Spectrum regulating and controlling device for mid-infrared pulse lasers
A pulsed laser and control device technology, applied in the laser field, can solve the problems of lack of detection means, laser pulse time asynchronous, non-periodically polarized crystals can not achieve the goal, etc., to simplify the complexity and eliminate the mismatch of group velocity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
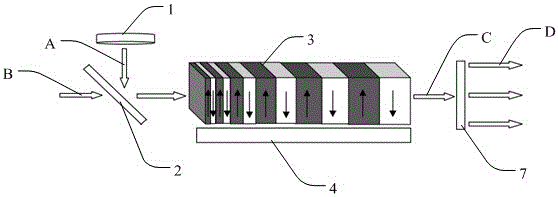
[0028] The invention provides a spectrum control device for mid-infrared pulsed laser. In order to make the object, technical solution and effect of the present invention more clear and definite, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
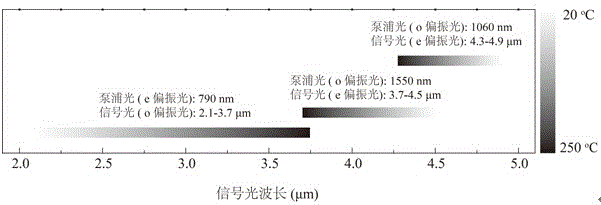
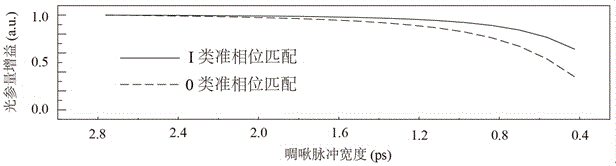
[0029] The crystal refractive index (n) will change with the temperature, and the group velocity (v) of the pulsed laser in the crystal is also a physical quantity related to temperature. In order to take advantage of the largest nonlinear coefficient (d33) of nonlinear crystals, non-periodically polarized crystals usually need to meet the quasi-phase matching conditions of type 0 (e+e-›e), requiring pump light, signal light and idler frequency The light is all e polarized light. There is a large difference in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com