Rhamnolipid producing plasmid, construction method thereof, engineered escherichia coli and application
A technology of Escherichia coli and rhamnolipid, which is applied in the field of Escherichia coli engineering bacteria and application, rhamnolipid production plasmid and its construction, and can solve the problems of low yield of rhamnolipid and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Embodiment 1 produces the construction of rhamnolipid engineering strain
[0063] 1. Construction of rhamnolipid synthesis gene vector
[0064] (1) Codon optimization and synthesis of SyrhlA gene, SyrhlB gene and SyrhlC gene
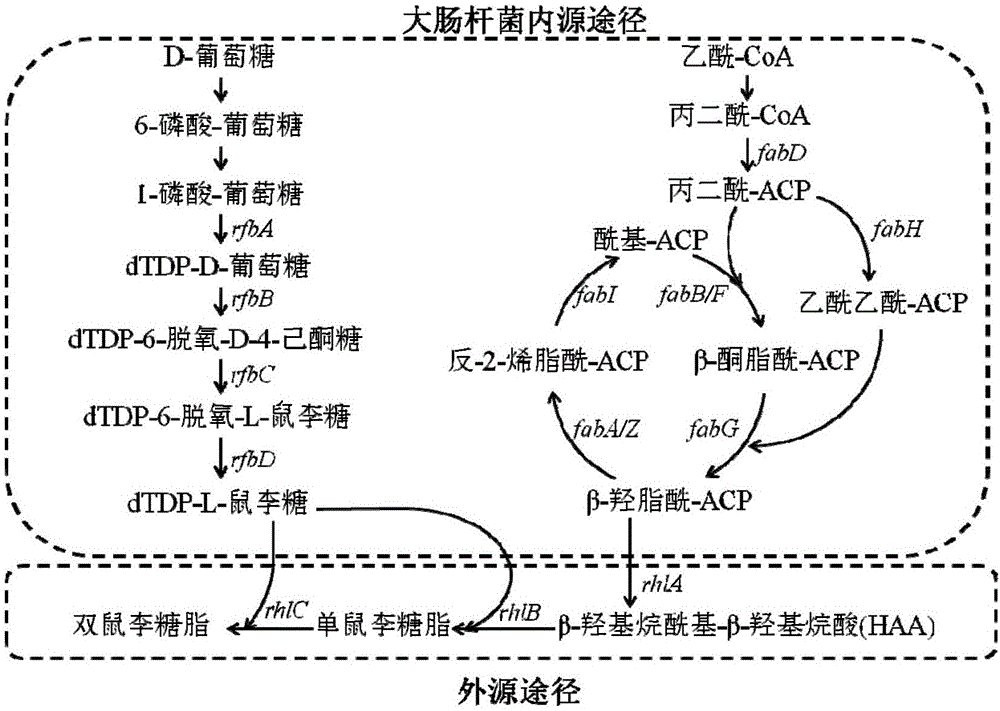
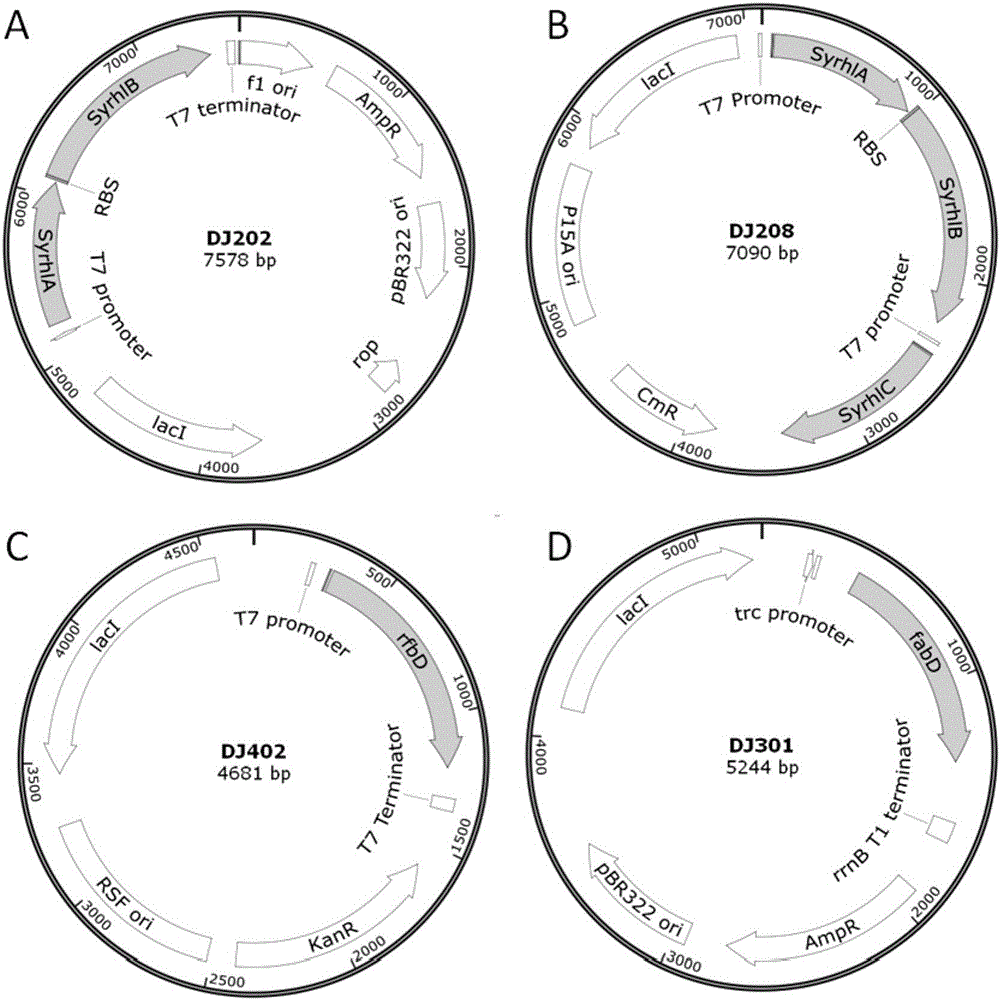
[0065] In this example, the original sequences of the rhamnosyltransferase genes rhlA, rhlB, and rhlC were all derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, and the rhlA was paired with reference to the Escherichia coli preferred codon table (see GenBank GI for the original gene sequence: 9949623), and properly avoid commonly used restriction sites. The optimized gene was named SyrhlA (sequence shown in Sequence Table 3), with NdeI and BamHI restriction enzyme sites added at both ends, synthesized by Suzhou Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. and connected to pET21-21a ( +) Between the NdeI and BamHI sites of the vector, the plasmid DJ201 was obtained. The same method is used to optimize the codon of rhlB (the original sequence is GenBank GI:9949622)...