Method for rapidly flaking hibiscus rosa-sinensis fiber
A fibrous, fast technology, applied in the field of biological non-slicing slices, which can solve the problems of difficult to observe, incomplete fiber structure, long time consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
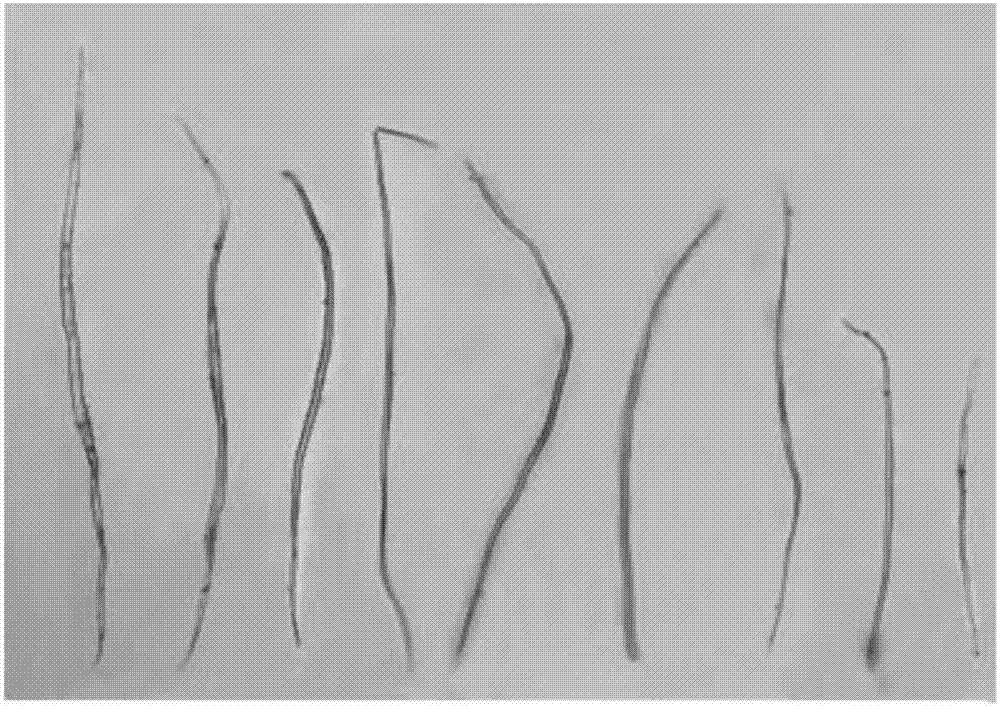
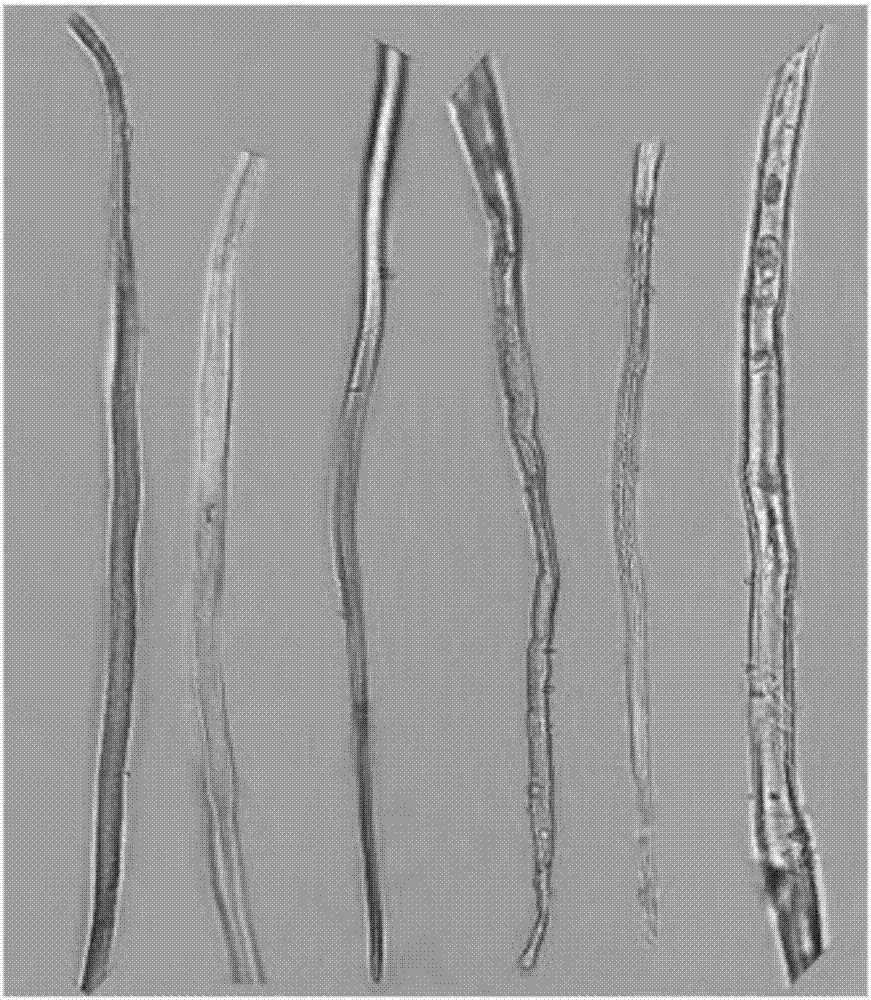
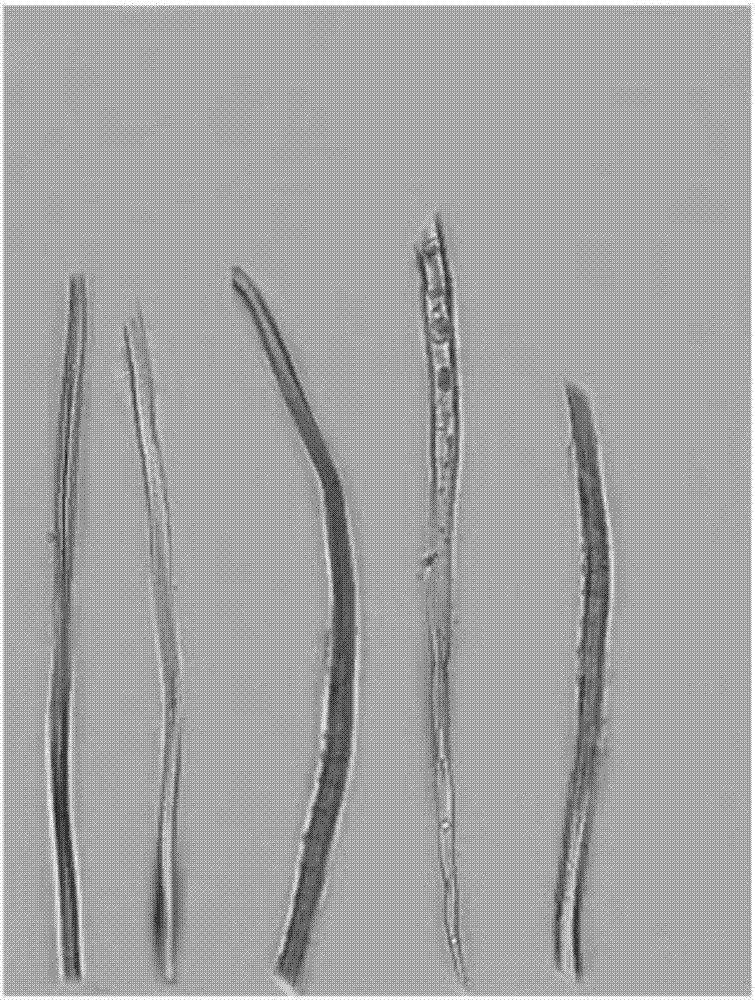
[0022] Use scissors to cut the old branches of hibiscus more than two years old, peel off the bark, soak the bark in a mixed solution of 15% potassium dichromate and 8% nitric acid by mass percentage, boil for 60min, and then add 10% by mass Hydrogen peroxide and 50% acetic acid mixture 20ml, continue to boil for 30min. Use tweezers to clip the treated plant tissue into a petri dish filled with clear tap water, pick out the plant fiber with a dissecting needle, place it on a clean glass slide, and drop 0.5-1ml of 0.1% safranin staining solution Dyeing for 10min. Then wash off excess safranin staining solution with 70% alcohol, then add 0.5-1ml of 50% glycerol dropwise, and cover with a cover slip to complete the mounting. Observe the plant fiber structure under an electron microscope. The result is as Picture 1-1 , Figure 1-2 , Figure 1-3 .
Embodiment 2
[0024] Use scissors to cut the old branches of hibiscus more than two years old, peel off the bark, soak the bark in a mixed solution of 20% potassium dichromate and 10% nitric acid by mass percentage, boil for 90min, and then add 12% by mass Hydrogen peroxide and 60% acetic acid mixture 10ml, continue to boil for 30min. Use tweezers to clip the treated plant tissue into a petri