Method for preparing non-fusion-tag inclusion body protein nanoparticles
A nanoparticle and fusion protein technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of removing fusion tags, restricting applications, unable to restore the nanostructure of inclusion body proteins, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
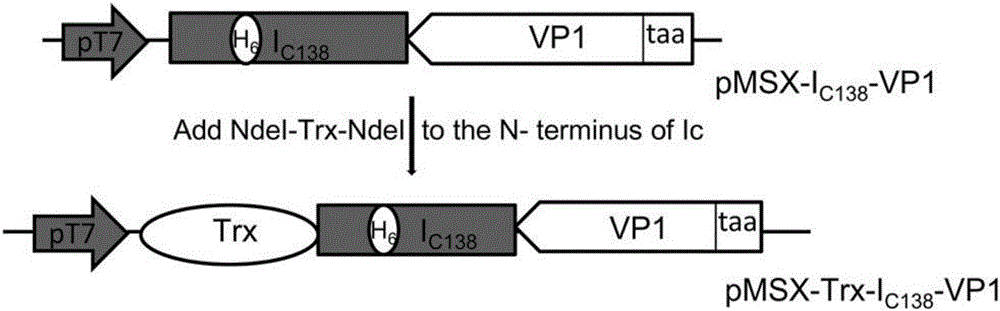
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the construction process of the fusion protein expression vector of the present invention is as follows: the C-terminal (Ic 138 ) fusion to obtain pMSX-I C138 -VP1 plasmid, then combine Trx (thioredoxin) with I C138 N-terminal fusion of pMSX-Trx-I C138 - VP1 plasmid.
[0030] The VP1 protein gene sequence was amplified by PCR and added AgeI and PstI restriction sites on both sides, and then cloned into I C138 The C-terminus of the plasmid pMSX-I was obtained C138 -VP1, then amplify the gene fragment of Trx by PCR amplification, add NdeI enzyme cutting sites on both sides, and connect to I C138 The N-terminus of the plasmid pMSX-Trx-I was obtained C138 -VP1, to obtain the gene encoding the fusion protein.
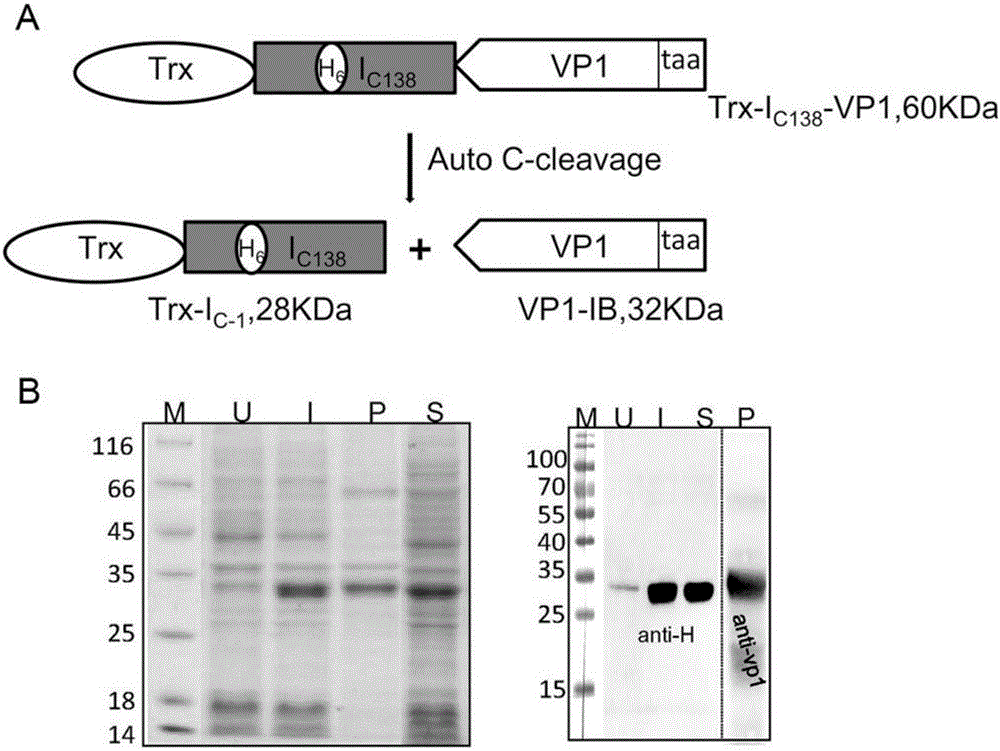
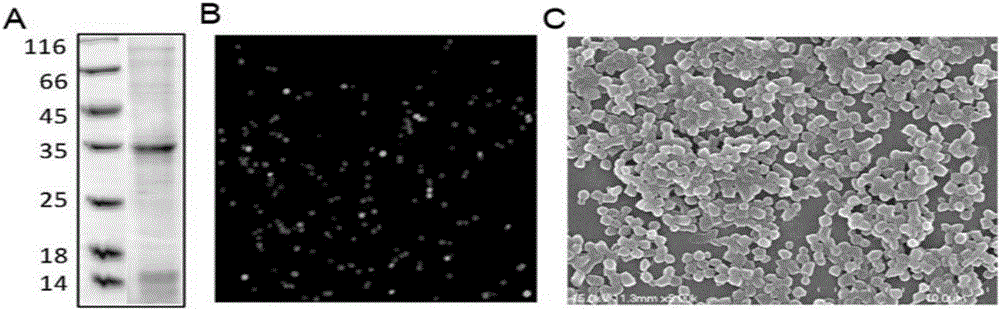
[0031] The gene encoding the fusion protein was induced and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 at 25°C by adding 0.25mM IPTG. During this process, the Ic of Ssp DnaX mini-intein 138 Spontaneous cleavage, the target protein is release...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com