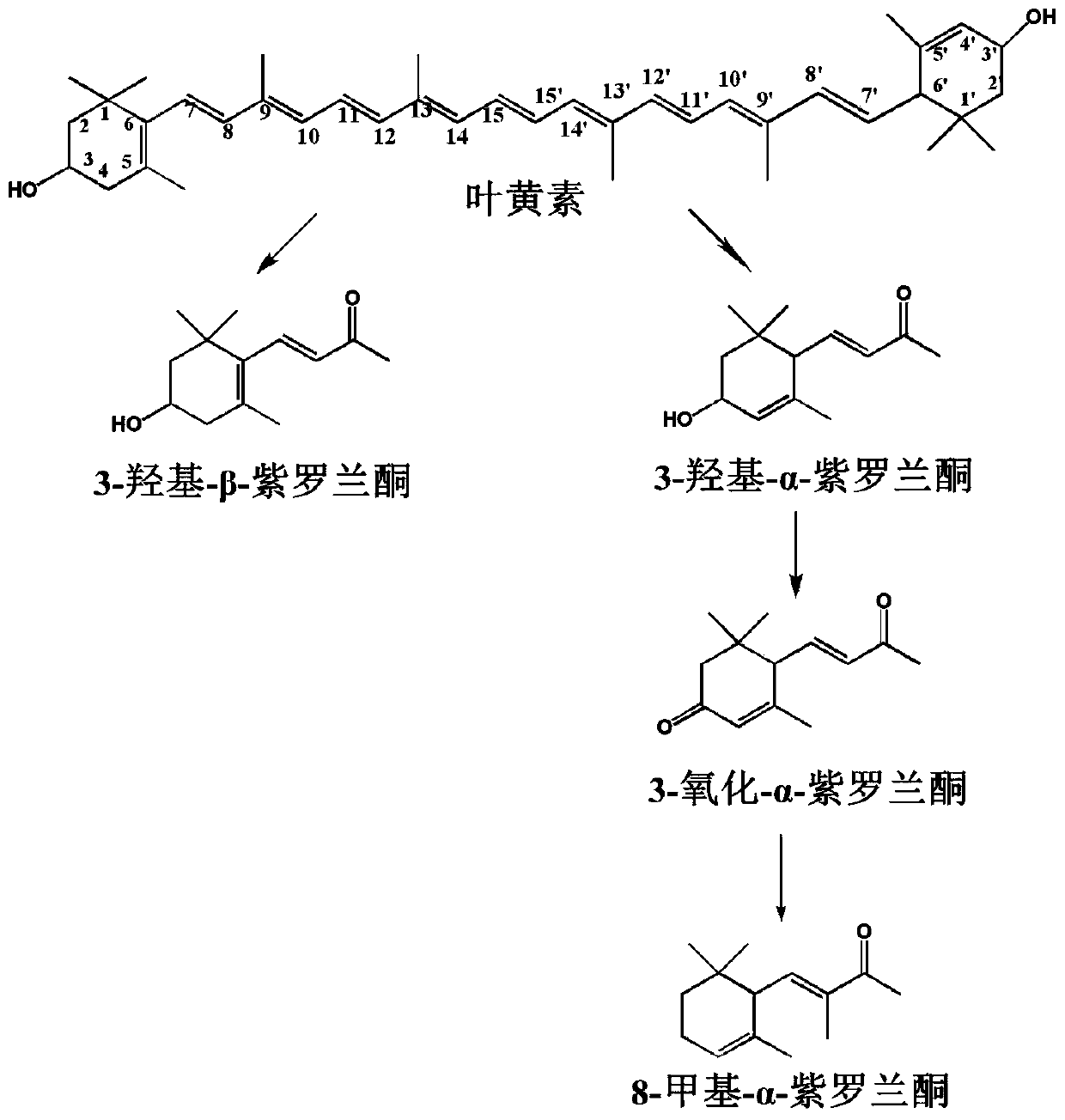
A method for biodegrading lutein to generate 8-methyl-α-ionone
A technology of ionone and biodegradation, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, to achieve the effects of low production cost, good social and economic benefits, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
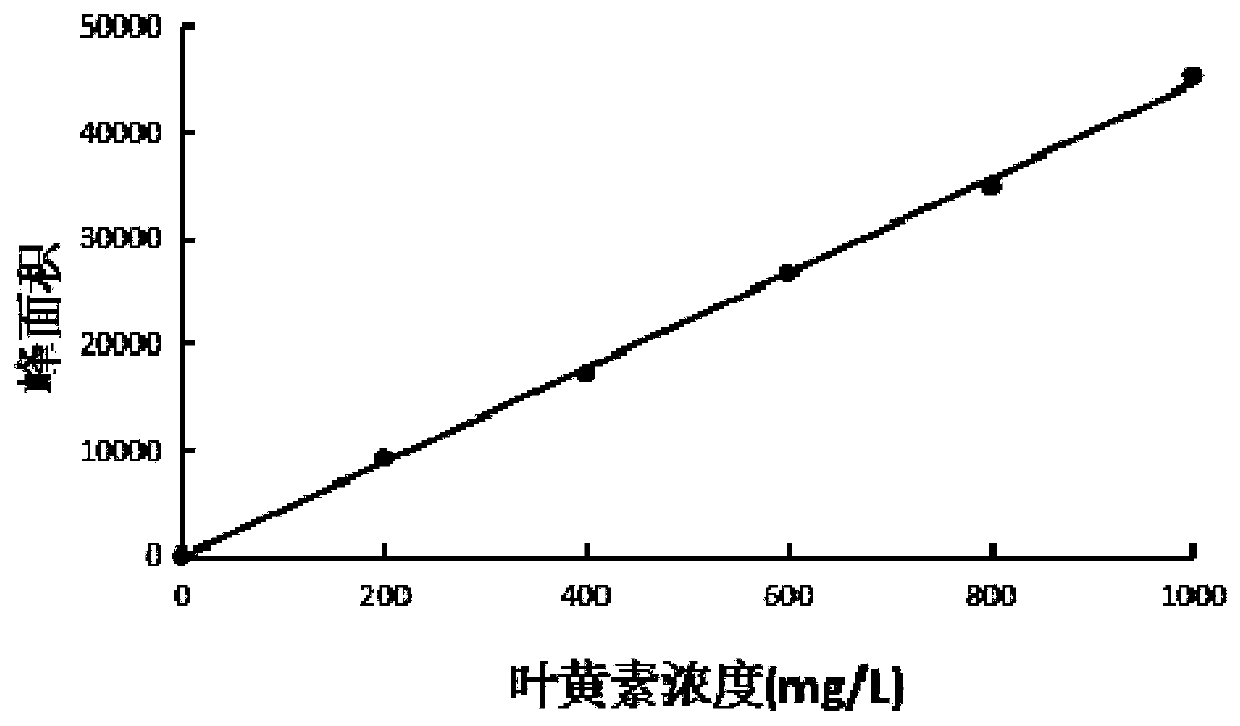
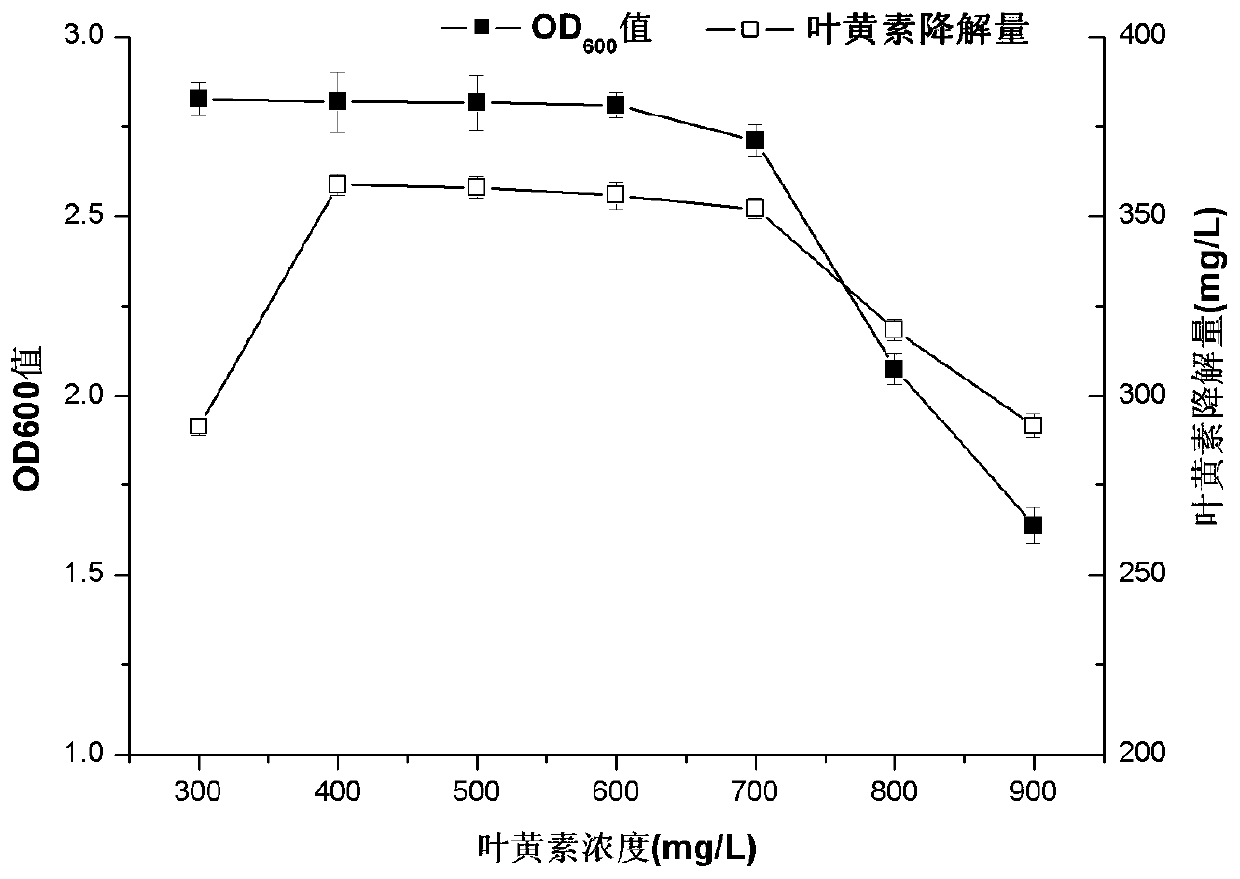
[0032] The screening of embodiment 1 lutein concentration
[0033] First configure the fermentation medium for lutein degradation: glucose 3g, asparagine 4.5g, yeast powder 3g, K 2 HPO 4 1.5g, MgSO 4 0.5g, FeSO 4 0.01g, 1L of distilled water, adjust the pH to 7.0, put each 100mL of fermentation medium into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, seal it, sterilize at 121°C for 20min, cool to room temperature for use.
