Method for developing simple sequence repeats molecular markers of genome of ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Maxim.) Chengf. plant
A simple repeat sequence, plant genome technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of limited level understanding, small number of SSRs markers, unable to meet research needs, etc., to save time and money , the effect of high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] Glossary
[0015] For ease of understanding, some nouns appearing in the following are explained as follows:
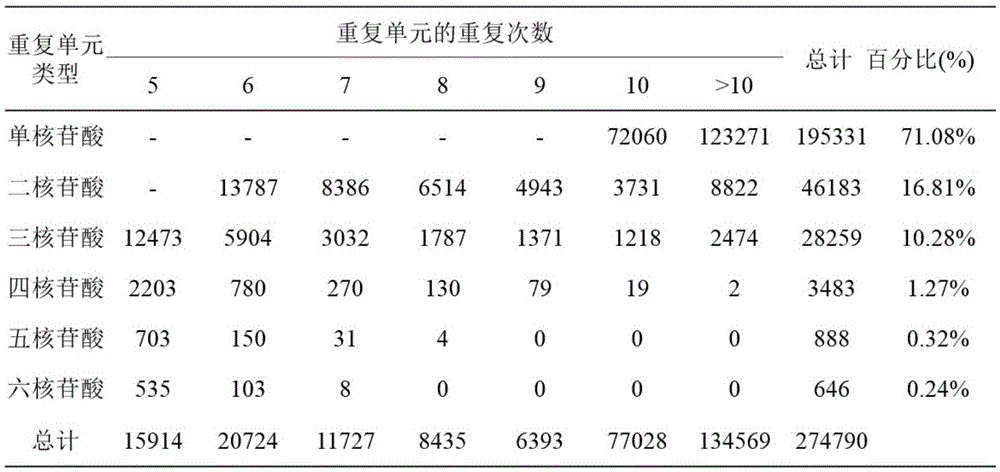
[0016] bp: DNA molecular fragment size unit, bp: base pair, base pair; kb: kilo-base pair, ie 1000 base pairs; mb: mega-base pair, million base pairs.
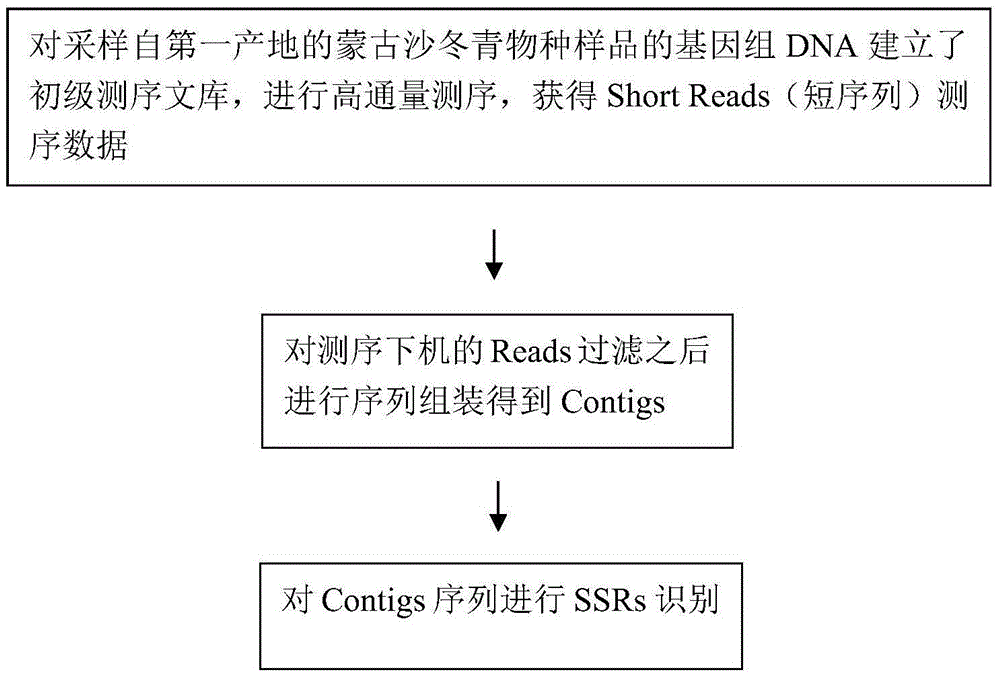
[0017] SOAP denovo software: Short sequence splicing software based on Illumina next-generation sequencing.
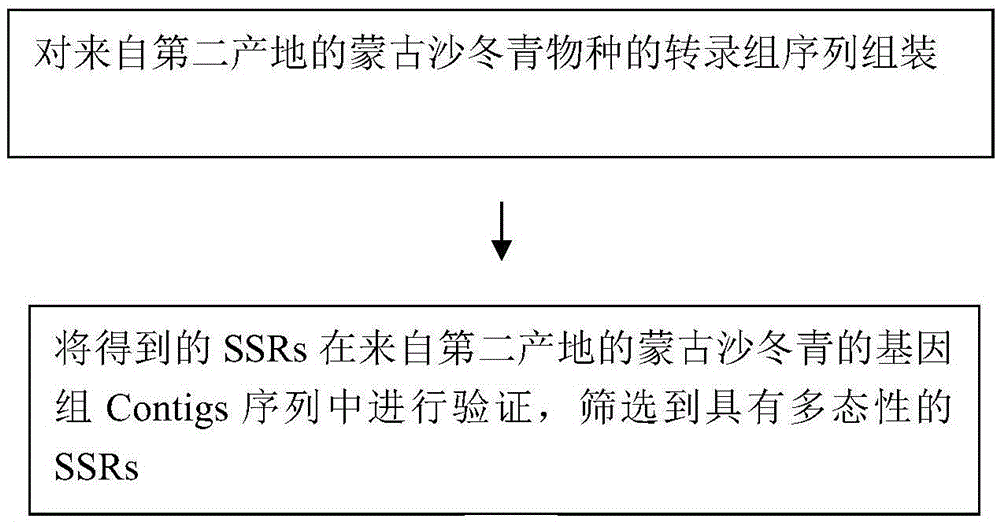
[0018] Contigs: "sequence contigs", which refer to a group of short DNA sequences that can be connected to each other through overlapping sequences at the ends to form large fragments. In high-throughput sequencing, each reaction on the chip will read a sequence, which is relatively short, called read, which is the original data; many reads can be assembled into a larger fragment by overlapping fragments, called is the contig, the sequence contig. Multiple contigs form a longer scaffold by overlapping fragments; after a contig is formed, it is identified as a gene encoding a protein, which is called ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com