Preparation method of high-performance neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A NdFeB high-performance technology, applied in magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the saturation magnetization of the main phase grains and reducing the remanence of the magnets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Table 1 NdFeB alloy and assisted diffusion alloy flakes
[0019]
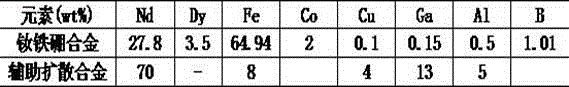
[0020] According to the components shown in Table 1, smelt NdFeB alloy flakes and auxiliary diffusion alloy flakes. The two alloys were ground into powder by HD, intermediate grinding, and jet milling respectively. The particle size of the NdFeB alloy powder was 5 μm, and that of the assisted diffusion alloy powder was 9 μm. The NdFeB alloy powder is pressed separately, sintered at 1050°C for 5 hours to form a magnet, and the magnet M1 is prepared; the auxiliary diffusion alloy powder is mixed with the NdFeB alloy powder at a ratio of 1.5wt%, pressed and formed, and sintered at 1050°C for 5 hours to form a billet. Magnet M2. Both magnets are processed into 15-15-4 flakes, and the surface is coated with mixed slurry (dysprosium metal powder is mixed with ethanol at a ratio of 4%). The weight gain ratio of the magnets before and after coating is 1.0%, and the diffusion treatment is 8h at 920°C. Then a...
Embodiment 2
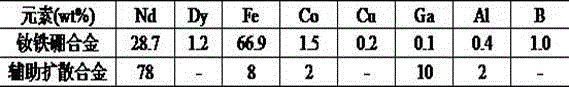
[0025] Table 3 NdFeB alloy and assisted diffusion alloy flakes
[0026]
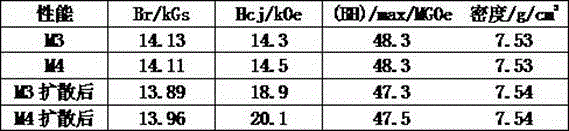
[0027] According to the components shown in Table 3, smelt NdFeB alloy flakes and auxiliary diffusion alloy flakes. The two alloys were ground into powder by HD, intermediate grinding, and jet milling respectively. The particle size of the NdFeB alloy powder was 6 μm, and the particle size of the assisted diffusion alloy powder was 8 μm. The NdFeB alloy powder is pressed separately, sintered at 1080°C for 4 hours to form a magnet, and the magnet M3 is prepared; the auxiliary diffusion alloy powder is mixed with the NdFeB alloy powder at a ratio of 1.2wt%, pressed and formed, and sintered at 1080°C for 4h to form a billet. Magnet M4. Both magnets are processed into 15-15-4 thin slices, and the surface is coated with mixed slurry (dysprosium fluoride powder is mixed with ethanol at a ratio of 4.5%). The weight gain ratio of the magnets before and after coating is 0.8%, and the diffusion treatment is at...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Table 5 NdFeB alloy and assisted diffusion alloy flakes
[0033]
[0034] According to the components shown in Table 5, smelt NdFeB alloy flakes and auxiliary diffusion alloy flakes. The two alloys were ground into powder by HD, intermediate grinding, and jet milling respectively. The particle size of the NdFeB alloy powder was 6 μm, and the particle size of the assisted diffusion alloy powder was 10 μm. The NdFeB alloy powder is pressed separately, sintered at 1060°C for 5h to form a magnet, and the magnet M5 is prepared; the auxiliary diffusion alloy powder is mixed with the NdFeB alloy powder at a ratio of 2.2wt%, pressed and formed, and sintered at 1060°C for 5h to form a billet. Magnet M6. Both magnets are processed into 15-15-4 flakes, and the surface is coated with mixed slurry (metal terbium powder is mixed with ethanol at a ratio of 3.5%). The weight gain ratio of the magnets before and after coating is 0.8%, and the diffusion treatment is at 920°C for 8 ho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com