Composite microbial inoculum for repairing OCP (Organochlorine Pesticide) polluted soil, preparation method and repairing method
A technology of pesticide-contaminated soil and compound bacterial agent, which is applied in the field of microbial bacterial agent for contaminated soil, can solve the problems of poor removal effect, low degradation efficiency, and high treatment cost, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple process, and remarkable degradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
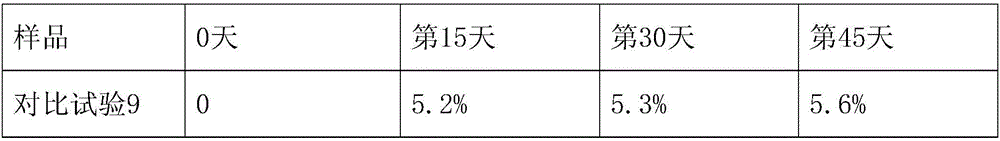
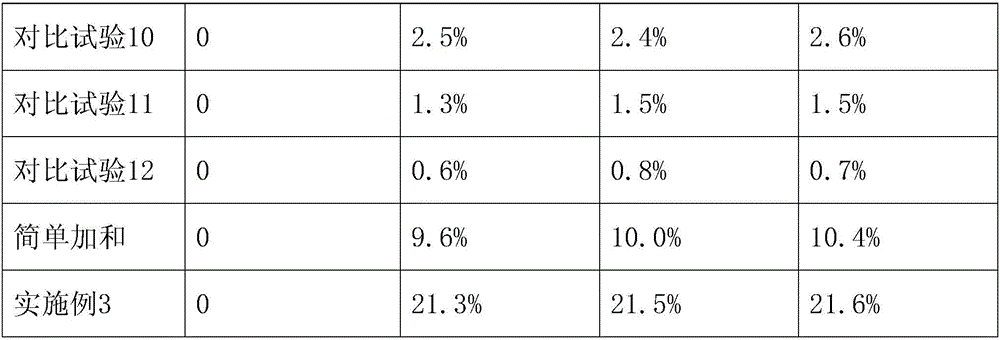
[0026] The microbial composite microbial agent for repairing soil contaminated by organochlorine pesticides of the present example 1. The microbial body of the microbial composite microbial agent includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonasputida, and maltophilic oligotrophic bacteria. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Flaimonas oryzihabitans; wherein the quality of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Xanthomonas oryzihabitans The ratio is 1:1.5:1:1.5.
[0027] The method for remediating soil using the microbial composite inoculant of Example 1 includes the following steps:
[0028] Step 1. Pretreatment of contaminated soil: crush the contaminated soil to a particle size of less than 2cm (preferably less than 1cm), and adjust the water content of the contaminated soil to 25%-40%;
[0029] Step 2: Add mung bean powder and the above-mentioned microbial compound inoculant to the contaminated soil treated in step 1, and plow and mix them to obtain...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The microbial composite inoculum for repairing soil contaminated by organochlorine pesticides of this example 2. The microbial body of the microbial composite inoculum includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Xanthomonas Wherein, the mass ratio of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Xanthomonas oryzae is 2:3:1:4.
[0044] The method of using the microbial composite microbial agent of Example 2 to repair soil includes the following steps:
[0045] Step 1. Pretreatment of contaminated soil: crush the contaminated soil to a particle size of less than 2cm (preferably less than 1cm), and adjust the water content of the contaminated soil to 25%-40%;
[0046] Step 2: Add mung bean powder and the above-mentioned microbial compound inoculant to the contaminated soil treated in step 1, and plow and mix them to obtain the soil to be degraded; wherein the control amount of mung bean powder is 1% of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The microbial composite inoculum for repairing soil contaminated by organochlorine pesticides of this example 3. The microbial body of the microbial composite inoculum includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Xanthomonas Wherein, the mass ratio of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Xanthomonas oryzae is 1.6:0.6:1:0.5.
[0059] The method for remediating soil using the microbial composite inoculant of Example 3 includes the following steps:
[0060] Step 1. Pretreatment of contaminated soil: crush the contaminated soil to a particle size of less than 2cm (preferably less than 1cm), and adjust the water content of the contaminated soil to 25%-40%;
[0061] Step 2: Add mung bean powder and the above-mentioned microbial compound inoculant to the contaminated soil treated in step 1, and plow and mix them to obtain the soil to be degraded; wherein the control amount of mung bean powder is 1% of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com