A method for synthesizing nucleic acid under constant temperature conditions
A nucleic acid and conditional technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as instability, errors, contamination of samples and reaction solutions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Example 1 For the amplification of fragments in MERS-orf1b
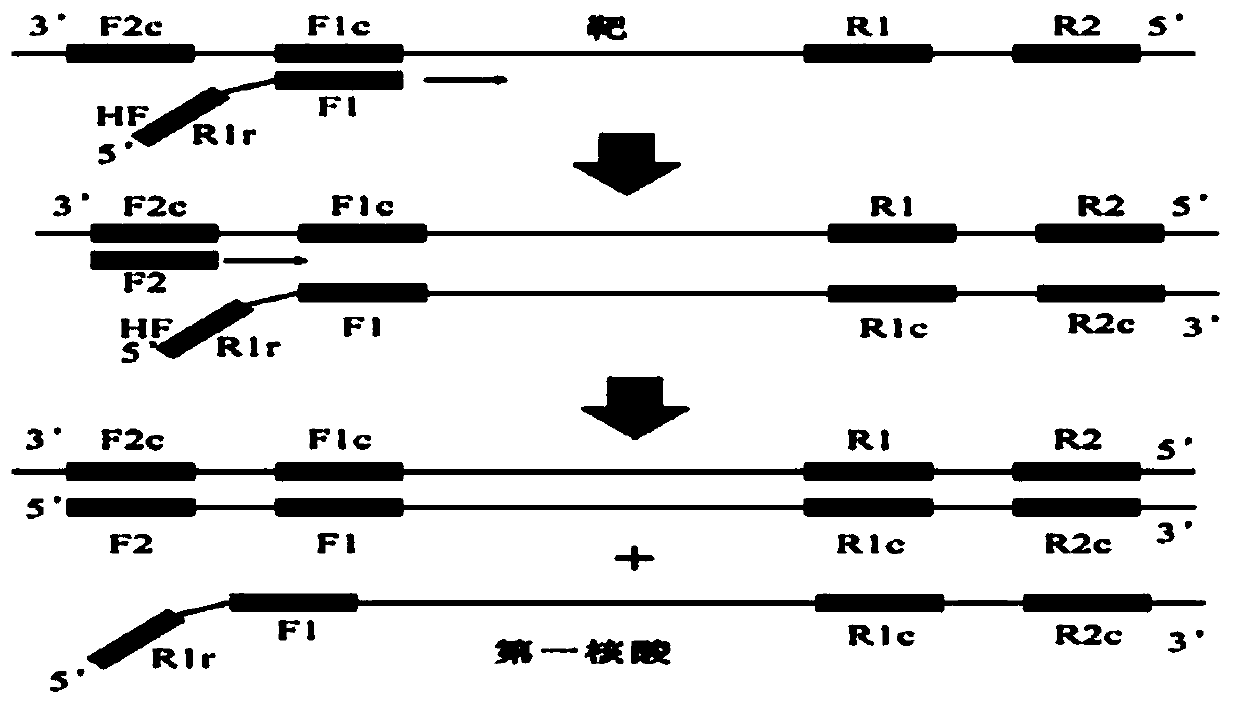
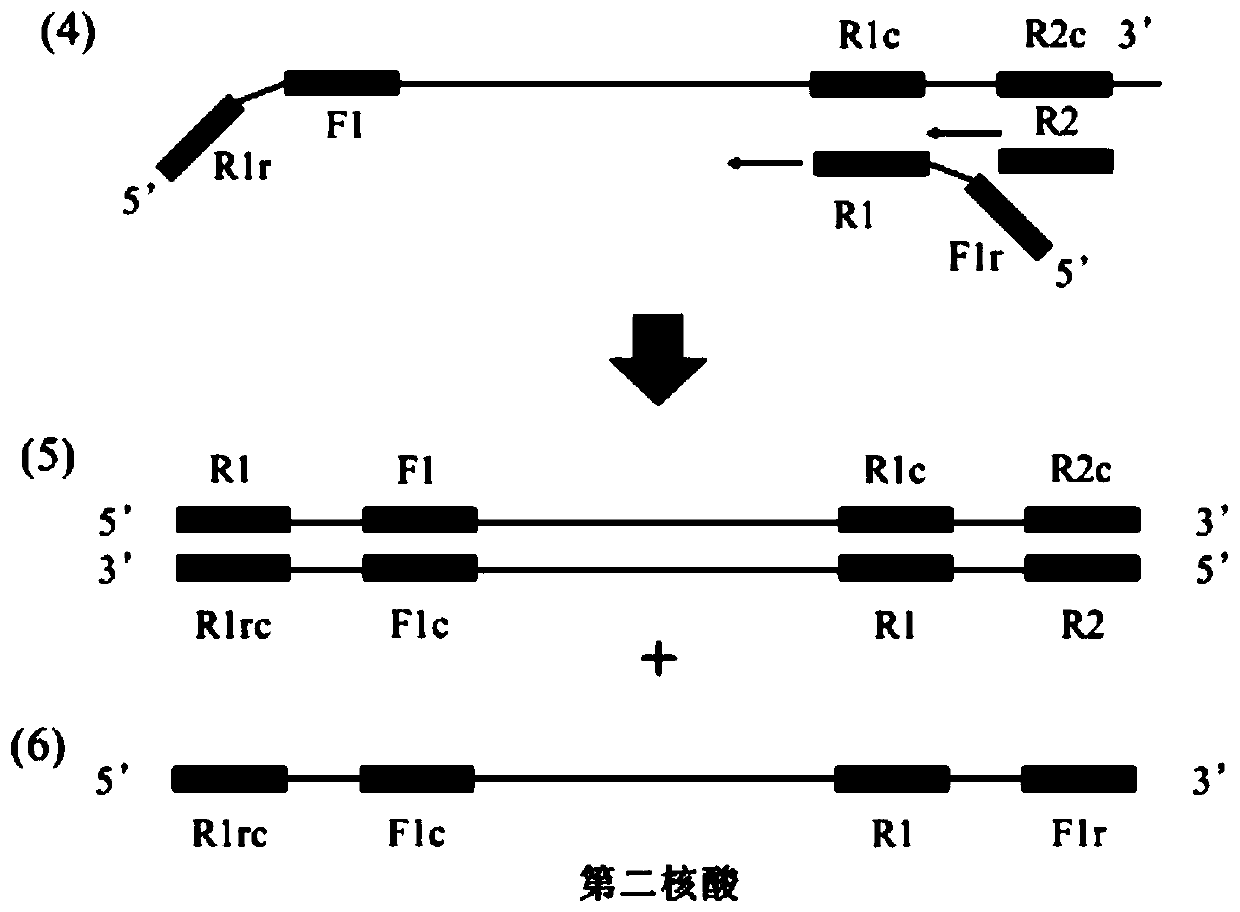
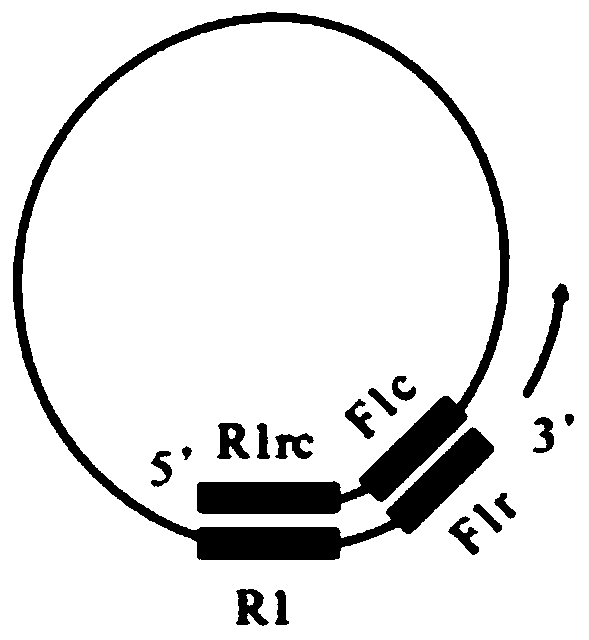
[0113] In the present invention, the nucleic acid with complementary strands connected into a single strand in the form of a helical loop was attempted using MERS-orf1b (from GenBank: NM_001012270.1) as a template. Four primers were used in the experiment, namely Mo1bHF, Mo1bHR, Mo1bF2 and Mo1bR2. Mo1bF2 and Mo1bR2 are outer primers that replace the first nucleic acid obtained from Mo1bHF and Mo1bHR respectively. Because the outer primer after Mo1bHF (or Mo1bHR) synthesis is used as the primer for the synthesis origin of the complementary chain. These are designed to anneal into ringed regions by exploiting the proximity packing phenomenon. In addition, setting these primers at high concentrations allows the annealing of Mo1bHF (or Mo1bHR) to occur preferentially.
[0114] The nucleotide sequences constituting each primer are shown in the sequence listing, and the structural features of the primers are summ...
Embodiment 2
[0145] Example 2 Confirmation of Reaction Products by Restriction Enzyme Digestion
