Method for passivating heavy metal lead in bottom mud by using modified nanochlorapatite
A technology of chloroapatite and heavy metals, which is applied in the field of physical and chemical treatment of heavy metals in polluted sediments, can solve the problems of water eutrophication, secondary pollution, and low repair effect, and achieve the purpose of inhibiting water eutrophication and enhancing passivation. The effect of chemicalization and inhibiting the growth of algae
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
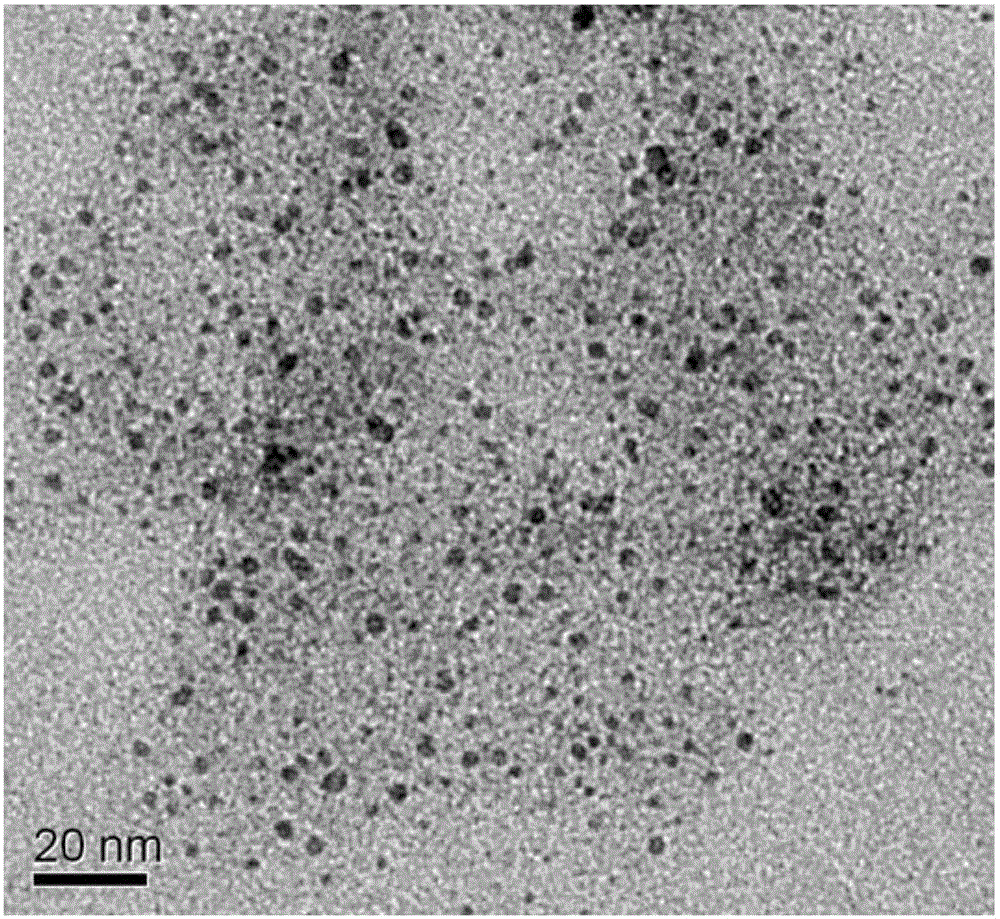
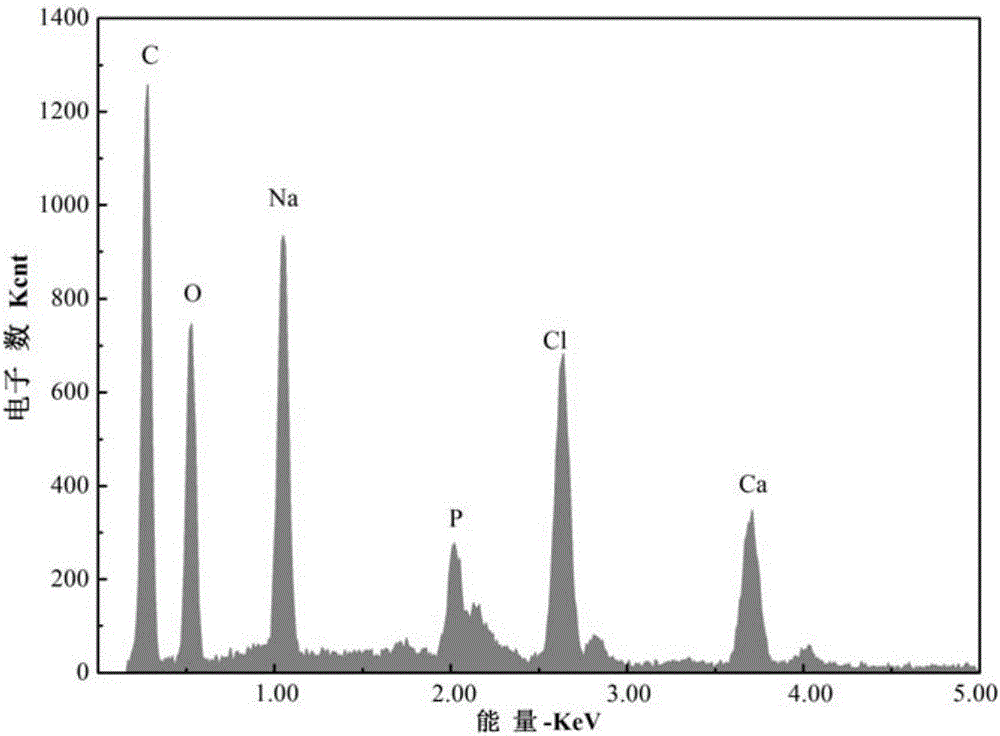
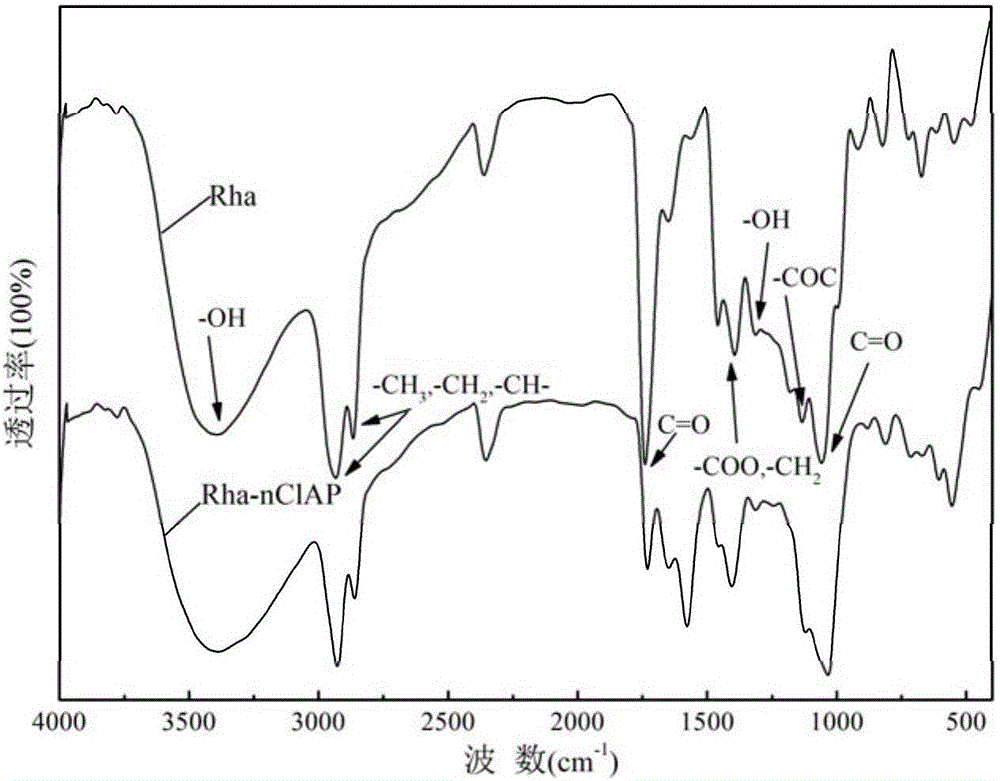
[0038] A modified nano-chloroapatite (Rha-nClAP) of the present invention, the modified nano-chloroapatite is composed of rhamnolipid (Rha) and nano-chloroapatite, and the rhamnolipid is modified on the nano On the surface of chloroapatite, the mass ratio of nano chloroapatite to rhamnolipid is 46.498:1.
[0039] In this embodiment, the modified nano-chloroapatite has a particle size of 2nm-5nm.
[0040] A preparation method of the modified nano-chloroapatite of the above-mentioned present embodiment, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) Preparation of rhamnolipid solution: take 30mg rhamnolipid (the purity of this rhamnolipid is 90%, the critical micelle concentration is 25mg / L, and monorhamnolipid and dirhamnose The mass ratio of lipid is 2:1) dissolved in 800mL ultrapure water, placed in ultrasonic wave for ten minutes, then adjusted the pH value of the solution to 8.4 with 0.1M sodium hydroxide to make it completely dissolved, and added an appropriate amount of ul...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A modified nano-chloroapatite (Rha-nClAP) of the present invention, the modified nano-chloroapatite is composed of rhamnolipid (Rha) and nano-chloroapatite, and the rhamnolipid is modified on the nano On the surface of chloroapatite, the mass ratio of nano chloroapatite to rhamnolipid is 27.8988:1.
