Polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposite material and its preparation method and application
A technology of nanocomposite materials and polyvinylidene fluoride, which is applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, electrostatic effect separation, etc., can solve the problems of obtaining β phase and difficulty in directing it, so as to improve the service life and simplify the power injection process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] The preparation of embodiment 1, β phase polyvinylidene fluoride
[0066] Normally, PVDF is mainly α-phase. In this patent, graphene oxide microchips and PVDF powder are dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), stirred, ultrasonically dispersed, centrifuged, and the supernatant is obtained by filtration. The solution was cast on a flat glass sheet and cured in a vacuum oven at 70°C for 15 hours. The crystal structure of PVDF crystalline state before and after doping is tested by XRD to determine whether it is a β phase, such as Figure 4 shown. Usually, the XRD peaks of α-phase PVDF are 17.9°, 18.6°, and 20.3°, corresponding to crystal planes (020), (100) and (110), respectively. When the β-phase appears after the incorporation of graphene oxide, a new peak is added at 19.3°, and 2θ=19.3° corresponds to the crystal planes (110) and (200) of β-phase PVDF. The XRD diffraction peaks of PVDF films doped with GO changed, and with the increase of doping concentration, the...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2, the optimal content of nanomaterials and the phase transition temperature of composite materials in PVDF nanocomposites
[0068] Using differential scanning calorimeter to test the phase transition temperature of PVDF nanocomposites modified with different contents of graphene oxide, the results are as follows Figure 5 shown. Pure PVDF has only one phase transition peak, while the PVDF nanocomposites modified with graphene oxide nanosheets have two phase transition peaks, indicating that the modified PVDF nanocomposites have α-phase transitions. Combined with the results of XRD, it can be judged as the β phase with pyroelectric effect, and its corresponding phase transition temperature can be determined. As the content of nanomaterials increases, the strength of β phase increases obviously, but when the content increases to a certain value, the change is not obvious. Combined with the actual use conditions and the mechanical properties of the composite ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Embodiment 3, PVDF nanocomposite pyroelectric effect
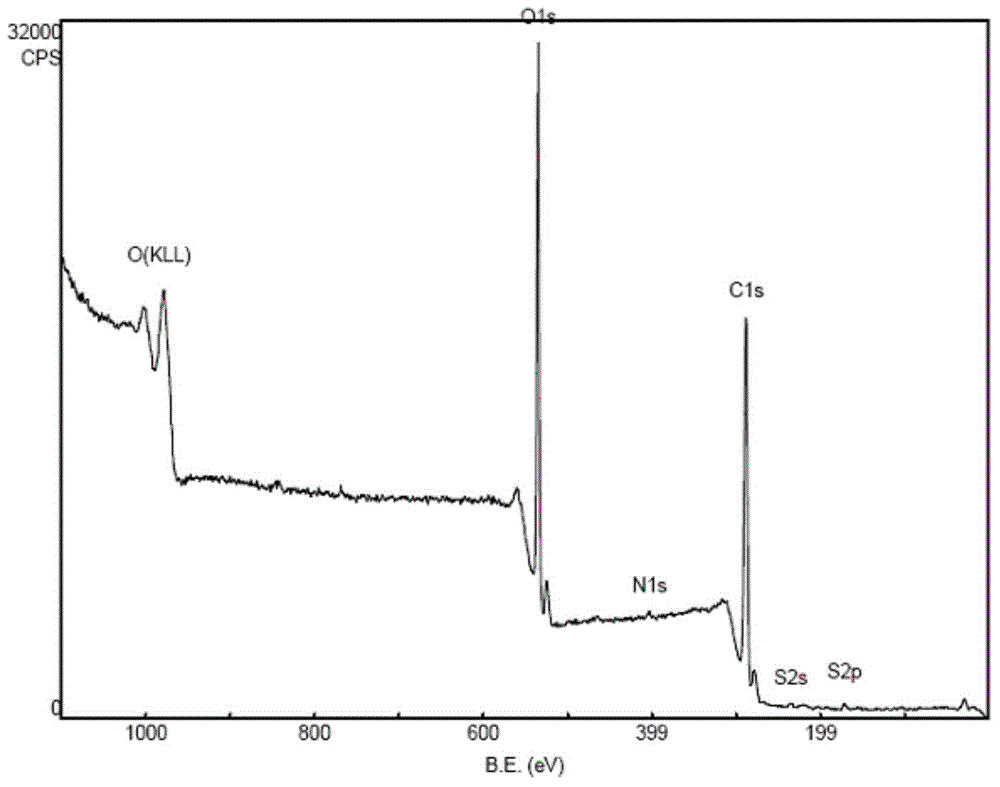
[0070] In order to characterize the pyroelectric effect of PVDF nanocomposites, it is necessary to measure the surface potential of PVDF film after temperature difference. In this embodiment, a template with a certain pattern is used to locally and selectively heat the PVDF film, so that the heated area appears electrical to the outside. The surface potential of the patterned and heated PVDF nanocomposite film (film thickness about 50nm) was measured by electrostatic force microscopy (EFM), as Image 6 As shown, the heated area is positively charged to the outside, which proves the pyroelectric effect of PVDF nanocomposites under the action of temperature difference. Since the PVDF film used for EFM testing is thin, and its charge is positively correlated with the film thickness, the charge is relatively small.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com