Rice lesion mimic gene and encoded protein thereof
A protein and lesion-like technology, which is applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, and the use of vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc., can solve the problem of low disease resistance and achieve good results, easy application, and simple identification and selection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Isolation and genetic analysis test of the lesion-like mutant a344 of the present invention
[0039] (1) Test materials
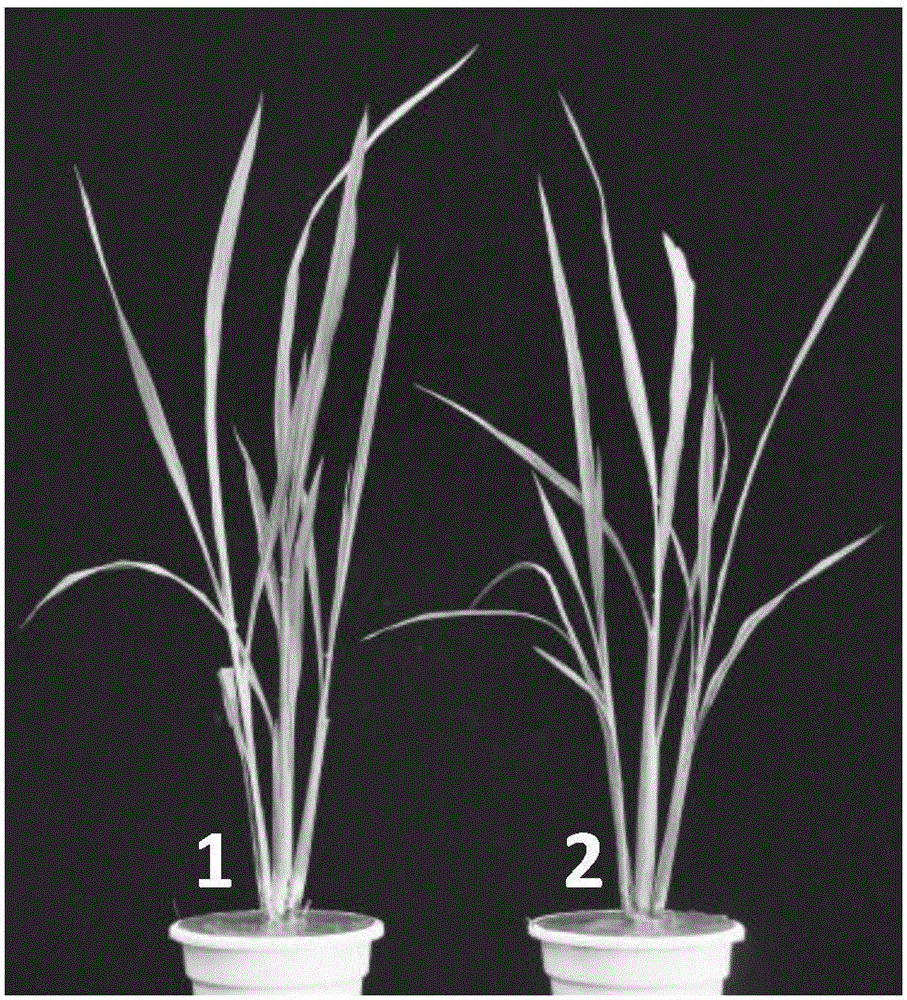
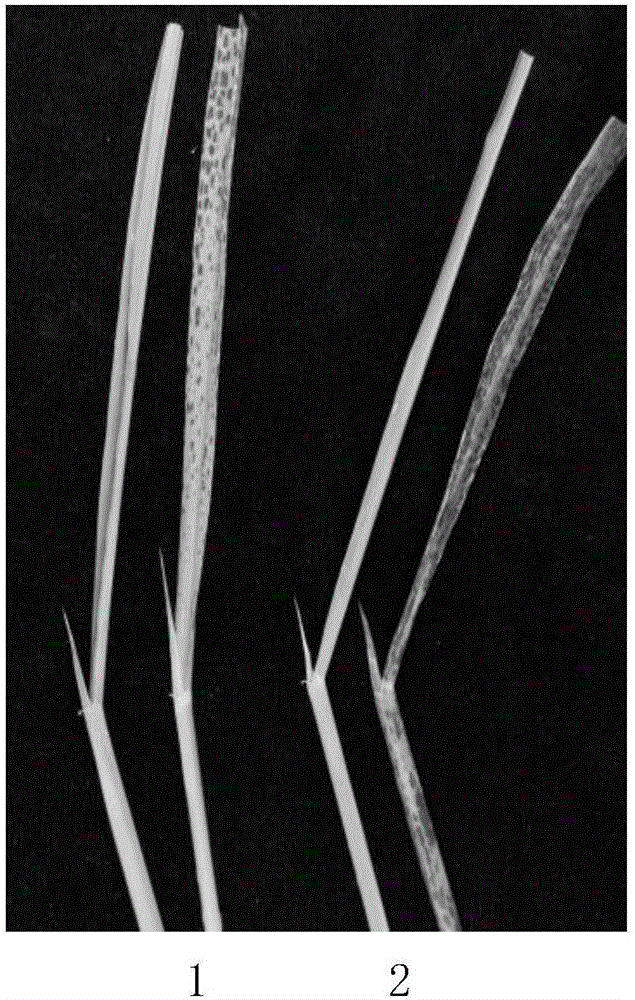
[0040] Lesion-like mutants a344, Hua B and Shuhui 498 were all from the Laboratory of Heterosis Utilization, Rice Research Institute, Sichuan Agricultural University. Among them, the lesion-like mutant a344 was derived from the EMS (ethyl methylsulfonate) mutagenesis library constructed by Shuhui 498. It was found after multiple generations of backcrossing with Shuhui 498 in Wenjiang, Sichuan and Lingshui, Hainan. The lesion phenotype can be stably inherited.
[0041] (2) Test method
[0042] Lesion-like mutants a344, Hua B and Shuhui 498 were all planted in Wenjiang Experimental Field of Rice Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University. F 2 Groups, Statistics F 1 and F 2 group separation ratio.
[0043] (1) Lesion-like phenotype analysis: Compared with wild-type Shuhui 498, mutant a344 appeared necrotic spots on the ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Comparison test of the present invention's lesion-like mutant a344 for identification of resistance to bacterial blight
[0049] (1) Test materials
[0050] 1. Rice material
[0051] (1), Mutants a344 and Shuhui 498 were all derived from the Laboratory of Heterosis Utilization, Rice Research Institute, Sichuan Agricultural University.
