Waste water treating device and method based on electrochemical principle
A wastewater treatment and electrochemical technology, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve the problems of increasing energy consumption, reducing treatment efficiency, and large electrode consumption, and achieve the effects of preventing electrode passivation, prolonging equipment life, and reducing equipment energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
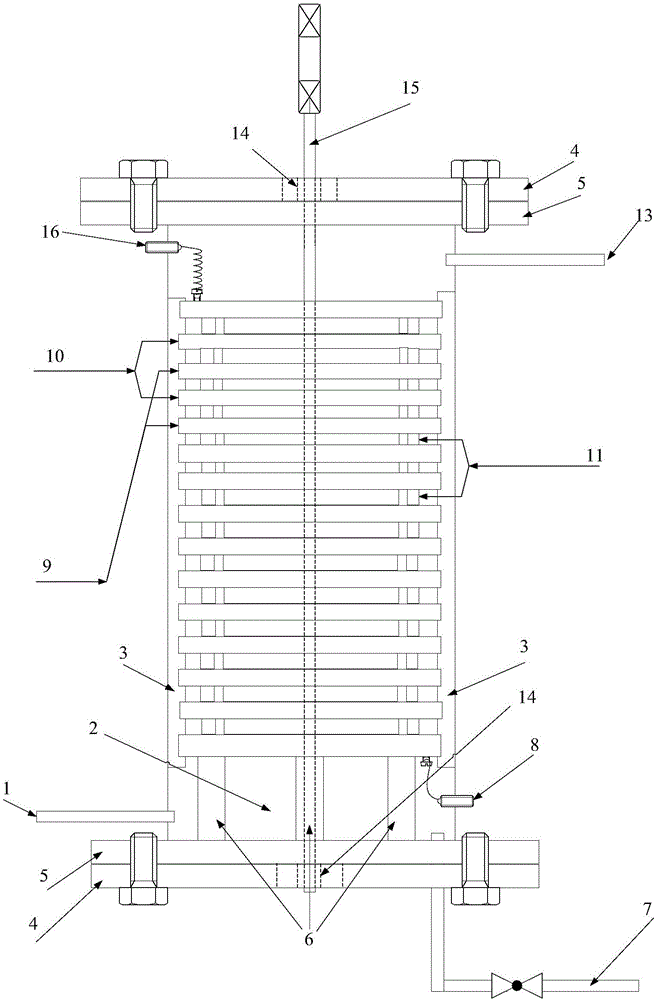
[0039] To treat coking wastewater, the coking wastewater used is the effluent from the secondary sedimentation tank after biochemical treatment. The distance between the plates is 8mm, the anode and cathode are made of aluminum electrodes, the input voltage of the pulse power supply is 220V, the input frequency is 50Hz, the duty ratio of the power supply is 60%, the output frequency is 3000Hz, and the output current is 1A / m 2 , processing time 10min. Stand still to separate and remove flocs, and the effluent meets the coking chemical pollutant discharge standard (GB16171-2012). The water quality indicators before and after treatment are shown in Table 1.
[0040] Table 1: Changes in water quality indicators after coking wastewater treatment
[0041]
Embodiment 2
[0043] Treatment of wastewater containing a variety of heavy metals. The distance between the plates is 10mm, the anode and cathode are made of aluminum electrodes, the pulse power input voltage is 220V, the input frequency is 50Hz, the duty ratio of the power supply is 70%, the output frequency is 500Hz, and the output current is 6A / m 2 , processing time 45min. The concentrations of heavy metals in water before and after treatment are shown in Table 2.
[0044] Table 2: Changes in concentration of heavy metal wastewater after treatment
[0045]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com