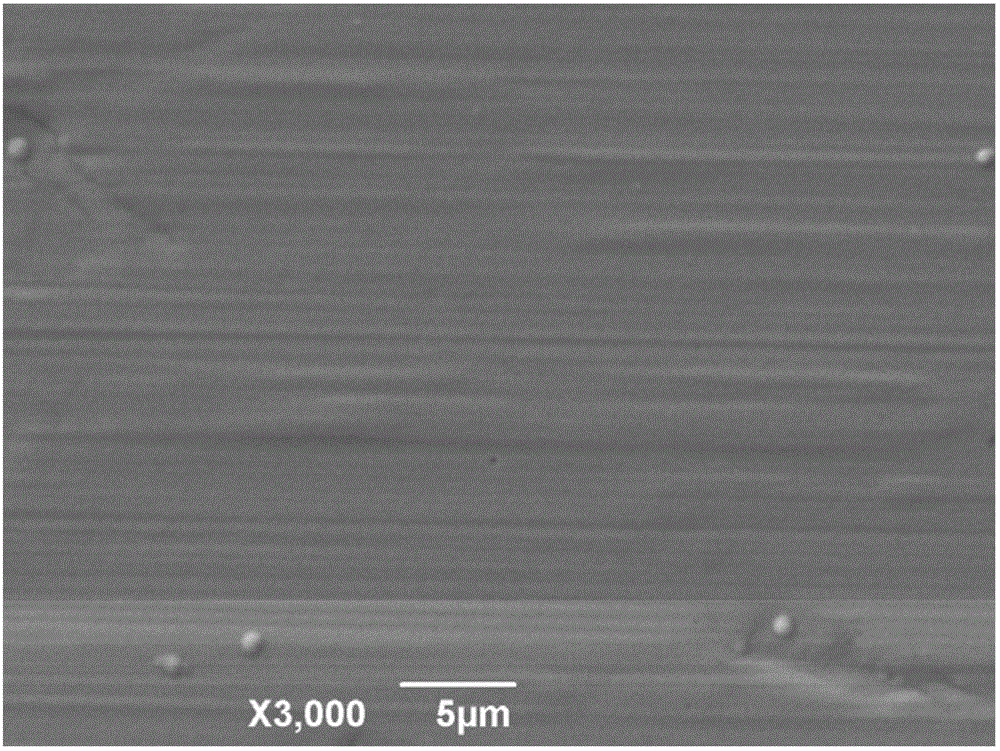
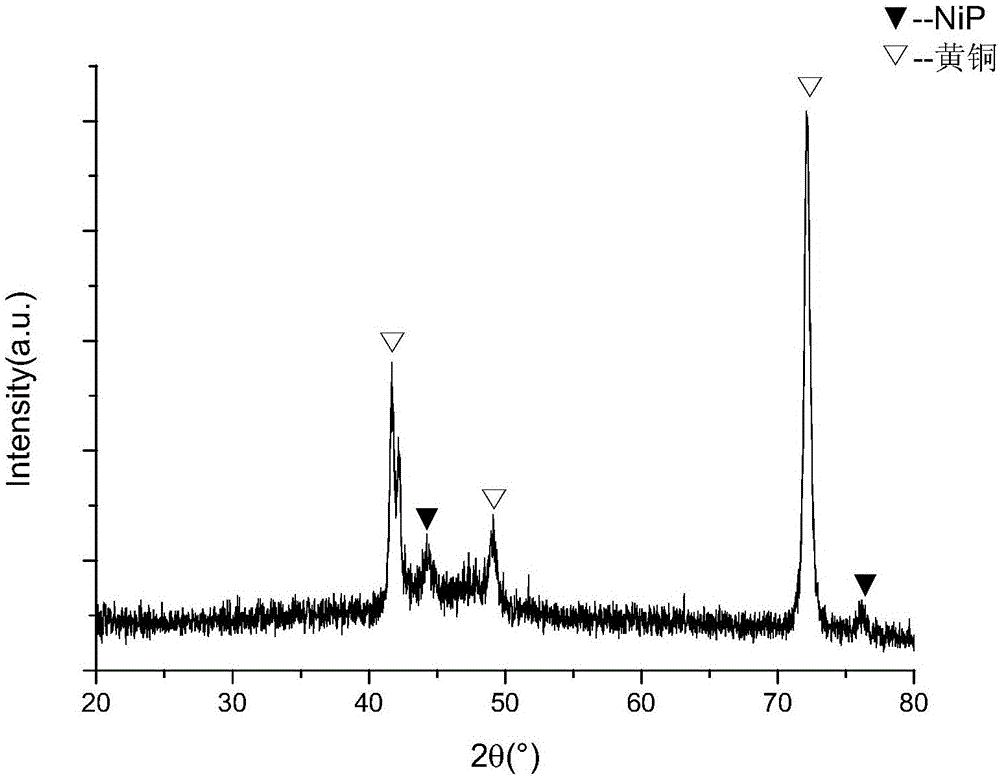
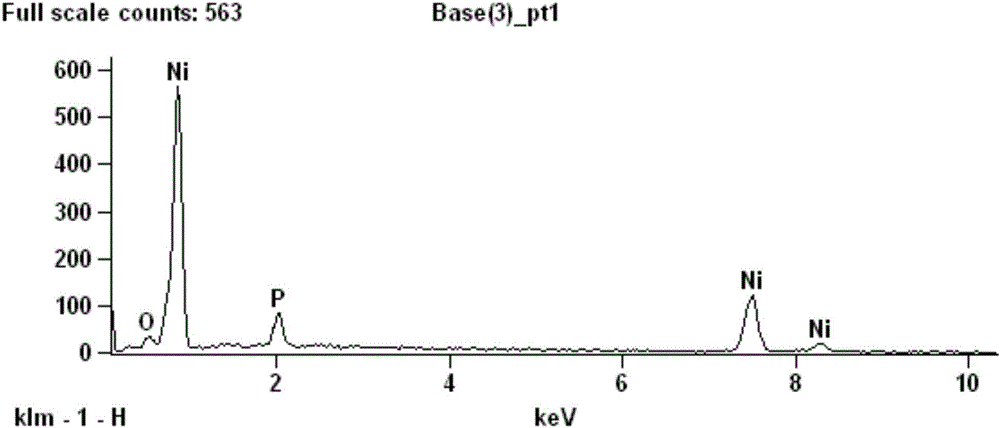
Electroplating method for nickel phosphorus alloy based on betaine-urea-water deep eutectic solvent
A low eutectic solvent and betaine technology, applied in the field of electroplating, can solve problems such as combustion and explosion, and achieve the effects of good corrosion resistance, safe and non-toxic process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] First weigh 0.2 mol of betaine, 0.4 mol of urea, and 0.6 mol of distilled water and place them in a beaker, seal the beaker with plastic wrap, and then stir at a constant temperature of 80°C to obtain a transparent deep eutectic solvent. Then weigh nickel chloride hexahydrate and sodium hypophosphite according to 0.3 mole per liter and 0.05 mole per liter respectively, join in the above-mentioned deep eutectic solvent, and stir at 80 ℃ of constant temperature to obtain the deep eutectic solvent containing nickel phosphorus, thereby As an electroplating solution for electroplating nickel-phosphorus alloys.
[0028] The pure nickel plate is used as the anode, and the brass is used as the cathode, immersed in a nickel-containing eutectic solvent heated to 70°C in a water bath for 30 minutes of constant current electroplating, wherein the direct distance between the cathode and the anode is 1cm, and the current density is 2mA / cm 2 .
[0029] After the electroplating is com...
Embodiment 2
[0031] First weigh 0.2 mol of betaine, 0.4 mol of urea, and 0.6 mol of distilled water and place them in a beaker, seal the beaker with plastic wrap, and then stir at a constant temperature of 80°C to obtain a transparent deep eutectic solvent. Then weigh nickel chloride