Method for degrading dyeing wastewater by using metal-free catalytic system
A technology for metal-free catalysis and printing and dyeing wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, textile industry wastewater treatment, special compound water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the practical application of catalytic systems, narrow pH value range, and difficult removal of iron ions , to achieve obvious removal effect, little environmental damage and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
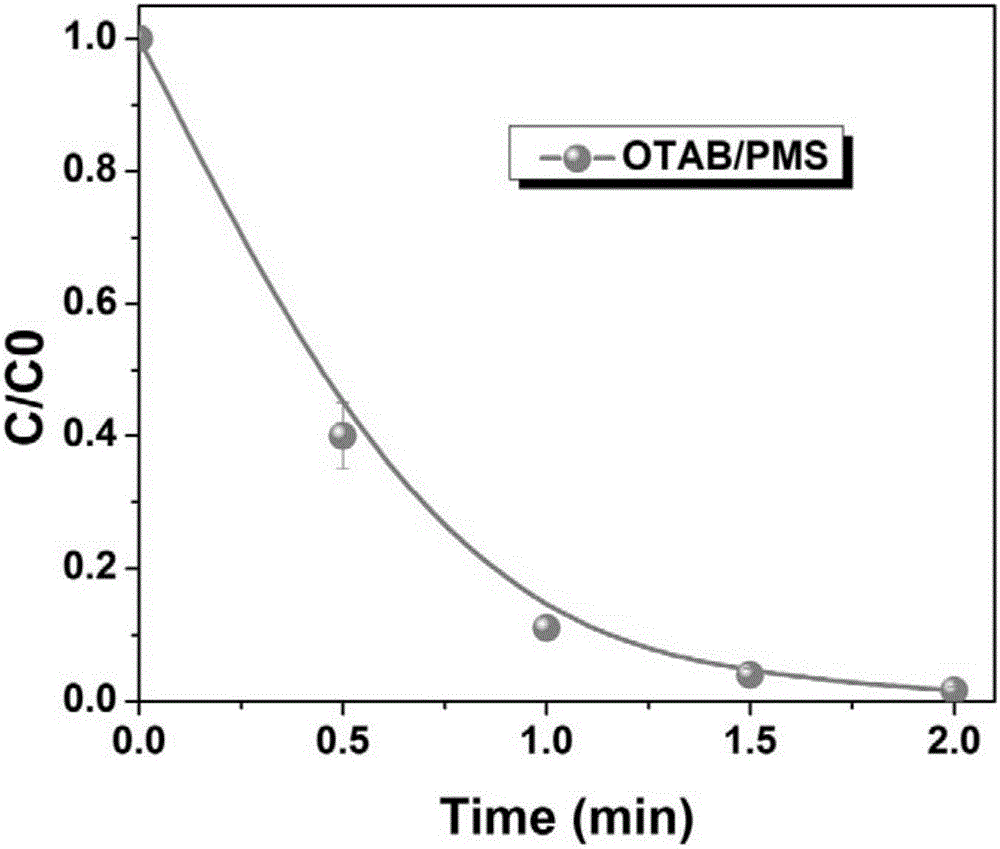
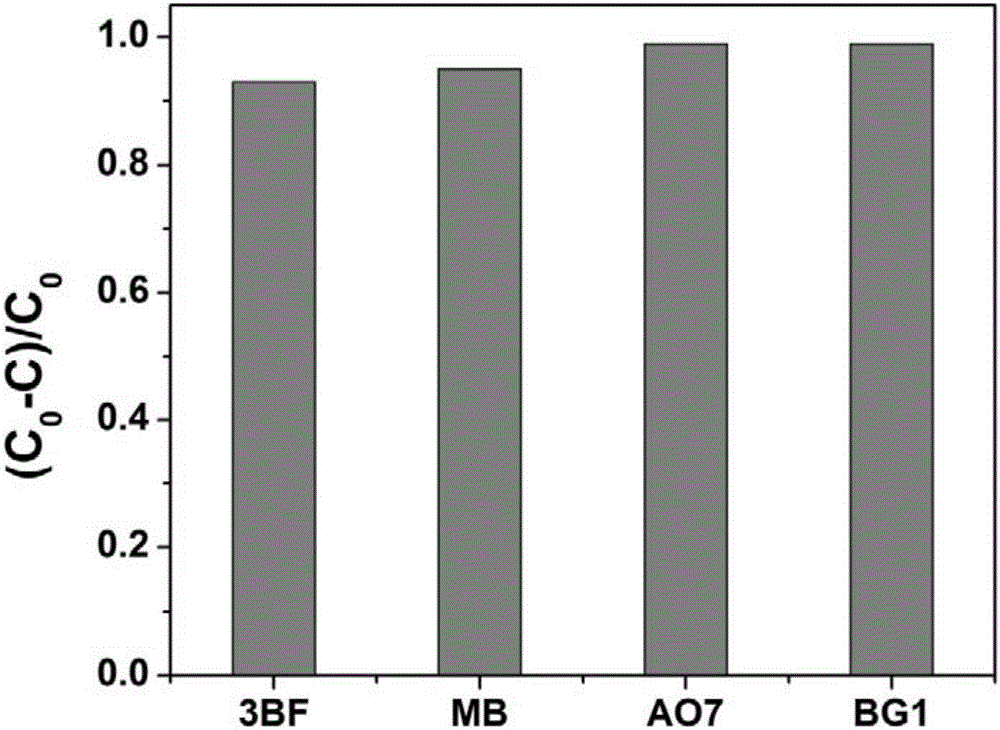
[0021] The selected metal-free catalyst is octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (OTAB), and the oxidant is permonomonosulfate (PMS). The reaction was carried out in a 40ml reaction vessel, and 0.92mM octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (OTAB) and 0.25mM permonomonosulfate (PMS) were successively added to acid orange with pH=7 and a concentration of 100μM. (AO7), after reacting at room temperature for 2 minutes, the removal rate of the dye AO7 reached over 98%, the effect diagram is as follows figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0023] The metal-free catalyst is cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and the oxidant is permonomonosulfate (PMS). The reaction was carried out in a 40ml reaction vessel, and 0.92mM cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and 0.25mM permonomonosulfate (PMS) were successively added to acid orange with pH=7 and a concentration of 100μM. In (AO7), the removal rate of dye AO7 reached 81.2% after reacting at room temperature for 2 minutes; after reacting at room temperature for 5 minutes, the removal rate of dye AO7 was as high as 99%. The effect diagram is as follows figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0025] The selected metal-free catalyst is tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide (TTAB), and the oxidant is permonomonosulfate (PMS). The reaction was carried out in a 40ml reaction vessel, and 0.92mM tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide (TTAB) and 0.25mM permonomonosulfate (PMS) were successively added to acid orange with pH=7 and a concentration of 100μM. (AO7), after reacting at room temperature for 40 minutes, the removal rate of dye AO7 reached 95%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com