Novel MI-SSSEP mixed brain-computer interface method and system thereof
A machine interface, a new type of technology, applied in the field of brain-machine interface, can solve the problem of not effectively improving the overall performance of MI-BCI, and achieve the effect of improving overall performance and enhancing robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
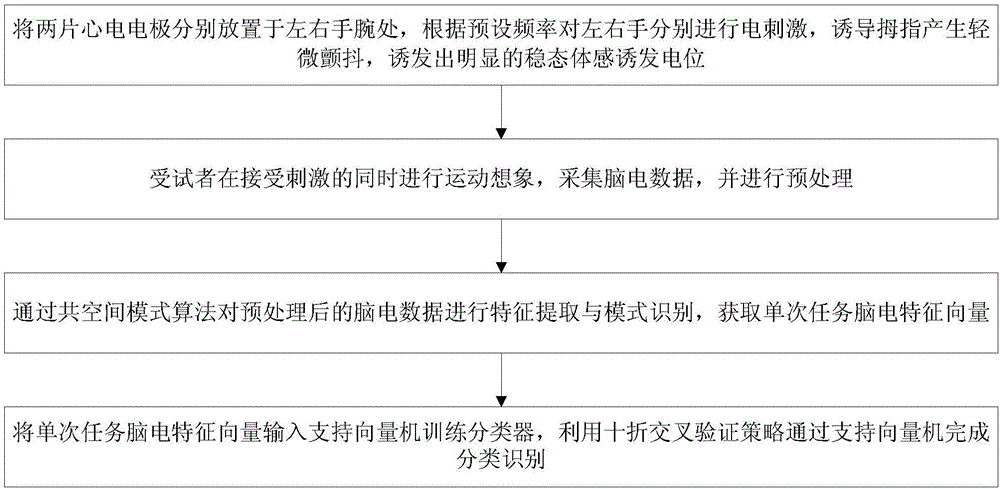
[0039] A novel MI-SSSEP hybrid brain-computer interface method, see figure 1 , the interface method includes the following steps:
[0040] 101: Place two ECG electrodes on the left and right wrists respectively, and perform electrical stimulation on the left and right hands respectively according to the preset frequency to induce slight tremors in the thumb and induce obvious steady-state somatosensory evoked potentials;
[0041] 102: The subject performs motor imagery while receiving stimulation, collects EEG data, and performs preprocessing;
[0042] 103: Perform feature extraction and pattern recognition on the preprocessed EEG data through the common space pattern algorithm, and obtain a single task EEG feature vector;
[0043] 104: Input the single-task EEG feature vector into the support vector machine to train the classifier, and use the ten-fold cross-validation strategy to complete the classification recognition through the support vector machine;
[0044] That is, ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Below in conjunction with specific drawings, the calculation formula introduces the scheme in embodiment 1 in detail, see the following description for details:
[0054] 201: Median nerve stimulation;
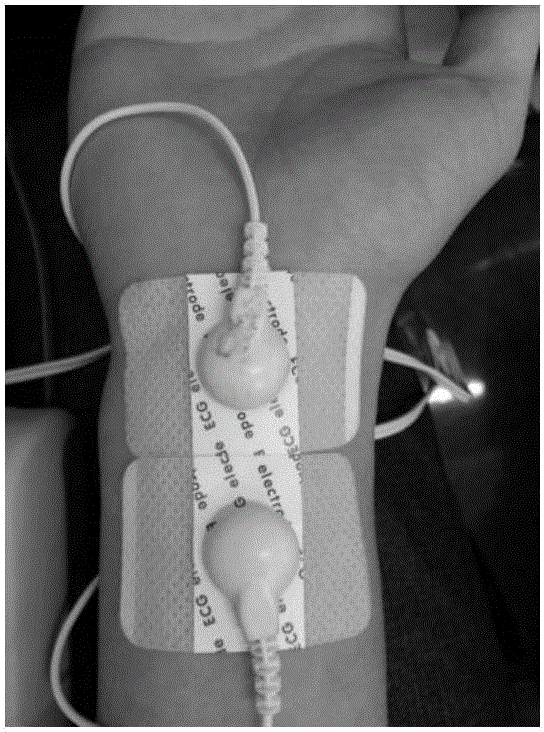
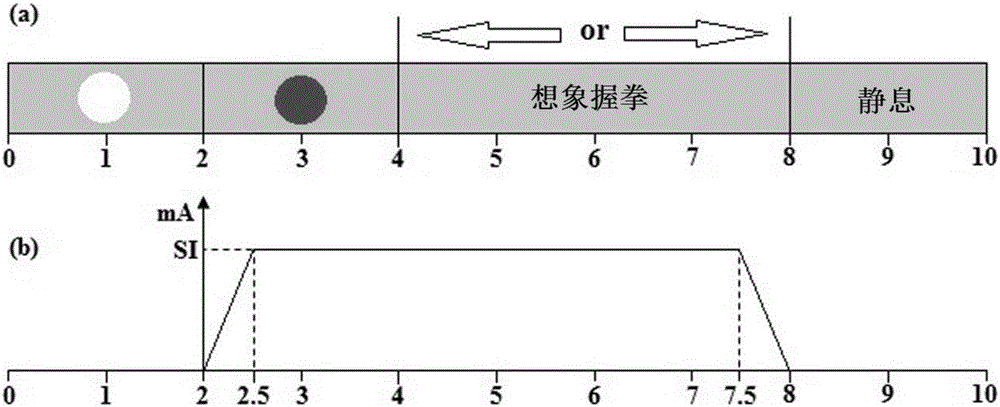
[0055] Among them, electrical stimulation was simultaneously applied to the bilateral median nerves through bidirectional pulses with a pulse width of 200 μs. Two ECG electrodes with a distance of 4 cm are placed on the left and right wrists respectively, such as figure 2 shown. The stimulation frequency was 26 Hz for the left hand and 31 Hz for the right hand. Adjust the position of the electrodes and the magnitude of the current on the left / right wrist respectively to induce a slight trembling of the thumb and elicit an obvious steady-state somatosensory evoked potential. Current intensities varied between 1.5-7 mA for all subjects.
[0056] Wherein, the embodiment of the present invention does not limit the distance between the two ECG electrodes, which can be se...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Below in conjunction with concrete test data, the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is done feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
[0083] Figure 5 Classification accuracy for 14 subjects using separate ERD features (ERD), separate SSSEP features (SSSEP) and fusion features (MI-SSSEP). It can be seen that the average correct rate exceeds 70%, and the correct rate obtained through the fusion of ERD and SSSEP features is the highest, with an average of 85%. Through one-way repeated measures analysis of variance, there is a significant difference in the correct rate obtained by using different feature extraction strategies (F(2,26)=7.182, p=0.010). Moreover, the correct rate under MI-SSSEP was significantly higher than that using ERD (p=0.0004) and SSSEP (p=0.042) features alone. The results show that the fusion of the two features of ERD and SSSEP contributes to the improvement of the classification accuracy rate in the mixed paradigm, which p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com