[0034] Preparation of lutein solution: Disperse 200mg of lutein in 2g Tween 80 to obtain a lutein dispersion, then dissolve the lutein dispersion in 400mL of dichloromethane, and dissolve the dichloromethane Evaporate under reduced pressure, and dissolve the residue after decompressed evaporation in 10 mL of ethanol; pass the lutein solution through a 0.45 μm organic filter to remove internal bacteria, and set aside.
[0035] Biodegradation process: Add the lutein solution to multiple fermentation media respectively until the final concentrations of lutein are 300, 400,...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The mensuration of embodiment 2 lutein degradation products
[0050] Degradation products of lutein fermented and degraded by Enterobacter hallii of the present invention are determined, and the specific method is as follows:
[0051] The fermentation broth was centrifuged at high speed (4°C, 6500r / min, 30min) under light-shielding conditions, and the separated supernatant was taken out, and an equal volume of dichloromethane was added to extract repeatedly 3 times to obtain the lutein fermentation extract. Add anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 Dry overnight, concentrate in vacuo to 1 mL, and perform GC-MS qualitative analysis.
[0052] Gas phase conditions: Chromatographic column: HP-5 (30m×0.25mm; 0.25μm); heating program: initial temperature of 45°C, keep for 5min, rise to 110°C at 4°C / min, hold for 5min, rise to 1°C / min 150°C, hold for 5min, rise to 200°C at 3°C / min, rise to 280°C at 5°C / min, hold for 5min; inlet temperature: 270°C; transfer line temperature: 270°C; split rati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com