Magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire for ferrous metallurgy and preparation method of magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire
A magnesium-calcium alloy, iron and steel metallurgy technology, applied in the field of composite material additives in the form of cored wires and their preparation, can solve the problems of precise control of unfavorable alloy components, high metallurgical process cost, large consumption, etc. Melting point, the effect of improving the degree of cold work hardening and improving the cleanliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
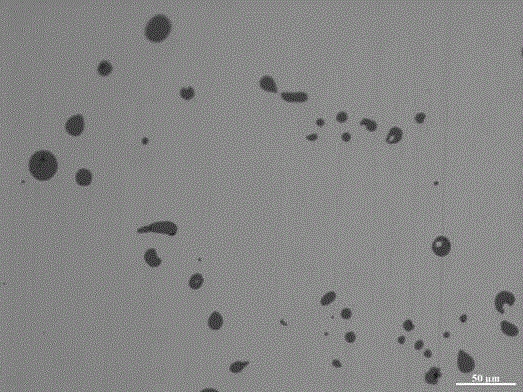
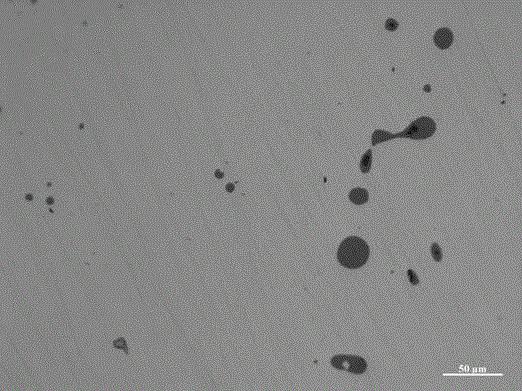
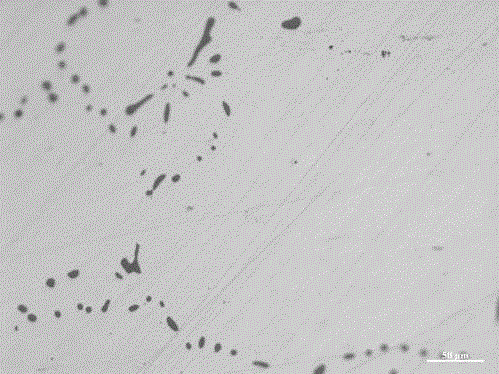
[0026] In this example, a method for preparing a magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire for iron and steel metallurgy uses Si-Mg alloy, Si-Ca alloy and industrial silicon powder with a silicon content of 99wt.% as raw materials. The main chemical composition mass percentage of the core material of the cored wire is as follows: Mg is 6%, Ca is 5%, and the rest of the raw materials are mainly silicon. Mix Si-Mg alloy, Si-Ca alloy and industrial silicon powder After that, it is cold-pressed into a magnesium-calcium alloy billet, preheated, and then hot-extruded into a magnesium-calcium alloy wire, and finally a cold-rolled steel strip with a thickness of 0.3 mm is used to wrap the magnesium-calcium alloy wire into a solid core Metal cored wire.
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0036] In this example, a method for preparing a magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire for iron and steel metallurgy uses Si-Mg alloy, Si-Ca alloy and industrial silicon powder with a silicon content of 99wt.% as raw materials. The main chemical composition mass percentage of the core material of the cored wire is as follows: Mg is 38%, Ca is 30%, and the rest of the raw materials are mainly silicon. Mix Si-Mg alloy, Si-Ca alloy and industrial silicon powder After that, it is cold-pressed into a magnesium-calcium alloy billet, preheated, and then hot-extruded into a magnesium-calcium alloy wire, and finally a cold-rolled steel strip with a thickness of 3 mm is used to wrap the magnesium-calcium alloy wire into a solid core Metal cored wire. The size of the inclusions in the magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire prepared in this example is obviously smaller in the steel sample treated with magnesium-...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment is basically the same as the previous embodiment, and the special features are:
[0039] In this example, a method for preparing a magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire for iron and steel metallurgy uses Si-Mg alloy, Si-Ca alloy and industrial silicon powder with a silicon content of 99wt.% as raw materials. The main chemical composition mass percentage of the core material of the cored wire is as follows: Mg is 10%, Ca is 10%, and the rest of the raw materials are mainly silicon. Mix Si-Mg alloy, Si-Ca alloy and industrial silicon powder After that, it is cold-pressed into a magnesium-calcium alloy billet, preheated, and then hot-extruded into a magnesium-calcium alloy wire, and finally a cold-rolled steel strip with a thickness of 0.3 mm is used to wrap the magnesium-calcium alloy wire into a solid core Metal cored wire. Compared with Example 1, the magnesium-calcium alloy cored wire prepared in this example undergoes magnesium-calcium composite treatmen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com