3D (three-dimensional) printing preparation method of orthopaedic external fixing support
A 3D printing and external fixation technology, applied in fractures, medical science, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low degree of fit, long customization time, etc., and achieve the effect of correcting mechanical strength and high degree of fit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
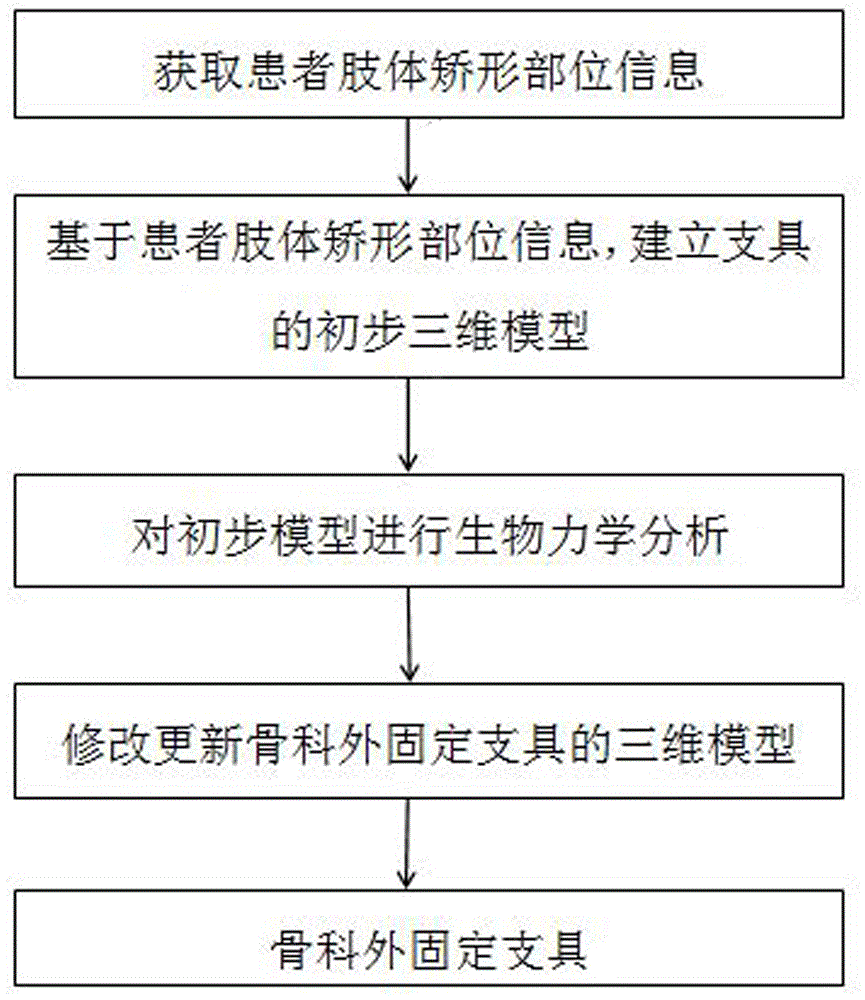
[0026] This embodiment provides a 3D printing preparation method for an orthopedic external fixation brace in order to meet the requirement that the material required for the supporting part of the orthopedic external fixation brace is relatively hard, while the material required for the contact part with soft tissue is relatively soft. Such as figure 1 As shown, the steps are:
[0027] 1) Obtain information on the orthopedic parts of the patient's limbs;
[0028] Since the orthopedic part of the patient's limb is composed of bones and soft tissues, and has a complex structure, it is necessary to use a 3D scanner to accurately obtain the 3D shape information of the orthopedic part of the limb, such as a professional 3D laser scanner or a hand-held 3D scanner. The scanning accuracy of the instrument is better than 0.1mm, and it can accurately obtain the information of the orthopedic parts of the patient's limbs in a short period of time, which is convenient and accurate;
[0...
