Medicine for enhancing osteoblast bone formation in targeting manner and synthesis method thereof
A technology of osteoblasts and synthetic methods, applied in the direction of drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., can solve non-bone tissue or organ toxic side effects, reduce drug therapeutic index, lack bone specificity of drugs, etc. problems, achieve high targeting, promote osteogenesis, and reduce side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
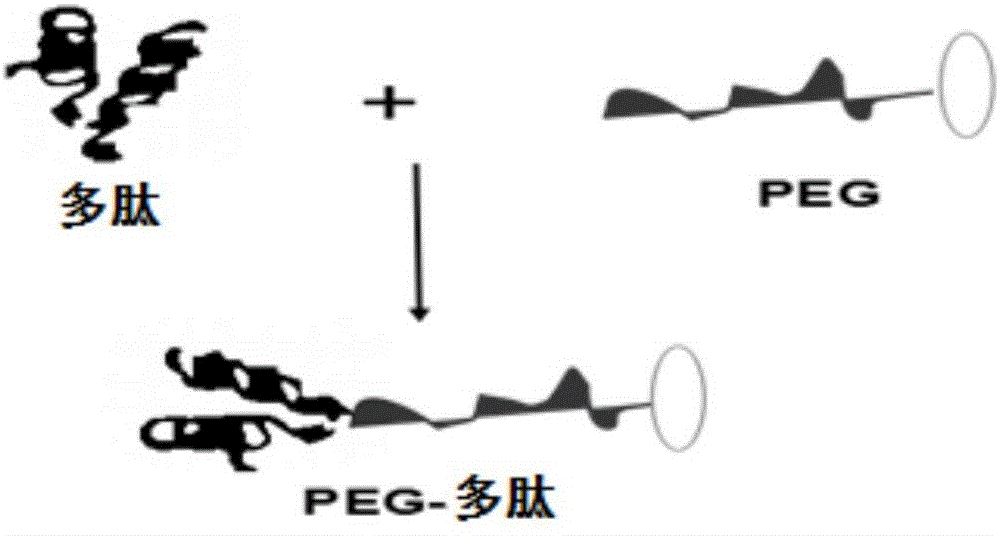
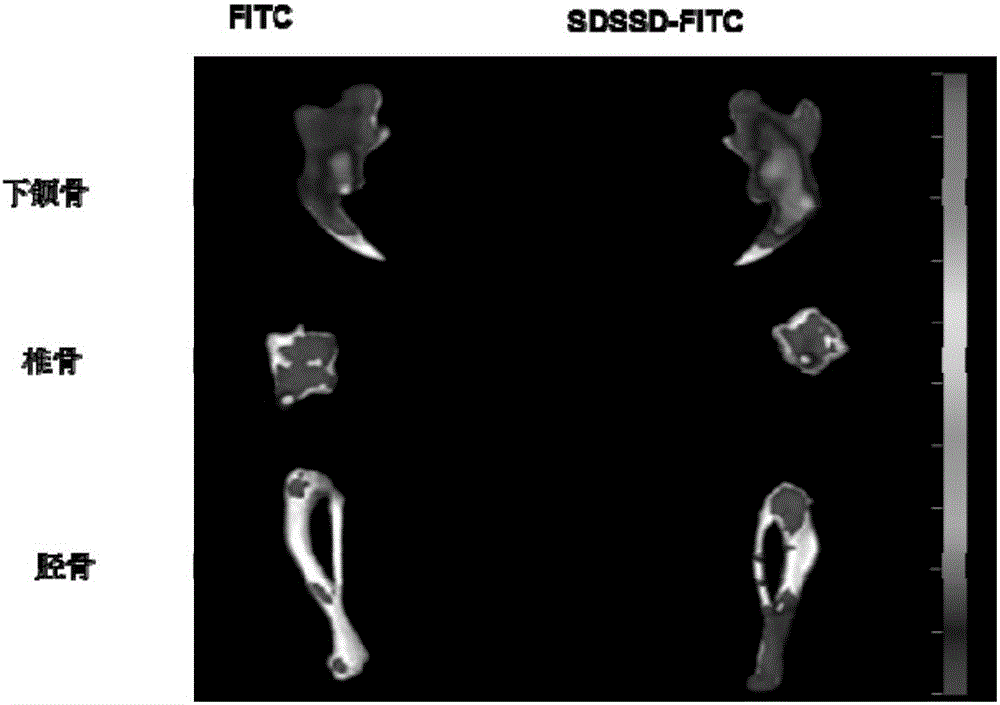
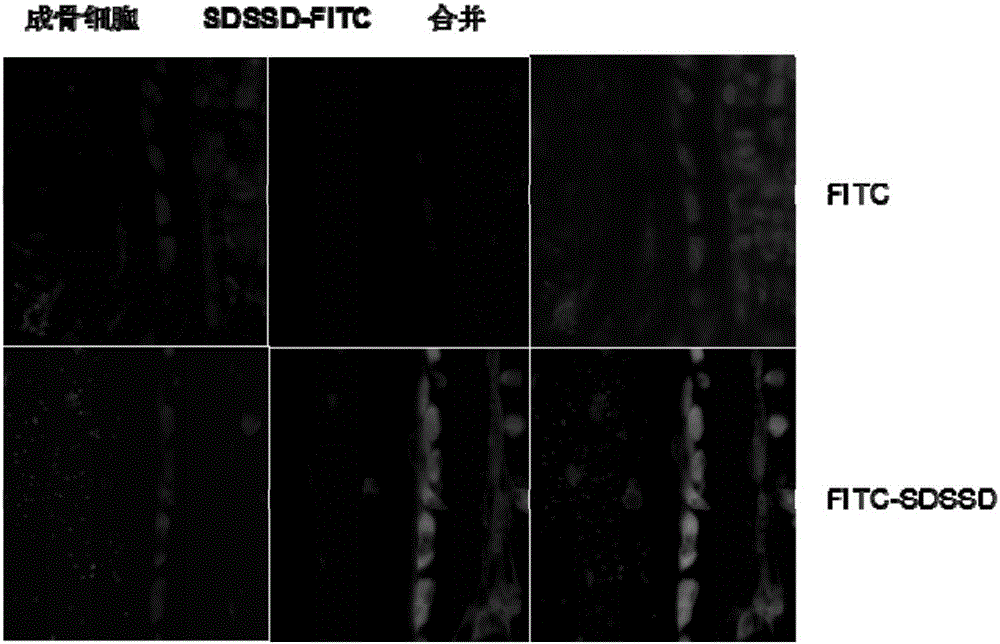
[0031] A drug for targeting and enhancing bone formation of osteoblasts, the active ingredient is a polypeptide, the polypeptide is composed of 3 serines and 2 aspartic acids, and its sequence is Ser Asp Ser Ser Asp, wherein, Ser represents serine, Asp Represents aspartic acid, wherein the surface of the polypeptide is modified with PEG.
[0032] The drug also includes physiological saline with a content of 55% of the active ingredient, which, when used, is injected directly into the human body by intravenous injection.
[0033] The above-mentioned medicine for targeting and enhancing osteoblast bone formation, its synthesis method is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0034] (1) Preparation of polypeptides: Condensed amino acids into polypeptides at the ratio of Ser:Asp=2:3 by a twelve-channel semi-automatic polypeptide synthesizer, and set aside for use;
[0035] (2) Activation of the polypeptide: dissolve the polypeptide obtained in step (1) in de...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A drug targeted at enhancing osteoblast bone formation, its active ingredient is a polypeptide, the polypeptide is composed of 1 serine and 1 aspartic acid, and its sequence is Ser Asp, where Ser stands for serine, and Asp stands for aspartate Amino acid, wherein the surface of the polypeptide is modified with PEG.
