Room-temperature liquid metal battery
A liquid metal battery and liquid alloy technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high operating temperature, safety risk, complex structure, etc., and achieve the effect of simple structure and easy design and manufacture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
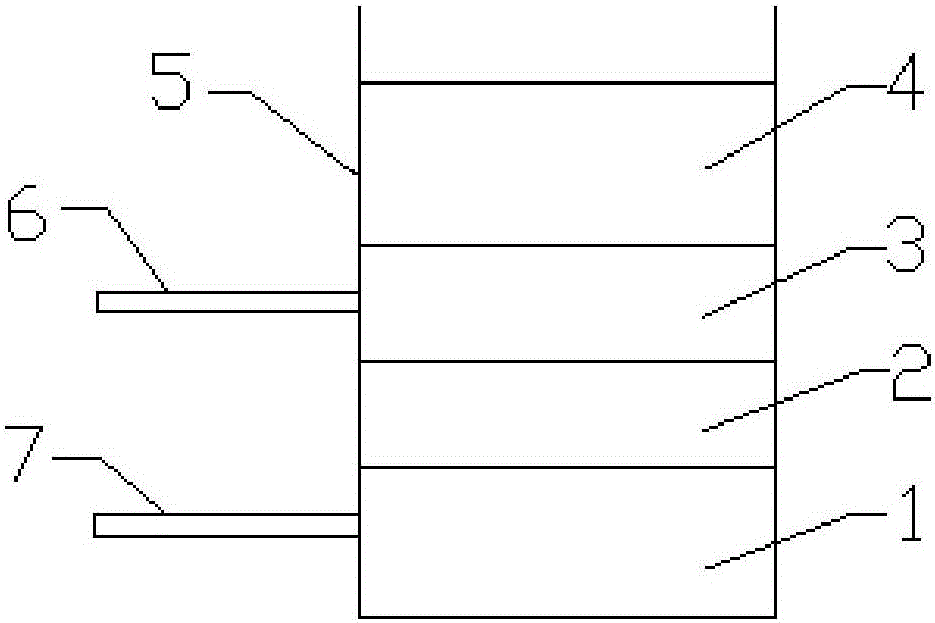
[0032] The liquid metal battery includes three parts: positive liquid metal 1, ionic liquid 2, and negative liquid metal 3. The liquids of the three parts are in contact with each other in sequence, and they are positive liquid metal 1, ionic liquid 2, and negative liquid metal 3 from bottom to top. Positive liquid metal 1 has a melting point of 15.6°C and a density of 6.3g / cm -3 Gallium Indium Alloy GaIn 24.5 ; Negative electrode liquid metal 3 has a melting point of -12.6°C and a density of 0.855g / cm -3 Sodium Potassium Alloy Na 23.3 K 76.7 ; Ionic liquid 2 is 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([BMIM]BF 4 ), the melting point is -52.3℃, and the density is 1.34g / cm -3 , the density of the ionic liquid 2 is greater than that of the negative liquid metal 3 and less than that of the positive liquid metal 1 .
[0033] The preparation process of the liquid metal battery is as follows: the materials of the positive electrode, the spacer layer and the negative elect...
Embodiment 2
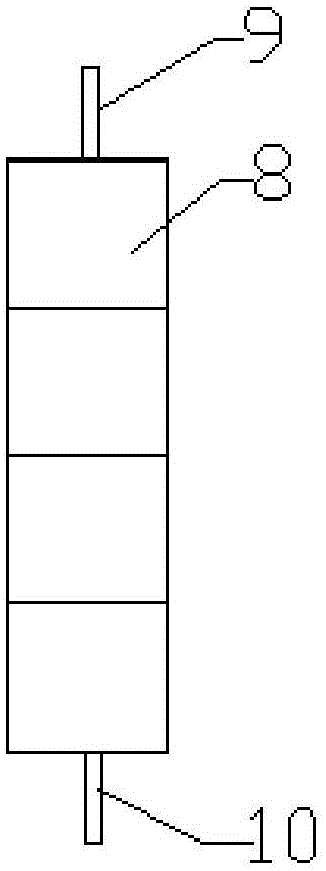
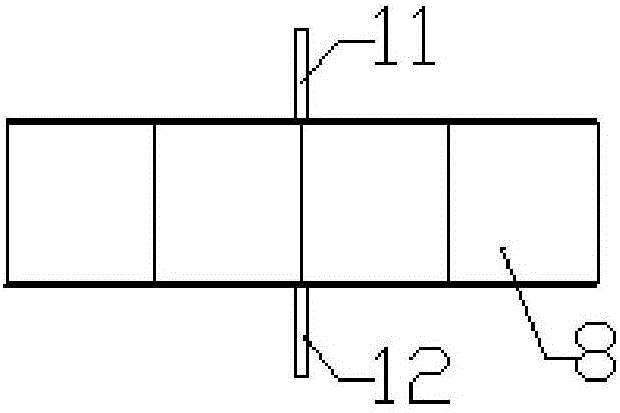
[0036] The thickness of the positive liquid metal 1 is 5 mm, the thickness of the ionic liquid 2 is 3 mm, and the thickness of the negative liquid metal 3 is 5 mm. The packaging layer 4 of the liquid metal battery is liquid paraffin covered on the negative liquid metal 3; the liquid metal battery shell 5 It is glass that does not react with the negative liquid metal 3, the ionic liquid 2, and the positive liquid metal 1; the material of the negative lead-out pole piece 6 of the battery and the positive lead-out pole piece 7 of the battery is copper. Schematic diagram of the structure of a liquid metal battery figure 1 shown. Other materials and preparation methods are the same as in Example 1.
[0037] The open circuit voltage of the liquid metal battery is 1.9V.
Embodiment 3
[0039]The thickness of the positive liquid metal 1 is 5 mm, the thickness of the ionic liquid 2 is 3 mm, and the thickness of the negative liquid metal 3 is 5 mm, and 5% KCl (accounting for the mass ratio of the ionic liquid) is added to the ionic liquid. The packaging layer 4 of the liquid metal battery is liquid paraffin covered on the negative liquid metal 3; the liquid metal battery shell 5 is a double-layer structure, the inner layer is plastic, and the outer layer is stainless steel, which can realize tight sealing; the battery case Open top. After evacuating through the opening of the shell and replacing it with argon gas, after sequentially adding the materials of the positive electrode, the spacer layer and the negative electrode into the battery shell, the argon gas forms the encapsulation layer; The material is copper. Other materials are with embodiment 1.
[0040] The open circuit voltage of the liquid metal battery is 2.0V.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com