Method and device for storing redundant heat of greenhouse and preventing high temperature of greenhouse
A greenhouse and heat technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of heat can not be reused, heat can not be used, high air humidity, etc., to achieve the effect of preventing freezing damage and low temperature damage, preventing high temperature in the greenhouse, and increasing the night temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
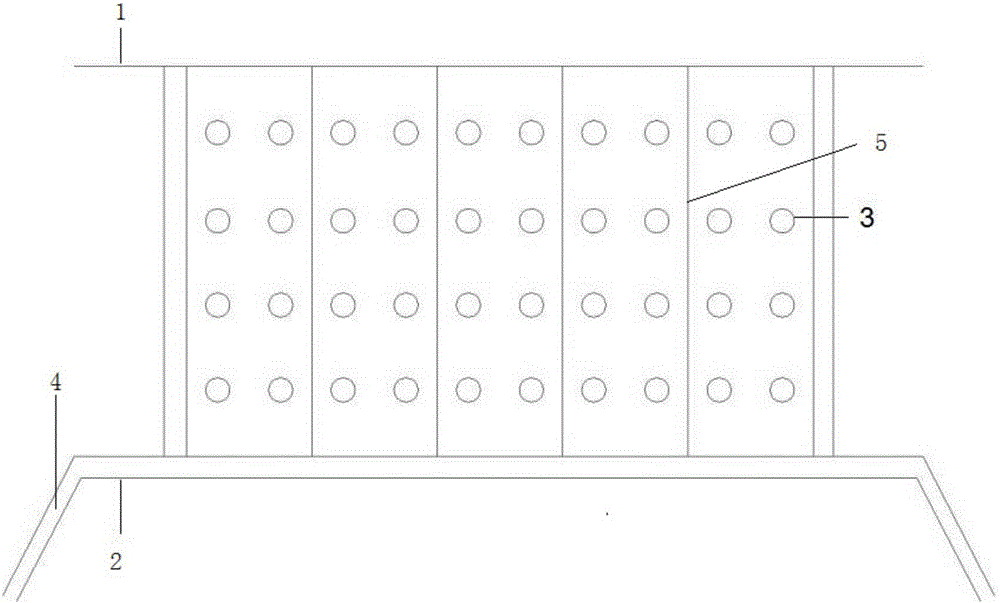
[0034] A method of storing excess heat in a greenhouse and preventing high temperatures in a greenhouse by means of a good conductor of heat aluminum container filled with a low-temperature hydrated salt calcium chloride hexahydrate and a good conductor of heat with an aluminum heat-conducting panel The aluminum cover transfers the solar energy and excess energy exceeding the melting point of 29 degrees Celsius in the greenhouse to the low-temperature hydrated salt calcium chloride hexahydrate. The low-temperature hydrated salt calcium chloride hexahydrate absorbs heat and maintains it in the form of latent heat, saving excess energy, while It will not continue to heat up until it is completely melted, so that the temperature in the greenhouse is controlled below the melting point of low-temperature hydrated salts of 29 degrees Celsius. The reduced indoor air releases heat, increases the temperature of the greenhouse at night, prevents the phenomenon of temperature inversion in...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A method for storing excess heat in greenhouses and preventing high temperatures in greenhouses, through a container filled with low-temperature hydrated salt sodium sulfate decahydrate composed of good thermal conductor stainless steel materials and stainless steel with stainless steel heat conduction panels composed of thermal good conductor stainless steel materials The cover transfers the solar energy and the excess air energy above the melting point of 32.4 degrees Celsius in the greenhouse to the low-temperature hydrated salt sodium sulfate decahydrate, and the low-temperature hydrated salt sodium sulfate decahydrate absorbs heat in the form of latent heat and saves the excess air in the temperature above 32.4 degrees Celsius without continuing to heat up, so that the temperature in the greenhouse is controlled below the melting point of low-temperature hydrated salts of 32.4 degrees Celsius. At night, when the ambient temperature is lower than 32.4-10 degrees Celsi...
Embodiment 3
[0039]A method for storing excess heat in greenhouses and preventing high temperatures in greenhouses, through a container filled with a low-temperature hydrated salt, disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, which is composed of a good thermal conductor iron material and a container made of a good thermal conductor iron material. The cover of the heat-conducting panel transfers the solar energy and excess energy exceeding the melting point of 35 degrees Celsius in the greenhouse to the low-temperature hydrated salt disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, and the low-temperature hydrated salt disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate absorbs heat in the form of latent heat and saves excess energy energy, without continuing to heat up, so that the temperature in the greenhouse is controlled below the melting point of low-temperature hydrated salts below 35 degrees Celsius. At night, when the ambient temperature is lower than 35 degrees Celsius, the molten low-temperature hyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com