hexahydrate and sodium hypophosphite according to 0.3 mole per liter and 0.05 mole per liter respectively, join in the above-mentioned deep eutectic solvent, and stir at 80 ℃ of constant temperature to obtain the deep eutectic solvent containing nickel phosphorus, thereby As an electroplating solution for electroplating nickel-phosphorus alloys.
[0032] The pure nickel plate is used as the anode, and the brass is used as the cathode, immersed in a nickel-containing eutectic solvent heated to 60°C in a water bath for 30 minutes of constant current electroplating, wherein the direct distance between the cathode and the anode is 2cm, and the current density is 2mA / cm 2 ;
[0033] After the electroplating is com...
Embodiment 3
[0035] First weigh 0.2 mol of betaine, 0.4 mol of urea, and 0.6 mol of distilled water and place them in a beaker, seal the beaker with plastic wrap, and then stir at a constant temperature of 80°C to obtain a transparent deep eutectic solvent. Then weigh nickel chloride hexahydrate and sodium hypophosphite according to 0.3 mole per liter and 0.05 mole per liter respectively, join in the above-mentioned deep eutectic solvent, and stir at 80 ℃ of constant temperature to obtain the deep eutectic solvent containing nickel phosphorus, thereby As an electroplating solution for electroplating nickel-phosphorus alloys.
[0036] The pure nickel plate is used as the anode, and the brass is used as the cathode, immersed in a nickel-containing eutectic solvent heated to 60°C in a water bath for 10 minutes of constant current electroplating, wherein the direct distance between the cathode and the anode is 2cm, and the current density is 3mA / cm 2 ;
[0037] After the electroplating is com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com