[0146] In order to elucidate the structure of the nucleic acid obtained in Example 1 of the present invention having complementary nucleotide sequences linked in a single strand in a circular structure, the product was digested with restriction enzymes. Any of these products would be expected to be native if the theoretical fragments would be produced by digestion, while disappearing as observed in Example 1 at high molecular weights resulting in an unclear smeared band pattern and bands that were not electrophoresed. The invention has nucleic acids in which complementary sequences are alternately linked within a single strand.
[0147] In Example 1, the reaction solution was deposited and purified by treatment with phenol and precipitation with ethanol, and the resulting precipitate was recovered and redissolved in ultrapure water, digested with restriction enzyme HindIII at 37° C. for 2 hour...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Embodiment 3 application EvaGreen verification reaction product
[0152] Similar to SYBR Green I, EvaGreen is a dye with a green excitation wavelength that binds to the minor groove region of all dsDNA double helices, and its inhibition on nucleic acid amplification reactions such as PCR is much smaller than that of the latter. In the free state, EvaGreen emits weak fluorescence, but once bound to double-stranded DNA, the fluorescence is greatly enhanced. Therefore, the fluorescence signal intensity of EvaGreen is related to the quantity of double-stranded DNA, and the quantity of double-stranded DNA existing in the nucleic acid amplification system can be detected according to the fluorescent signal.
[0153] Combinations of reaction solutions for the method of synthesizing the nucleic acid of the present invention using these primers are shown below.
[0154] Reaction solution mix (25 μL)
[0155] 20mM Tris-HCl pH8.8
[0156] 10mM KCl
[0157] 10mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com