dish filled with clear tap water, pick out the plant fiber with a dissecting needle, place it on a clean glass slide, and drop 0.5-1ml of 0.1% safranin staining solution Dyeing for 10min. Then wash off excess safranin staining solution with 70% alcohol, then add 0.5-1ml of 50% glycerol dropwise, and cover with a cover slip to complete the mounting. Observe the plant fiber structure under a biological microscope. Observe the plant fiber structure under a biological microscope. The result obtained by this method is not much different from the result obtained in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Cut the old branches of Hibiscus hibiscus more than two years with scissors, peel off the bark, soak the bark in the mixed solution of 25% potassium dichromate and 15% nitric acid by mass percentage, boil for 60-90min, and then add the mass percentage of Pour off the mixed solution of 25% potassium dichromate and 15% nitric acid, then add 10-20ml of mixed solution of 15% hydrogen peroxide and 65% acetic acid in mass percentage, and continue boiling treatment for 30-60min. Use tweezers to clip the treated plant tissue into a petri dish filled with clear tap water, pick out the plant fiber with a dissecting needle, place it on a clean glass slide, and drop 0.5-1ml of 0.1% safranin staining solution Dyeing for 10min. Then wash off excess safranin staining solution with 70% alcohol, then add 0.5-1ml of 50% glycerol dropwise, and cover with a cover slip to complete the mounting. Observe the plant fiber structure under a biological microscope. The result obtained by this me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com