A method for producing high-concentration ferrate by step-by-step electrolysis
A ferrate, high concentration technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of low ferrate concentration, easy passivation of electrodes, and low current efficiency, and achieve high product concentration, high reaction efficiency, and high current efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
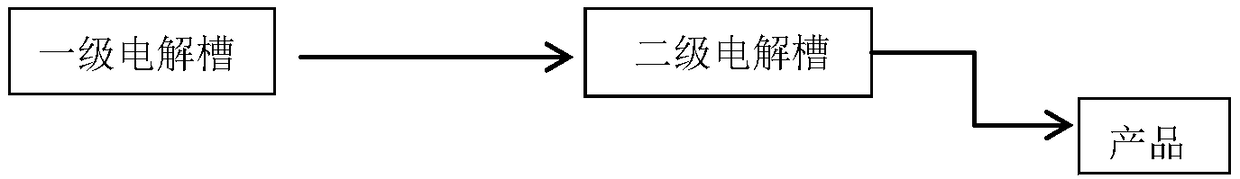
[0023] Embodiment 1 The structure of the secondary electrolyzer of the present invention
[0024] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the secondary electrolysis device of the present invention is given. Both electrolyzers have the same structure as the electrolyzers of the prior art. The cathodic chamber and the anode chamber are separated by perfluorinated cation exchange membranes, barbed wire or other iron materials are used as anodes, and nickel mesh or other metal materials are used as cathodes. , passing direct current between the anode and cathode. The first-stage electrolytic cell uses sodium hydroxide as the electrolyte, and the second-stage electrolytic cell starts to use the sodium hydroxide and ferrate obtained by electrolysis in the first-stage electrolytic cell as the raw material anolyte, and still uses sodium hydroxide as the catholyte. Continue electrolysis. The raw material anolyte can be transported from the first-stage electrolyzer to the second-stage electr...
Embodiment 2
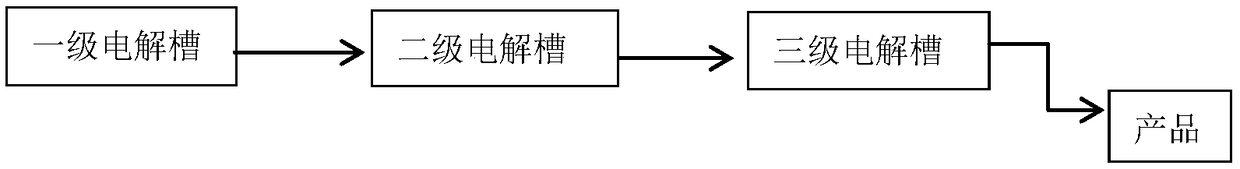
[0025] Embodiment 2 The structure of the three-stage electrolyzer of the present invention
[0026] figure 2 A schematic diagram of the three-stage electrolysis device of the present invention is given. Three electrolytic cells all have the same structure as the electrolytic cell of the prior art, and the specific structure is the same as that of embodiment 1. The first-stage electrolyzer uses sodium hydroxide as the electrolyte, the second-stage electrolyzer uses the sodium hydroxide and ferrate obtained by electrolysis in the first-stage electrolyzer as raw material anolyte, and the third-stage electrolyzer uses the second-stage electrolyzer The sodium hydroxide and ferrate obtained by electrolysis in the tank are used as the raw material anolyte, and the three electrolytic cells all use sodium hydroxide as the catholyte for electrolysis. The raw material anolyte obtained by the electrolysis of the first and second electrolyzers is transported by a pump, or circulated by ...
Embodiment 3
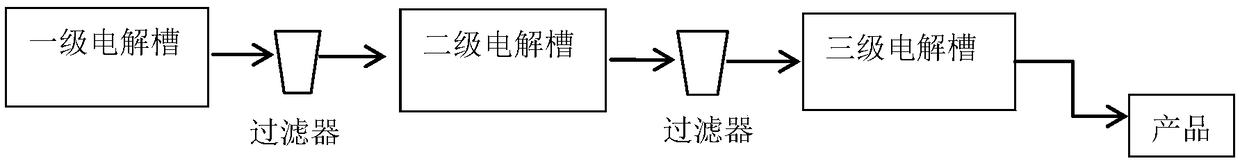
[0027] Embodiment 3 Production technique of the present invention and the comparison of prior art
[0028] Using electrolyzers and electrodes of the same structure and size, under the same current and water bath temperature, under the same electrolyte volume flow rate, that is, the same output, using the production device technology of the present invention, the product concentration is the same as that of the original first-level electrolysis About 2 times more than the tank process. For example a secondary or tertiary electrolytic process of the present invention (asfigure 1 , figure 2 ) compared with the original one-stage electrolysis process: the anode volume of the electrolytic cell is 150mL, at 48°C, the current density is 40mA / cm 2 , the material flow rate of the anolyte is 2.5mL / min, that is, the residence time in the anode chamber of each electrolytic cell is 1 hour, and with electrodes of the same material, structure, and size, regardless of whether the primary, s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com