Self-adaptive cardiac valve prosthesis
A heart valve, self-adaptive technology, applied in the field of medical devices, to achieve the effect of avoiding traction, reducing impact, and optimizing valve performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0081] For a long time, whether it is Edwards or Medtronic, major valve manufacturers have adopted the expansion ratio of stent-annulus radial expansion to obtain sufficient stent anchoring force, which has been used in the field of aortic valve interventional replacement and pulmonary valve interventional replacement. It has been fully applied and has become a consensus (generally 10%-15% is the ideal circumference expansion ratio). Later, Jenavalve and Symetic applied the clamping leaflet mechanism to their products, and they still have a certain expansion ratio for the patient's valve. However, atrioventricular valves (including mitral valves and tricuspid valves) are often very difficult to accurately position and fix products due to their complex physiological structures and disease mechanisms. The current technologies for atrioventricular valve interventional replacement, such as Edwards, Medtronic and Tiara, all need to provide a certain radial expansion ratio to meet t...
specific Embodiment 2
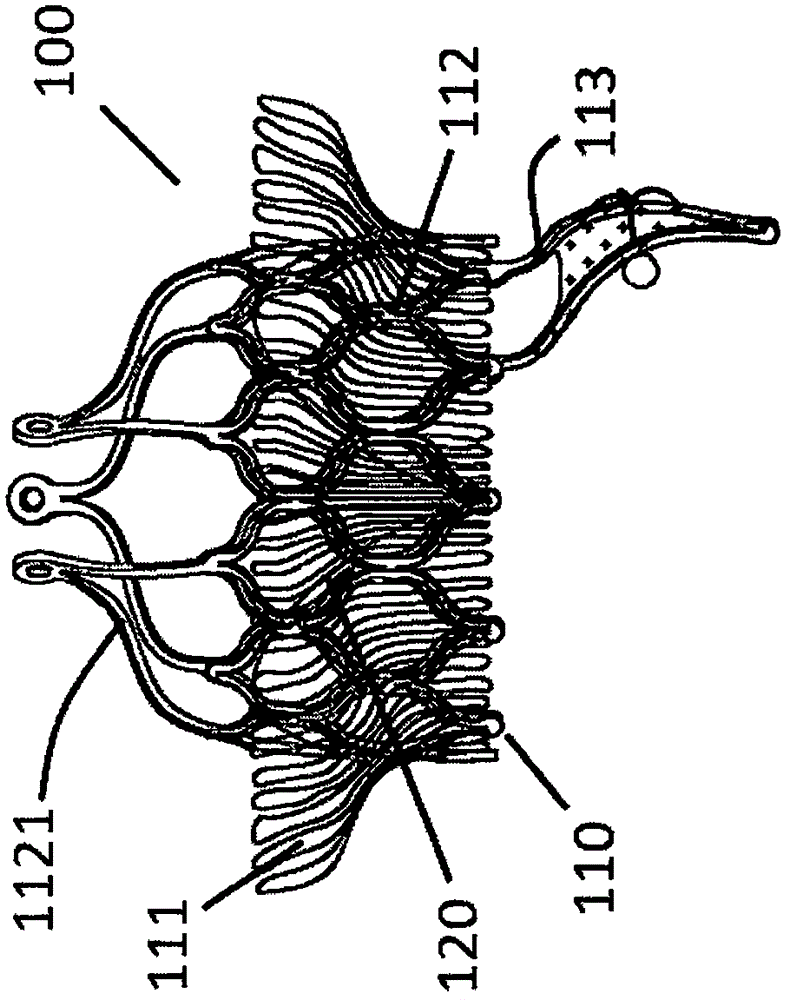
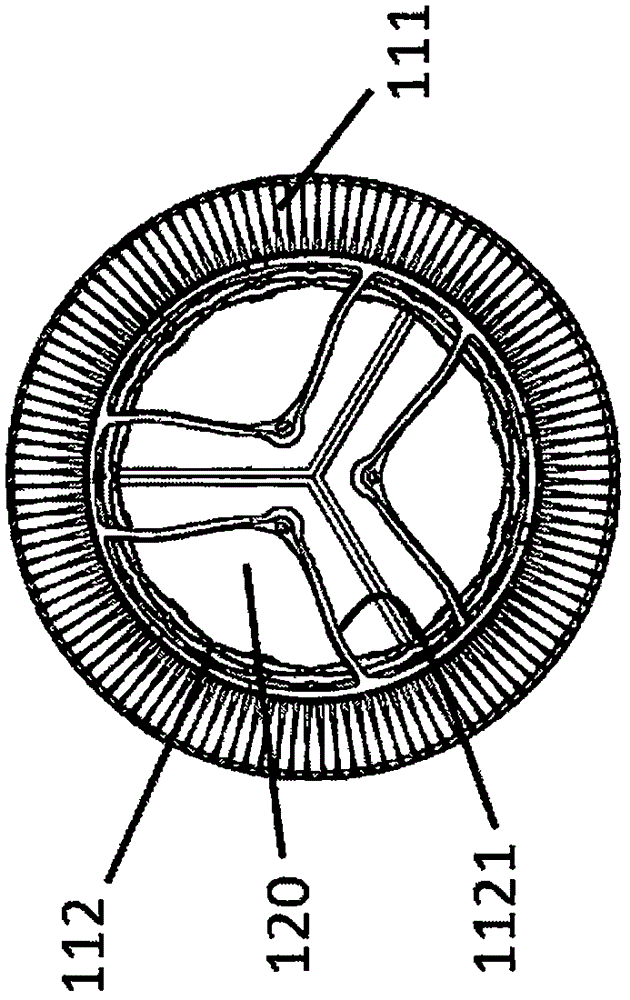
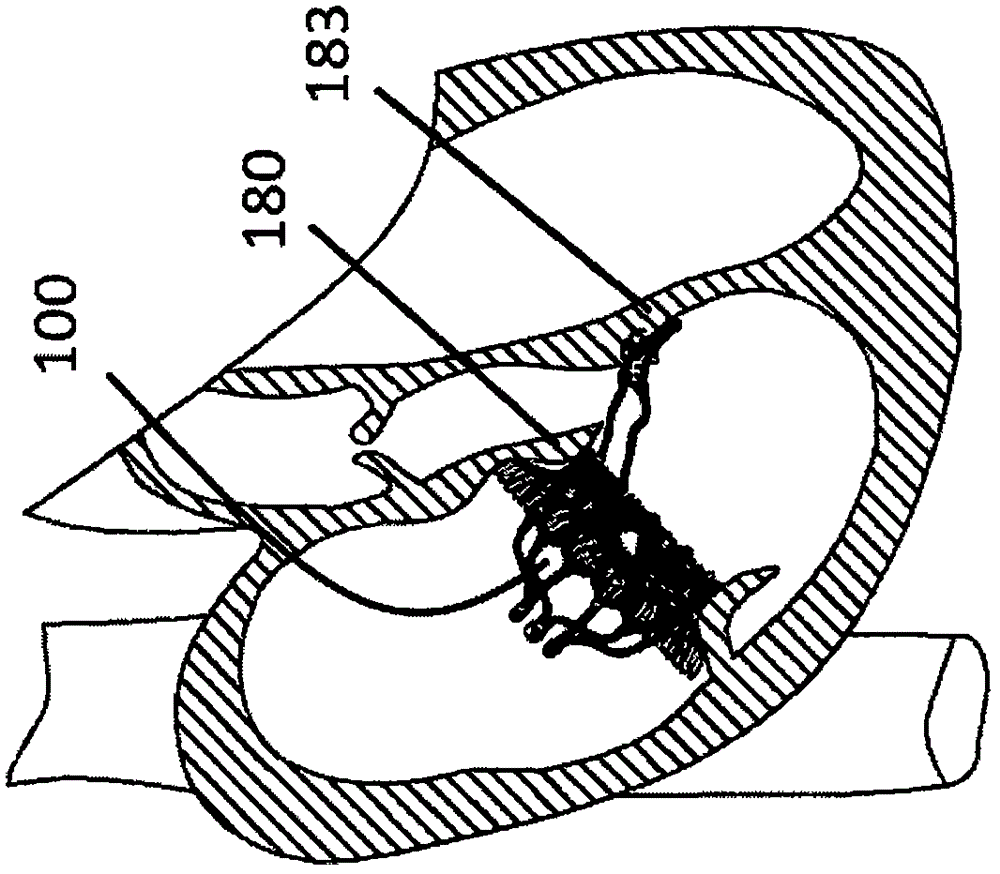
[0090] In one embodiment, as Figure 4a and Figure 4b As shown, an adaptive heart valve prosthesis 200 is used for mitral valve interventional replacement therapy, including a stent 210 and an artificial valve (not shown), and the stent 210 includes an anti-leakage ring 211 and a valve sewing segment 212, The artificial valve