Embodiment 1
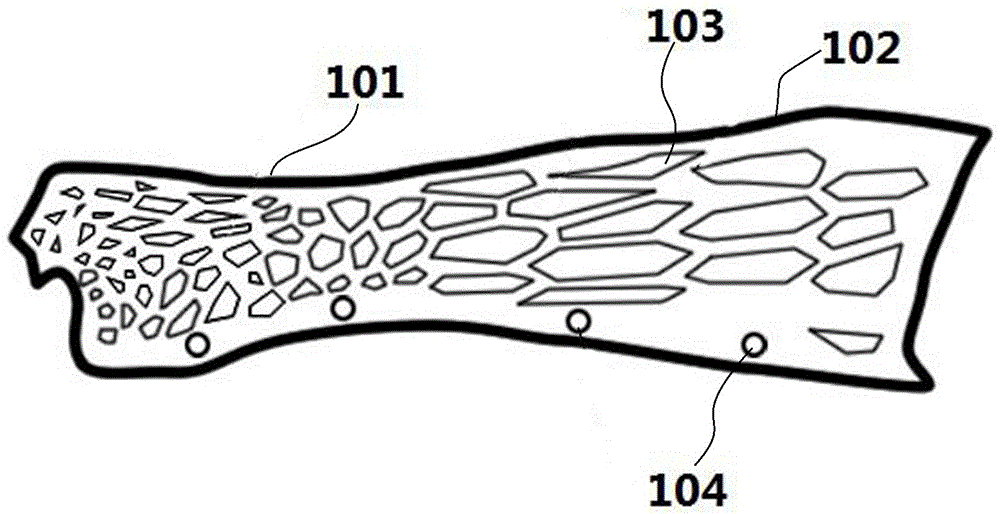
[0044] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a structural diagram of a wrist fracture fixation brace, which includes a wrist 101 with a relatively high local hardness, a forearm 102 with a relatively low hardness, and a buckle 104 is provided at the opening of the brace; The ratio is small and the hardness is high; the proportion of the hollow 103 at the forearm 102 is large and the hardness is low.
[0045] According to biomechanical analysis, the required Rockwell hardness of the wrist 101 is 1.8, and the Rockwell hardness of the forearm 102 is 1.4 (the Rockwell hardness of the skin is 1.5). The material used in this embodiment is polyethylene, and the softness and hardness are changed by adjusting the filling structure and material filling density of different parts of the physical structure. The area ratio is 40-80%.
[0046] The material used in the brace is added with 2% of the total mass of bamboo charcoal fiber powder and 2% of the total mass of seagull stone, which can ...
Embodiment 2
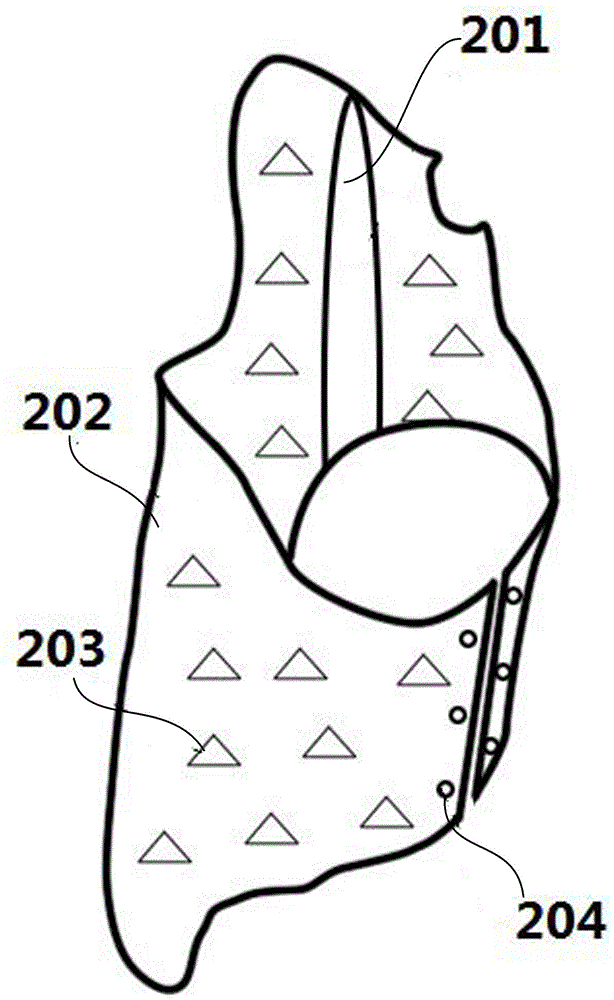
[0049] Such as image 3 As shown, it is a structural diagram of a scoliosis orthopedic brace, including a spine part 201 with relatively high local hardness, a peripheral part 202 with low hardness, and a buckle 204 at the opening of the brace; the spine part 201 is not hollowed out or only There is a small part of hollows; the surrounding part 202 is covered with hollows 203, and the hardness is low. The hardness is changed by changing the ratio of soft and hard materials or the filling rate of the honeycomb structure, and the hardness is higher than that of the peripheral part 202 .
[0050] According to biomechanical analysis, the Rockwell hardness of the required spine part 201 is 2.5, and the Rockwell hardness of the peripheral part 202 is 1.6 (the Rockwell hardness of the skin is 1.5). In this embodiment, the spine part 201 is made of polypropylene, the peripheral part 202 is made of polyvinyl chloride, the area ratio of the hollowed out spine part 201 is 0-20%, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com