Method for selectively removing one valent anion impurities from sulfuric acid system electrolytes
An anionic impurity, sulfuric acid system technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of fluorine and chlorine accumulation, low reliability, waste of Zn resources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
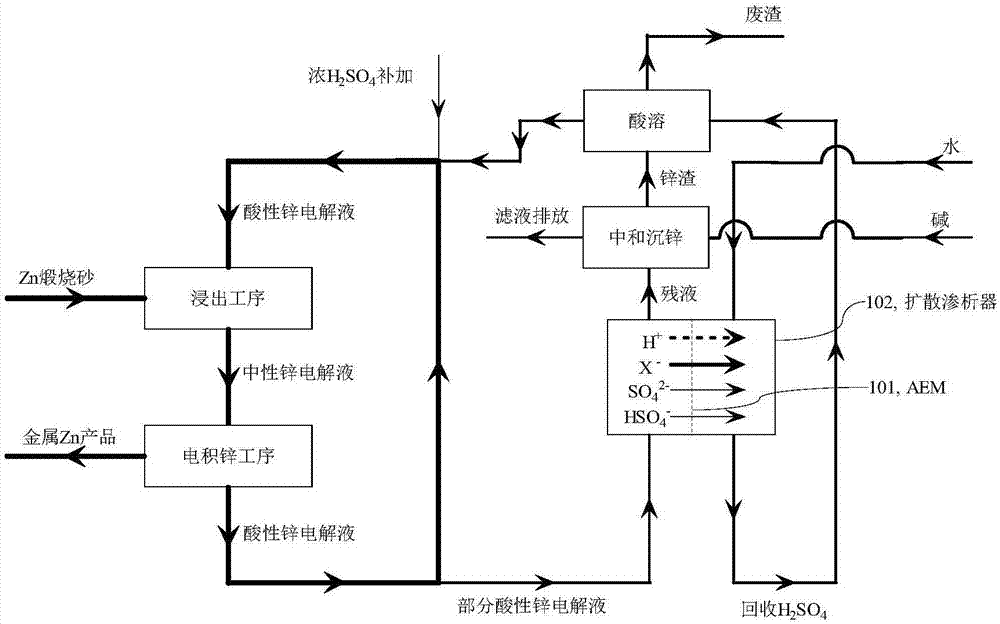
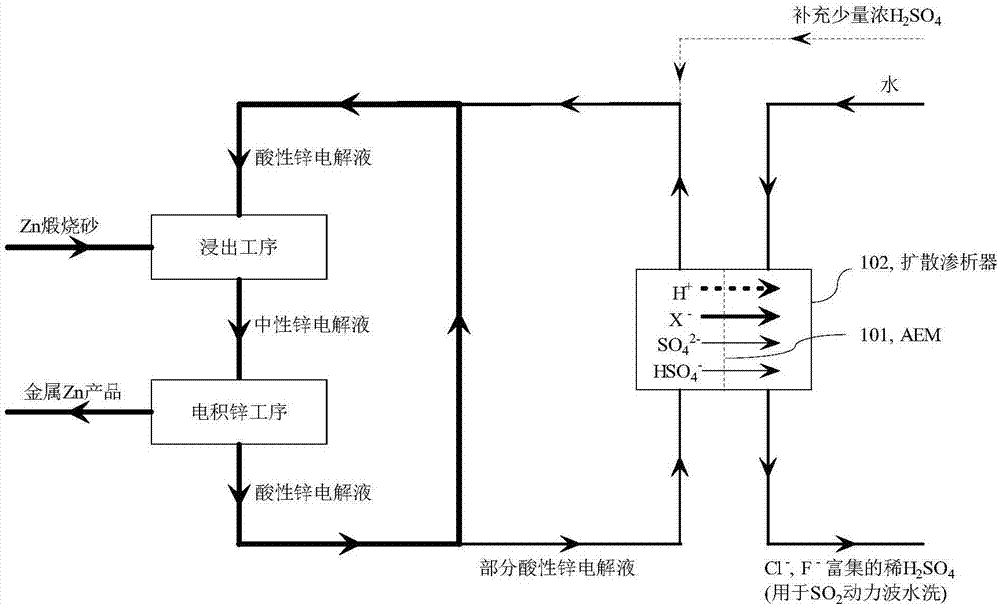
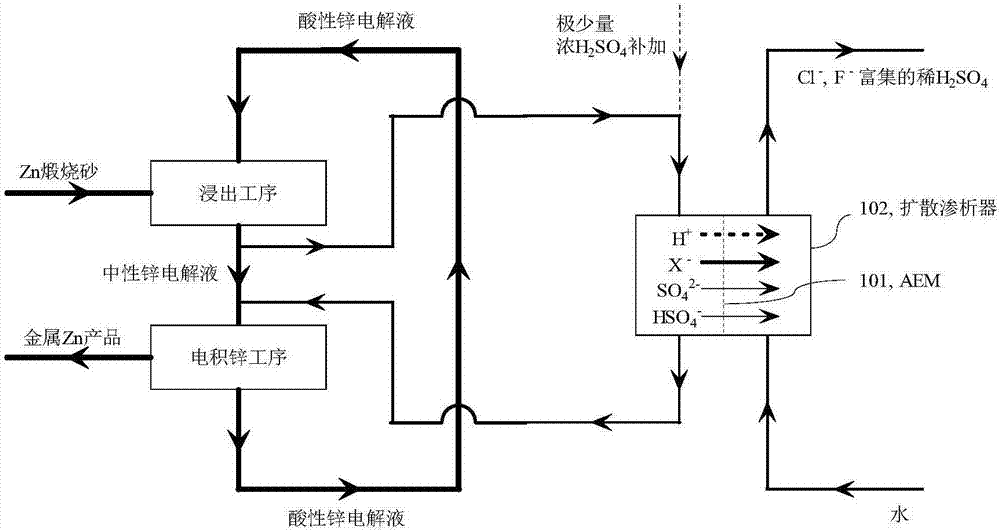
[0046] Embodiment 1: Taking the typical electro-zinc process flow of 240,000 tons of metal zinc as an example with an annual production scale, the circulation volume required for the main circulation of its zinc electrolyte is about 8,000 tons / day; in order to maintain the stability of chlorine impurities, it is necessary to discharge The acid electrolyte is 200 tons / day. That is to say, in order to achieve chlorine balance, the total amount of chlorine impurities that production enterprises need to remove every day is about 200 tons of all chlorine impurities contained in the acid electrolyte. If Cl ‐ The removal rate is lower than 100%, and the same Cl can be achieved by increasing the bypass purification process ‐ Removal. The typical acidic electrolyte composition in the current