Binding agent, preparation method and grinding wheel
A bonding agent and grinding wheel technology, used in the field of abrasives, can solve the problems of long sintering process time, increased grinding wheel cost, lack of universality, etc., and achieve sharp grinding efficiency, fast hardening speed, and universality. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
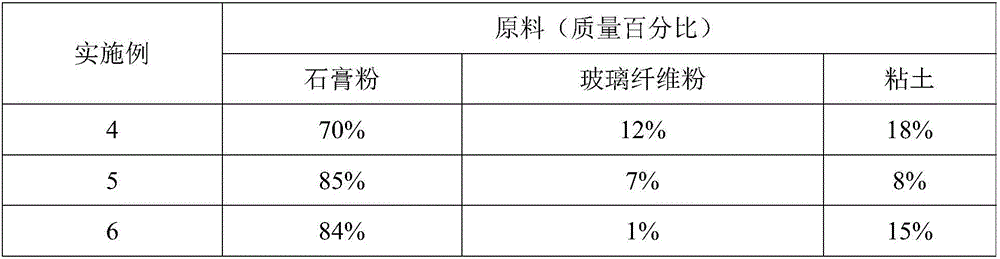
[0037] The binder of this embodiment is made of the following raw materials in mass percentage: 83% of gypsum powder, 3% of glass fiber powder, and 14% of clay.
[0038] The preparation method of the binding agent of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0039]1) Mix the gypsum powder, glass fiber powder and clay in the formula, put them into a ball mill and mill them at a speed of 180 rpm for 5 hours, and then pass them all through a 300-mesh sieve for 3 times to obtain powder;
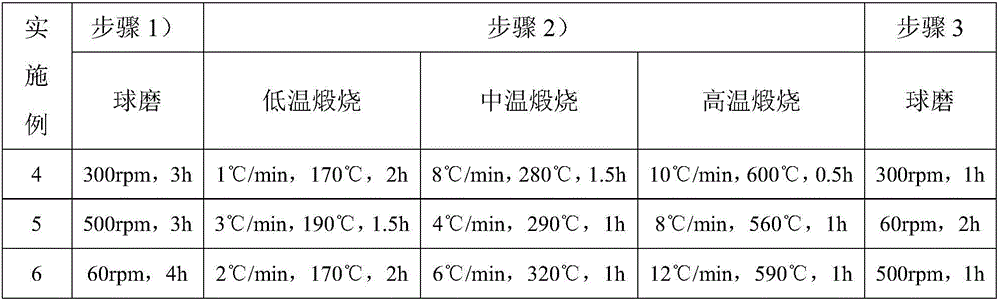
[0040] 2) Put the powder obtained in step 1) into a high-temperature furnace, heat up to 180°C at a rate of 2°C / min for calcination for 1.5 hours, then heat up to 300°C at a rate of 5°C / min for 1 hour, and then heat up to 300°C for 1 hour at a rate of 8°C / min. The rate of min is raised to 580°C for 0.5h and calcined to obtain the calcined material;
[0041] 3) Put the calcined material obtained in step 2) into a ball mill and continue ball milling at a speed of 180 rpm for 2 hours,...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The binder of this embodiment is made of the following raw materials in mass percentage: 80% of gypsum powder, 5% of glass fiber powder, and 15% of clay.
[0049] The preparation method of the binding agent of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0050] 1) Mix the gypsum powder, glass fiber powder and clay in the formula, put them into a ball mill and mill them at a speed of 180 rpm for 5 hours, and then pass them all through a 300-mesh sieve for 3 times to obtain powder;
[0051] 2) Put the powder obtained in step 1) into a high-temperature furnace, heat up to 180°C at a rate of 2°C / min for calcination for 1.5 hours, then heat up to 300°C at a rate of 5°C / min for 1 hour, and then heat up to 300°C for 1 hour at a rate of 8°C / min. The rate of min is raised to 580°C for 0.5h and calcined to obtain the calcined material;
[0052] 3) Put the calcined material obtained in step 2) into a ball mill and continue ball milling at a speed of 180 rpm for 2 hours...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The binder of this embodiment is made of the following raw materials in mass percentage: 85% of gypsum powder, 5% of glass fiber powder, and 10% of clay.
[0060] The preparation method of the binding agent of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0061] 1) Mix the gypsum powder, glass fiber powder and clay in the formula, put them into a ball mill and mill them at a speed of 180 rpm for 5 hours, and then pass them all through a 300-mesh sieve for 3 times to obtain powder;
[0062] 2) Put the powder obtained in step 1) into a high-temperature furnace, heat up to 180°C at a rate of 2°C / min for calcination for 1.5 hours, then heat up to 300°C at a rate of 5°C / min for 1 hour, and then heat up to 300°C for 1 hour at a rate of 8°C / min. The rate of min is raised to 580°C for 0.5h and calcined to obtain the calcined material;
[0063] 3) Put the calcined material obtained in step 2) into a ball mill and continue ball milling at a speed of 180 rpm for 2 hours...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com