[0048] In this embodiment, the particle size of the modified nano-chloroapatite particles is 2nm-5nm.
[0049] A preparation method of the modified nano-chloroapatite of the above-mentioned present embodiment, comprising the following steps:
[0050] (1) Preparation of rhamnolipid solution: take 50mg rhamnolipid (the purity of this rhamnolipid is 90%, the critical micelle concentration is 25mg / L, and monorhamnolipid and dirhamnose The mass ratio of lipid is 2:1) dissolved in 800mL ultrapure water, placed in ultrasonic wave for ten minutes, then adjusted the pH value of the solution to 8.4 with 0.1M sodium hydroxide to make it completely dissolved, and added an appropriate ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A modified nano-chloroapatite (Rha-nClAP) of the present invention, the modified nano-chloroapatite is composed of rhamnolipid (Rha) and nano-chloroapatite, and the rhamnolipid is modified on the nano On the surface of chloroapatite, the mass ratio of nano chloroapatite to rhamnolipid is 19.9277:1.
[0058] In this embodiment, the particle size of the modified nano-chloroapatite is 2nm-5nm.
[0059] A preparation method of the modified nano-chloroapatite of the above-mentioned present embodiment, comprising the following steps:
[0060] (1) Preparation of rhamnolipid solution: take by weighing 70mg rhamnolipid (the purity of this rhamnolipid is 90%, the critical micelle concentration is 25mg / L, and monorhamnolipid and double rhamnose The mass ratio of lipid is 2:1) dissolved in 800mL ultrapure water, placed in ultrasonic wave for 10 minutes, then adjusted the pH value of the solution to 8.4 with 0.1M sodium hydroxide to make it completely dissolved, and added an approp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com