process is Zn 2+ 58g / L, SO 4 2‐ 365g / L, H + with H 2 SO 4 160g / L, Cl ‐ 540mg / L, F ‐ 120mg / L. The diffusion dialysis test uses the TWDDA anion exchange membrane of Shandong Tianwei Membra...
Embodiment 21
[0059] Example 21: Taking the neutral electrolyte of the electric zinc factory in Example 1 as an example, the composition of the neutral zinc electrolyte is Zn 2+ 158g / L, SO 4 2‐ 365g / L, Cl ‐ 540mg / L, F ‐ 120mg / L, pH 5.5 (free H + concentration is 0). The diffusion dialysis test uses the TWDDA anion exchange membrane of Shandong Tianwei Membrane Technology Co., Ltd. to simulate image 3 in the purification process. Take 50L of the acidic electrolyte, add 98% concentrated sulfuric acid thereinto, the concentration is 5.0g / L. The acidity-adjusted electrolyte and pure water (or tap water) are passed into the diffusion dialyzer in a reverse flow manner, the flow ratio of the electrolyte to water is controlled to be 1:1, and the operating flow rate is 5.0L h ‐1 m ‐2 , after the system reached steady state operation, it was found that Cl in the acidic zinc electrolysis ‐ The removal rate reached 49.0%, F ‐ The removal rate reached 30.4%, SO 4 2‐ The loss rate is 0.80%, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com