[0052] (2) IR24, a variety highly susceptible to bacterial blight, and IRBB21, a variety highly resistant to bacterial blight, were both from the Major Disease Research Office of the Rice Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University.
[0053] 2. Physiological races of Xanthomonas oryzae: J9, 8248, P2, P6, J3 or J7, all from the Major Disease Research Office of the Rice Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University.
[0054] (2) Test method
[0055] 1. Cultivation of rice bacterial blight
[0056] Take the bacterial blight of rice preserved in glycerol, smear evenly on the solid medium, and incubate in the...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: the localization test of mutant a344 candidate gene
[0065] Proceed as follows:
[0066] 1. Location of candidate genes
[0067] (1) Construction of near isogenic pool
[0068] F obtained from crossing mutant a344 with flower B 2 In the population, randomly select 30 leaves of a single plant with a lesion-like phenotype and 10 leaves of a normal single plant, and mix and extract DNA from every 10 leaves in equal amounts to build a pool, including 3 recessive pools and 1 dominant pool A total of 4 pools were used for polymorphism detection between mutant a344 and flower B genome. F obtained by crossing a344 with Shuhui 498 2 In the population, 70 leaves of individual plants with lesion-like phenotype were randomly selected, and equal amounts of leaves from every 10 plants were mixed to extract DNA to build a pool. A total of 7 pools were used for co-segregation analysis of mutation sites. Leaf DNA was extracted by the improved CTAB method.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com