Method for screening nitrogen fixing blue green algae with biofertilizer application potential
A technology of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and screening method, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of increasing effective nitrogen content and having only reference value and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
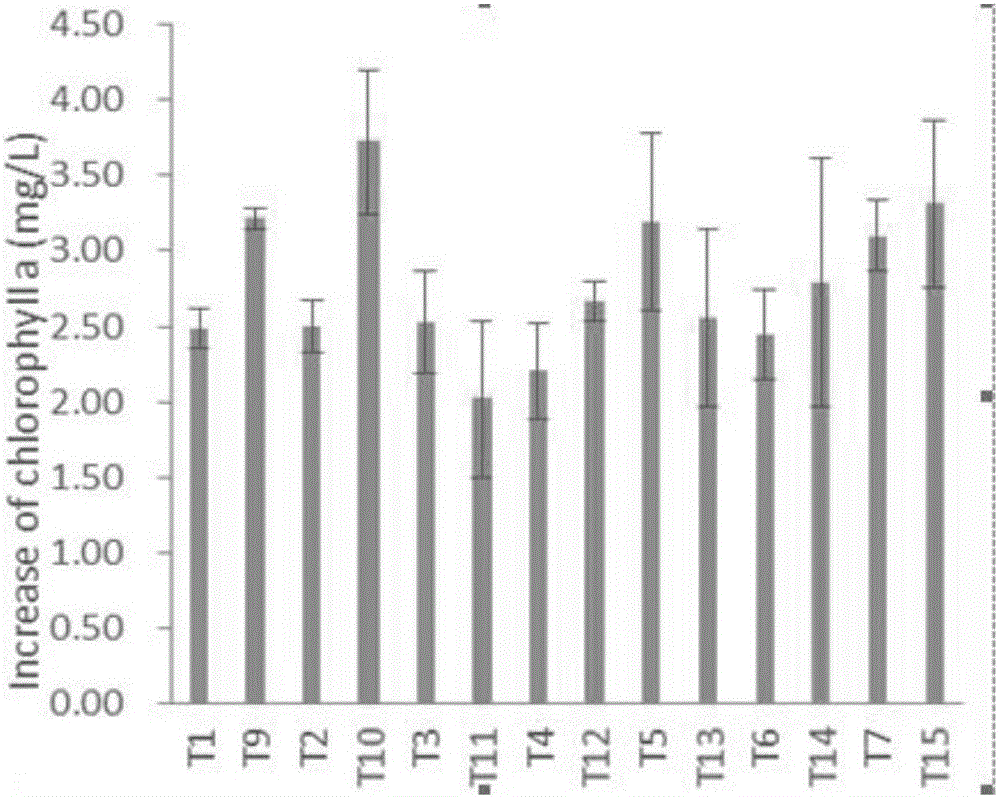
[0034] Symbiotic experiment of embodiment 1 nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and two kinds of bacteria
[0035] Nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria Anabaena B1611 (purchased from the UTEX algae bank of the University of Texas), Nostoc F280 and Anabaena F243 (respectively purchased from the FACHB freshwater algae bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), three soil microorganisms Bacillus thuringiensis Kenya species (Btsk), Pseudomonas fluorescens (Pf) (purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) respectively), with numbers 1.1012 and 1.867, respectively.
[0036] According to the principle of high-throughput experiments, a total of 31 experiments were designed for the symbiosis experiment between nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and bacteria. Cycle (light:dark=14:10), medium is BG11 medium, culture time is 7 days, the change of chlorophyll a content of three kinds of cyanobacteria, the number of CFU of two kinds of bacteria are measured. The experimental ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2 pot experiment
[0049] For judging the impact of single cyanobacteria and different cyanobacteria combinations on soil fertility in Example 1, potted soil experiments were carried out, 8 groups of experiments were designed, the culture temperature was 22°C, the light intensity was 64.33 ± 17.62mol / m2 / s, and the light-dark cycle (light : dark=14:10), the content of available phosphorus, soluble organic carbon, and total soluble nitrogen in the soil was measured on the 6th day, and the experimental design scheme is shown in Table 2.
[0050] The determination of soil available phosphorus refers to methods such as Watanabe [Watanabe F.S., S.R.Olsen, Test of an Ascorbic Acid Method for Determining Phosphorus in Water and NaHCO Extracts from Soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1965.29 (6): 677-678]; The determination of carbon and total soluble nitrogen content refers to the method of Techtmann et al [TechtmannS.M., J.L.Fortney, K.A.Ayers, et al., Th...
