stable genetics were selected.
[0036] (2) Re-screening of mutagenized strains Take the 10 excellent strain...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: Identification and yield determination of mutagenized strains
[0046] (1) Strain mutagenesis identification
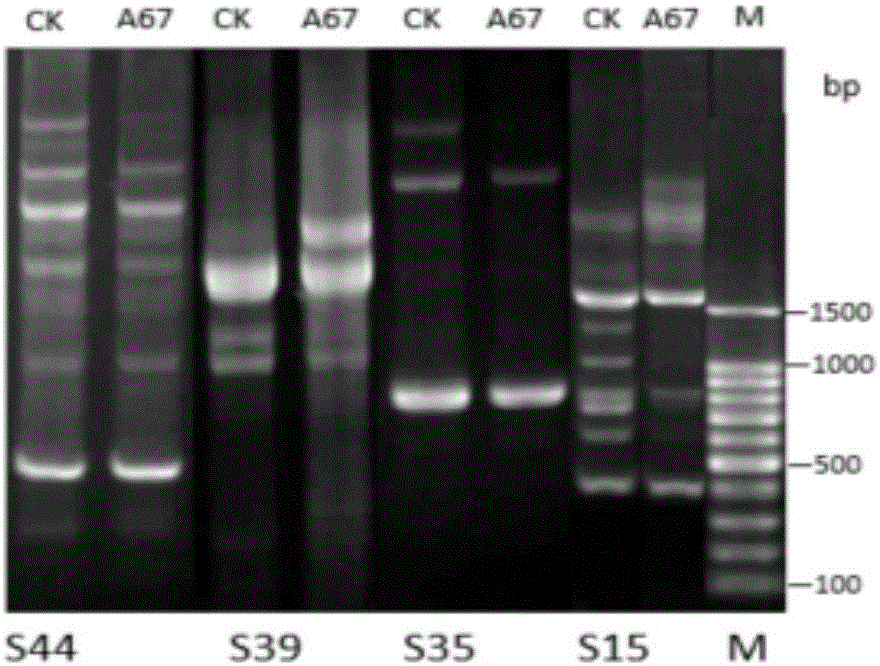
[0047] Antagonism experiment: Antagonism experiment is a method that can quickly identify genetic differences between strains. It can not only be used to determine the relationship between strains of different species, but also to identify whether strains of the same species have mutated. The results showed that the mutagenized strain A67 produced obvious antagonism with the original starting strain SH1, and it was confirmed that the genetic material of the strain had changed from the aspects of hyphal morphology.
[0048] RAPD random primer amplification:
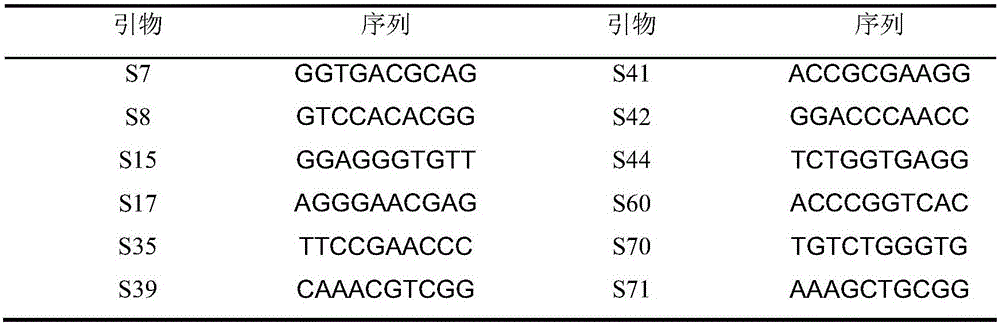
[0049] Using the CTAB method to extract the DNA of the mutagenized strain and the starting strain, 12 primers with good repeatability were screened out from 52 RAPD primers, which could reflect the differences between bacterial strains (see the primer sequence for details). figure 2 ).
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com