is fixedly connected to the valve sewing section 212, and the leak-proof ring 211 is connected to the valve sewing section 212. In a free state, the leak-proof ring 211 is located in the patient's atrium and On the patient's own valve annulus 280, the anti-leakage ring 211 can conform to the uneven contour of the atrial cavity wall or the patient's own valve annulus without restricting the systolic function of the atrium, and the valve sewing section 212 is at least partially positioned on the patient's own Between the valve leaflets, on a cross-section perpendicular to the central axis of the artificial valve, the cross-sectional area of the valve se...
specific Embodiment 3
[0095] In one embodiment, as Figure 5a As shown, an adaptive heart valve prosthesis 300 is used for tricuspid valve interventional replacement therapy, including a stent 310 and an artificial valve (not shown), and the stent 310 includes an anti-leakage ring 311 and a valve sewing segment 312, The artificial valve is fixedly connected to the valve sewing section 312, the valve sewing section 312 is a cylindrical wave-shaped structure, the fixing device 313 is an inverted cone structure, and the fixing device 313 has a large diameter One end of the valve sewing section 312 is connected to the proximal end of the valve sewing section 312 by known techniques such as suture, buckle or welding, and the small diameter end of the fixing device 313 is provided with a connecting rod 315, and the connecting rod 315 is rigid. One end of the connecting rod 315 is connected to the end of the fixing device 313, the proximal part of the connecting rod 315 is provided with a fixing part 314,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com