[0045] The medicine also includes physiological saline, the content of the active ingredient is 50%, and when used, it enters the human body directly through intravenous injection.
[0046] The above-mentioned drugs targeted to enhance bone formation of osteoblasts include the following steps:
[0047] (1) Preparation of polypeptides: condense amino acids into polypeptides by using a 12-channel semi-automatic polypeptide synthesizer according to the ratio of Ser:Asp=1:1, and wait for use;
[0048] (2) Activation of the polypeptide: dissolve the polypeptide obtained in step (1) in deionized water, then add EDC and NHS equal in mass to the polypeptide to act...
Embodiment 3
[0053] A drug targeted at enhancing bone formation of osteoblasts, the active ingredient of which is a polypeptide, which consists of 10 serines and 40 aspartic acids, and its sequence is:
[0054] Ser Asp Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Ser AspAsp Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Ser AspAsp Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Ser Asp Asp Asp Asp Asp Asp, where , Ser represents serine, Asp represents aspartic acid, wherein the surface of the polypeptide is modified with PEG.
[0055] The medicine also includes physiological saline, and the content of the active ingredient is 60%. When used, it enters the human body directly through intravenous injection.
[0056] The above-mentioned drugs targeted to enhance bone formation of osteoblasts include the following steps:
[0057] (1) Preparation of polypeptides: condense amino acids into polypeptides according to the ratio of Ser:Asp=1:4 through a twelve-channel se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com