Method for improving property of magnesium oxychloride cementing material by composite modification
A gelling material and composite modification technology, applied in the field of magnesium oxychloride gelling material, to achieve the effect of improving water resistance, inhibiting moisture absorption and return to halogen, and prolonging the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A composite modification method for improving the properties of magnesium oxychloride cementitious materials. The specific raw material dosages are: 1000 g of light burned magnesium oxide, 340 g of magnesium chloride, 30 g of pullulan, 6 g of ethyl orthosilicate, and 402 g of water. The specific operations are as follows:
[0037] The light-burned magnesium oxide and pullulan are mixed uniformly in a mixer, and then the prepared ethyl orthosilicate and magnesium chloride aqueous solution are slowly added to the powder and stirred to form a slurry.
[0038] The slurry was injected into the mold for curing for 24 hours, and its 3 d, 7 d, 28 d compressive strength and softening coefficient were measured.
[0039] The compressive strength of the modified cementitious material reached 126.65 Mpa at 28 d, and the softening coefficient of 28 d immersed in water was 0.85, which was 58.21% higher than the 28-d compressive strength of the blank sample before modification of 80.05 Mpa. ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The compound modification method for improving the performance of magnesium oxychloride cementitious material, except that the organic silicon used is sodium methyl silicate, the amount of raw materials, operation sequence, curing method, test method, etc. are the same as in Example 1, and the preparation The 28d compressive strength of the sample is 118.64 Mpa, the softening coefficient of 28d in water reaches 0.88, which is 32.52% higher than the 28d compressive strength of the blank sample before modification of 80.05 Mpa, and the softening coefficient is 26.14% higher than the 0.65 before modification. .
Embodiment 3
[0043] The compound modification method for improving the performance of magnesium oxychloride cementitious materials, the organic silicon used is ethyl orthosilicate, the amount is 4g (0.4% of the mass fraction of light burned magnesium oxide), and the amount of pullulan is 10g ( 1% of the mass fraction of light burned magnesia). The amount of other raw materials, operation sequence, curing method, test method, etc. are the same as in Example 1. The 28d compressive strength of the prepared sample is 110.81 Mpa, and the softening coefficient of 28d soaking in water reaches 0.79, which is higher than the 28d resistance of the blank sample before modification. The compressive strength of 80.05 Mpa is increased by 27.75%, and the softening coefficient is 36.71% higher than the 0.65 before modification.
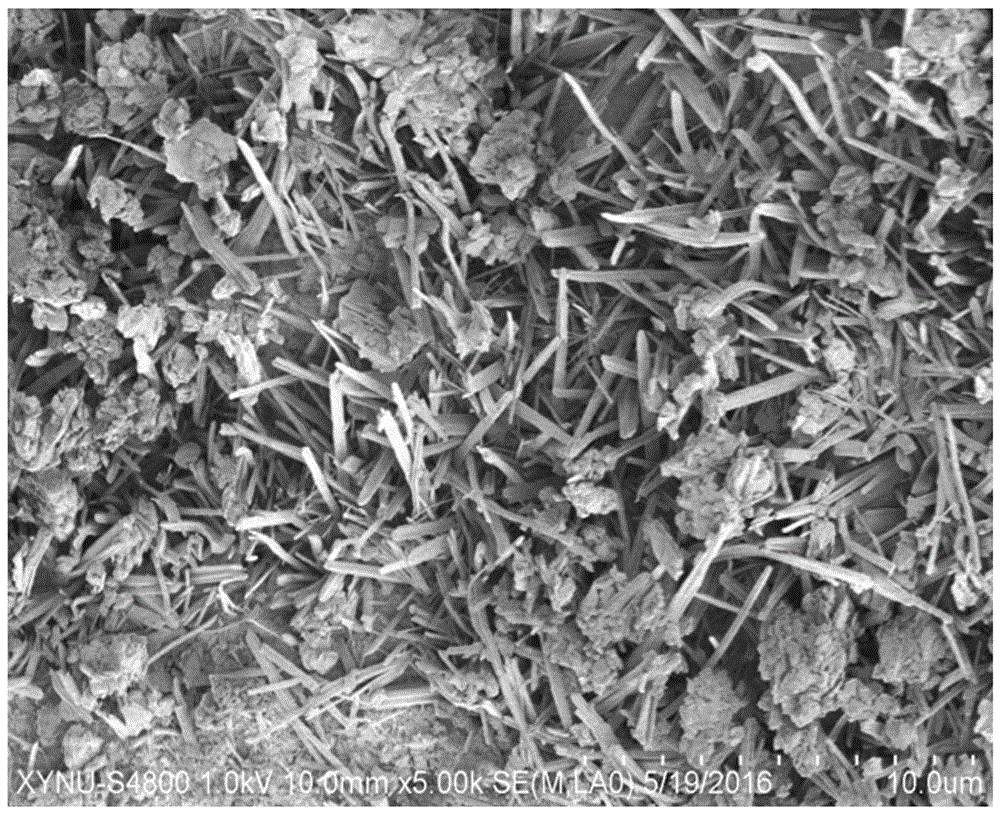
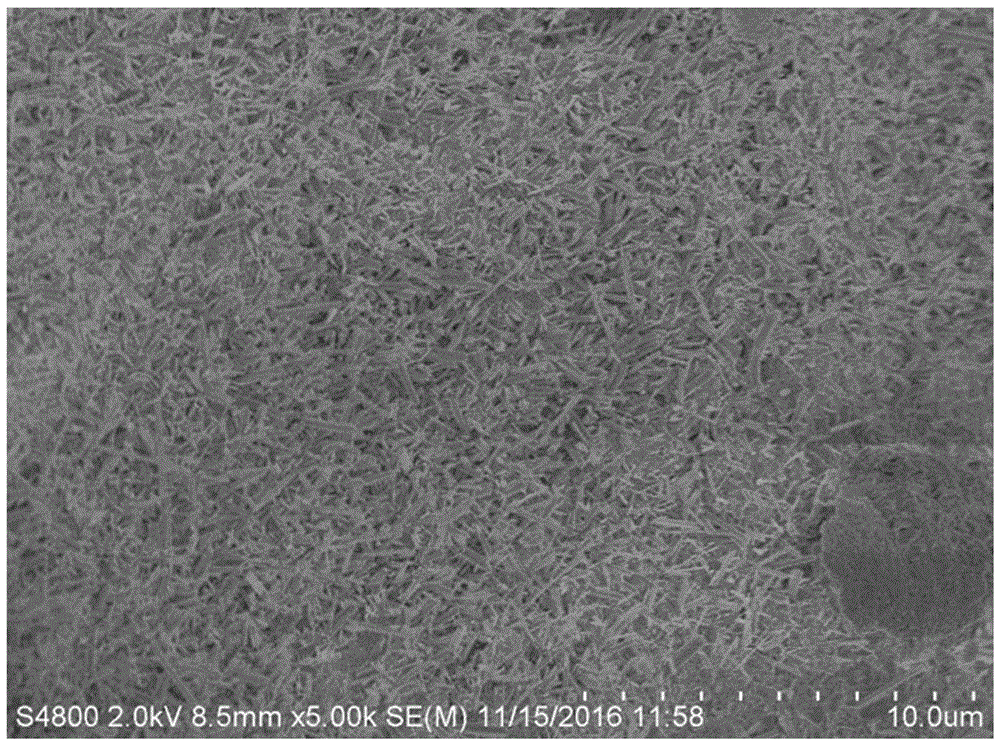
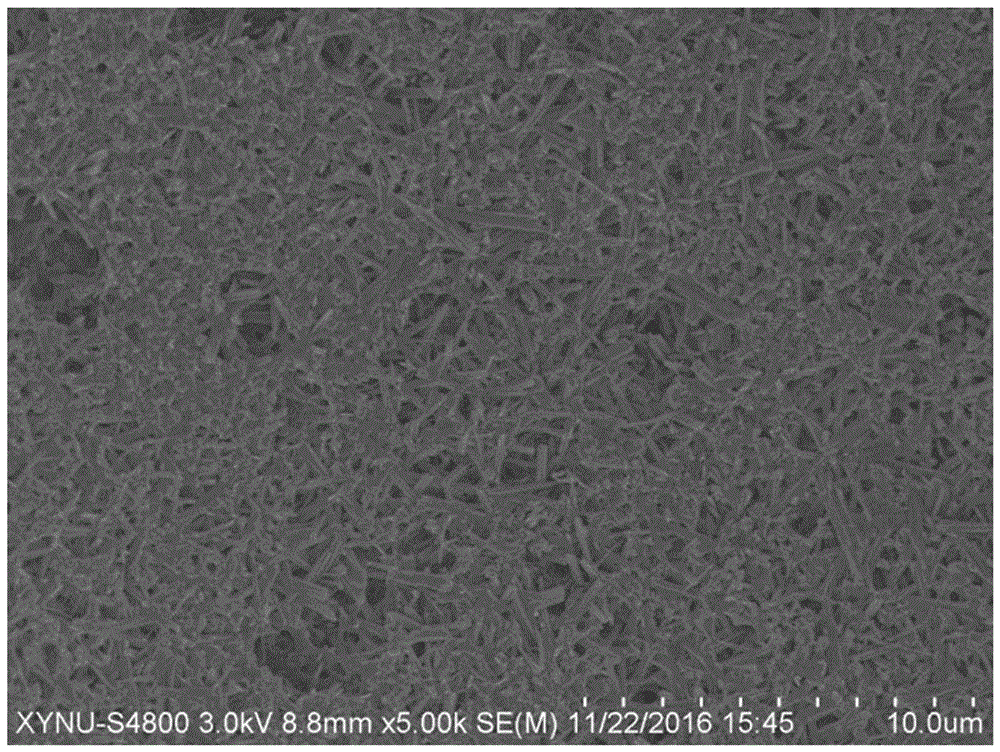
[0044] figure 1 Is the micro-topography of the unmodified sample, figure 2 It is 0.6% tetraethyl orthosilicate and 3% pullulan modified sample. Compare figure 1 , figure 2 It can...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com