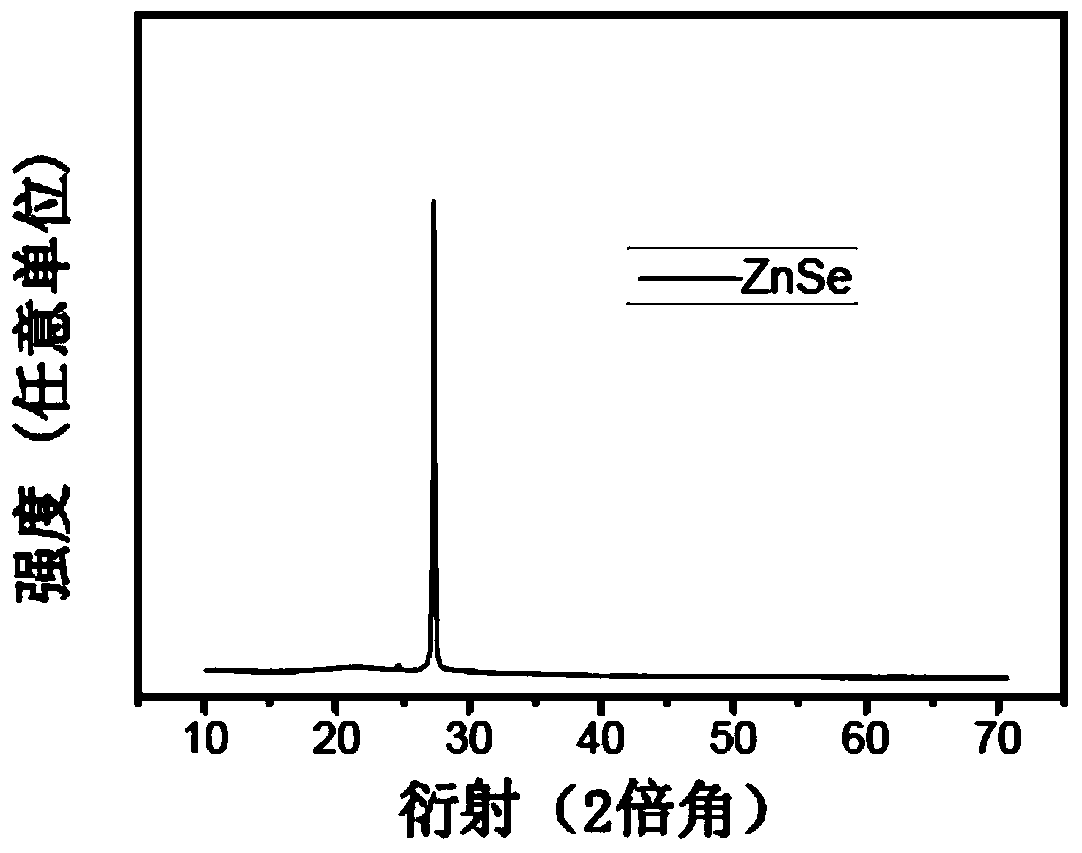
A kind of ge-se-zn chalcogenide film material for optical waveguide and preparation method thereof
A ge-se-zn, chalcogenide thin film technology, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of easy devitrification of deposited thin films, easy photo-induced changes, poor stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The present invention is a kind of Ge-Se-Zn chalcogenide film material used for optical waveguide, its chemical structure formula is Zn x Se y Ge z , wherein 28<x<40, 30<y<45, 15<z<40, x+y+z=100, the specific preparation process is as follows:
[0024] In the magnetron sputtering coating system, the quartz sheet or silicon oxide sheet is used as the substrate, the ZnSe alloy target is installed in the magnetron radio frequency sputtering target, and the Ge target is installed in the magnetron DC sputtering target. The sputtering chamber of the magnetron sputtering coating system was evacuated until the vacuum degree in the chamber reached 2.4×10 -4 Pa, then feed into the sputtering chamber a high-purity argon with a volume flow rate of 50ml / min until the air pressure in the sputtering chamber reaches the required initiation pressure of 0.25Pa for sputtering, and then control the sputtering power of the ZnSe alloy target to be 70W, The sputtering power of the Ge singl...