Embodiment 3
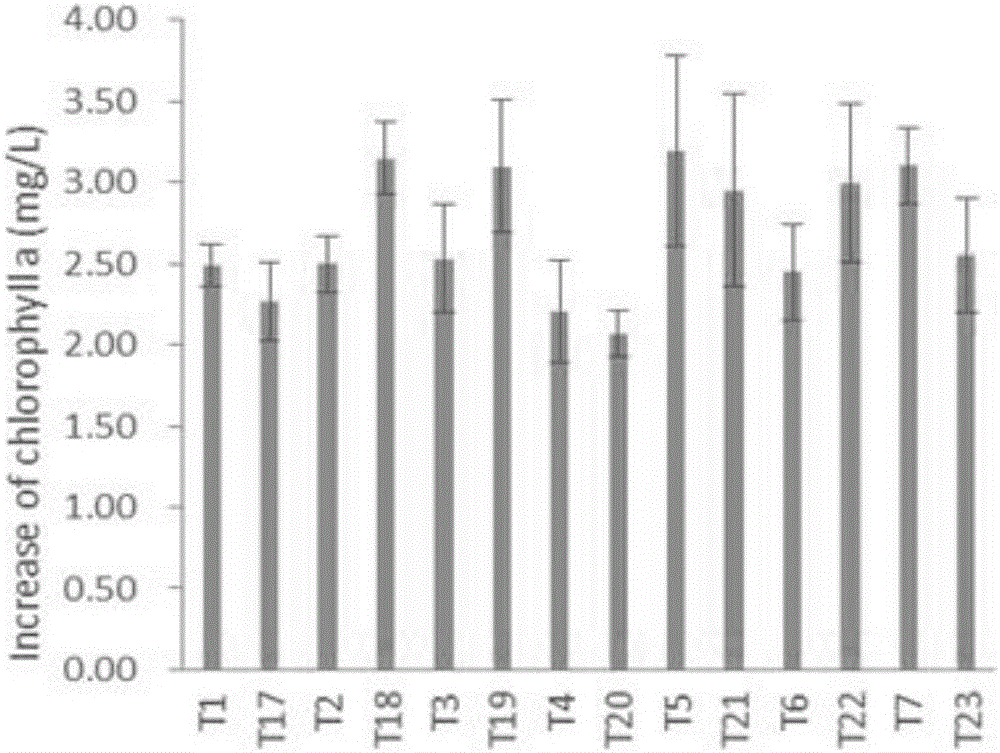
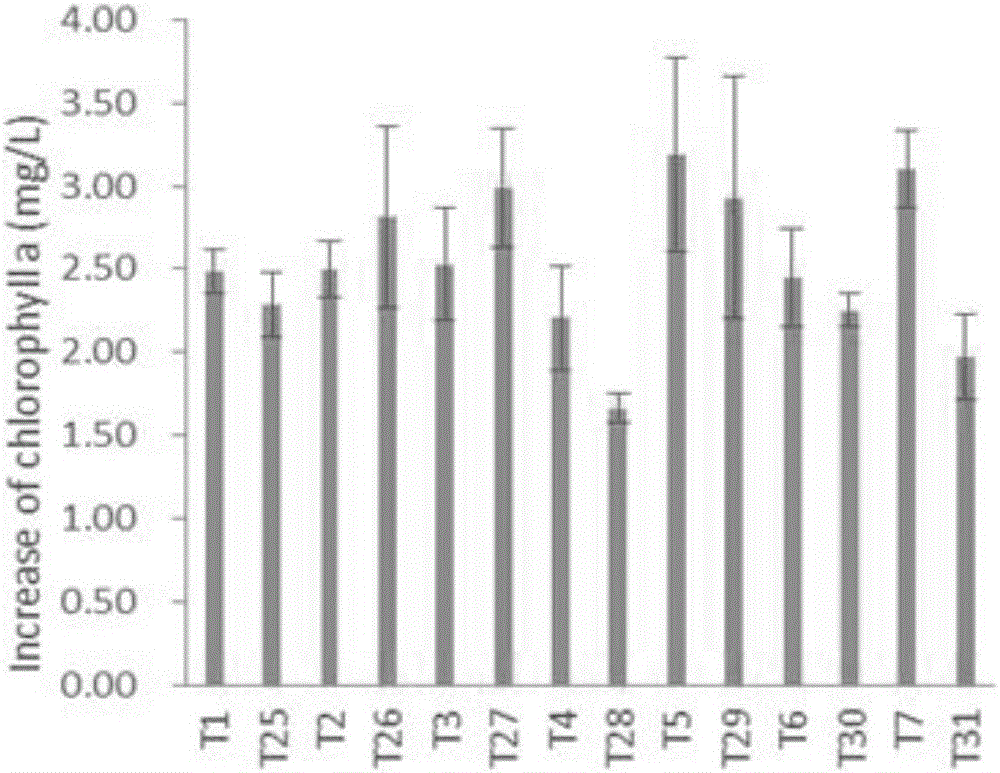
[0058] Symbiotic experiment of embodiment 3 nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and two kinds of bacteria
[0059] Nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria Anabaena B1611 (purchased from the UTEX algae bank of the University of Texas), Nostoc F280 and Anabaena F243 (respectively purchased from the FACHB freshwater algae bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), three soil microorganisms Bacillus thuringiensis Kenya species (Btsk), Pseudomonas fluorescens (Pf) and Bacillus subtilis (Bs) (purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) respectively), with numbers 1.1012, 1.867 and 1.4255, respectively.
[0060] According to the principle of high-throughput experiments, a total of 63 groups of experiments were designed for the symbiosis experiment of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and bacteria. The culture volume of each group of experiments was 3 mL, the culture temperature was 20 °C, the light intensity was 87.63±3.44 μmol / m2 / s, and the light-dark cycle ( Light: dark...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com