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2 rhamnolipid-producing Escherichia coli engineering bacteria shake flask fermentation verification
[0078] 1. Fermentation process
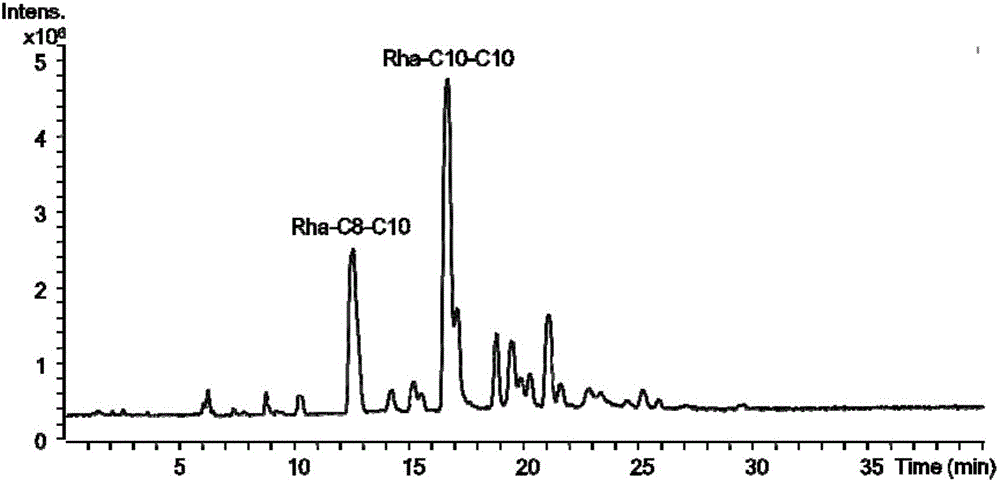
[0079] Pick a single colony of Escherichia coli engineering bacteria BL202 in a 5mL liquid LB test tube containing 100μg / mL ampicillin, culture overnight at 37°C with shaking at 180r / min, and inoculate 1% of the inoculum into a 50mL test tube containing 100μg / mL ampicillin In the fermentation medium, 37°C, 180r / min shaking culture to OD 600 When the temperature is 0.6-0.8, 1 mM IPTG is added to induce the expression of the gene, and cultured for 46 hours to obtain a fermented liquid.
[0080] Ferment the engineering bacteria BL208, BL208 / 402, and BL208 / 301 with the same culture method, wherein 50 μg / mL chloramphenicol is added to the medium of BL208, and 50 μg / mL chloramphenicol and 50 μg of chloramphenicol are added to the medium of BL208 / 402 / mL kanamycin sulfate, 50 μg / mL chloramphenicol and 100 μg / mL ampicillin were adde...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com