Embodiment 2
[0027] It is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is that in the sputtering process, the sputtering power of the alloy ZnSe target is controlled to be 70W, the sputtering power of the Ge simple substance target is 8W, and the film thickness is controlled at 1µm, and the obtained Zn x Se y Ge z Thin film, where x=35.1, y=39, z=25.9, namely Zn 35.1 Se 39 Ge 25.9 .
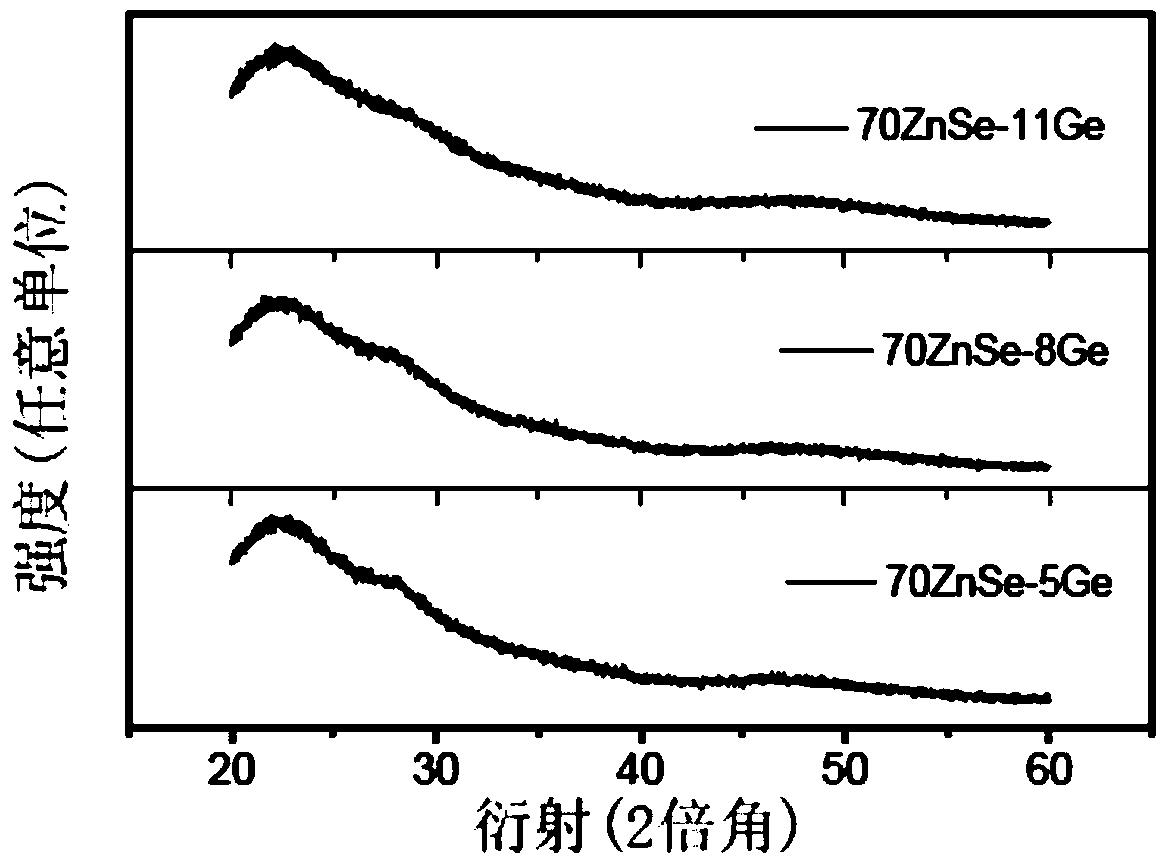
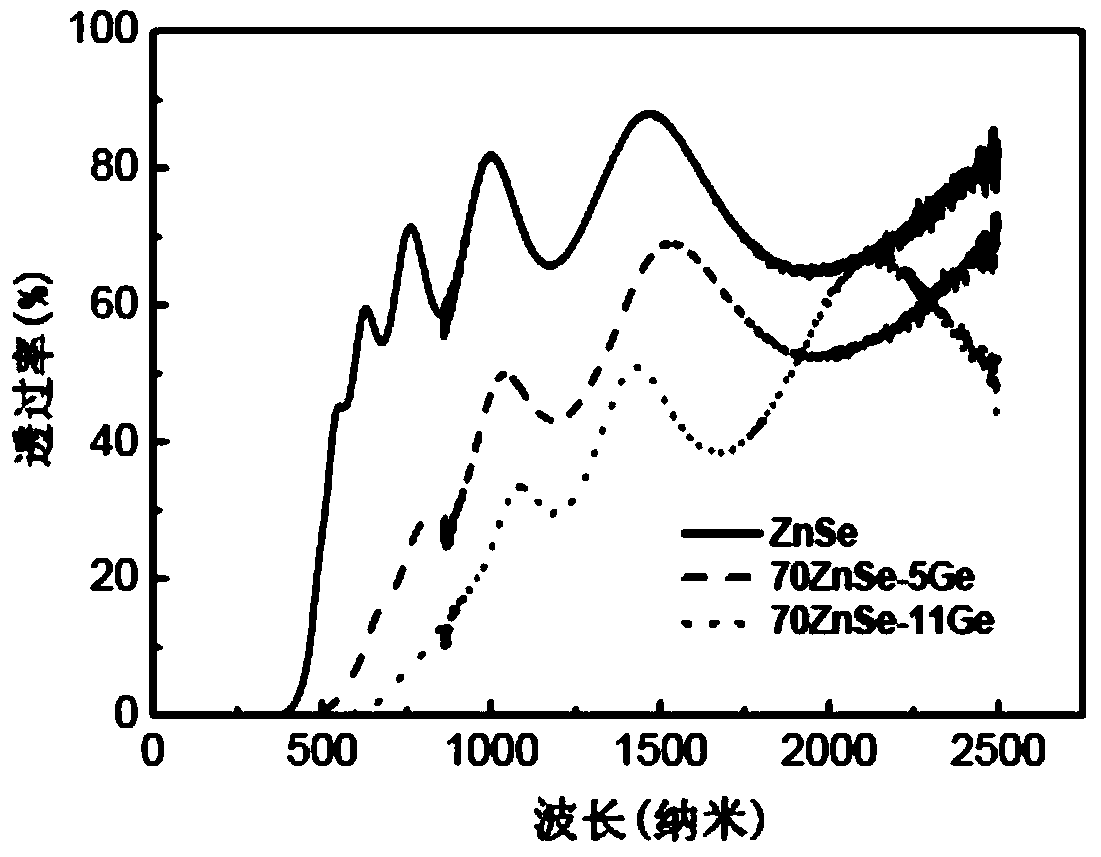
[0028] The prepared film was subjected to XRD and AFM performance tests, and the test results were as follows figure 2 and Table 1, from figure 2 It can be seen from Table 1 that the performance indicators of the film prepared in Example 2 are as follows; the deposited film is amorphous, the roughness is 1.745, the transmittance is 50%, and the short-wave cut-off edge is 850nm.
Embodiment 3
[0030] It is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is that in the sputtering process, the sputtering power of the alloy ZnSe target is controlled to be 70W, the sputtering power of the Ge simple substance target is 11W, and the film thickness is controlled at 1 μm, and the obtained Zn x Se y Ge z Film, where x=33.4, y=35.1, z=31.5, namely Zn 33.4 Sb 35.1 Te 31.5 .
[0031] The prepared film was subjected to XRD and AFM performance tests, and the test results were as follows figure 2 and Table 1, from figure 2It can be seen from Table 1 that the performance indicators of the thin film prepared in Example 3 are as follows: the deposited thin film is amorphous, the roughness is 1.214nm, the transmittance is 40%, and the short-wave cut-off edge is 1000nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com