Negative electrode material phosphorus-sulfur double-doped hard carbon microsphere for sodium ion battery and preparation method of negative electrode material
A sodium-ion battery and negative electrode material technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve problems such as poor rate performance, capacity fading, and low discharge platform potential, and achieve good charge and discharge performance, large reversible capacity, and small capacity fading.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Pour 37mL of 1 mol / L sucrose solution into a 50mL hydrothermal kettle and keep it at 190°C for 5 hours to obtain the product after hydrothermal reaction. The hydrothermal product was washed and dried, and then kept in a tube furnace at 1000°C for 5h. After cooling down, the product was evenly mixed with elemental sulfur and elemental phosphorus at a ratio of 8:4:1, then kept in a tube furnace at 400°C for 5 hours, and the final product was obtained after cooling down.
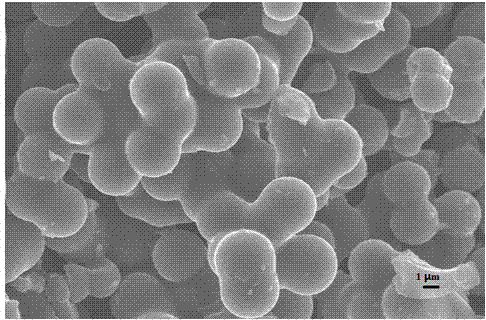
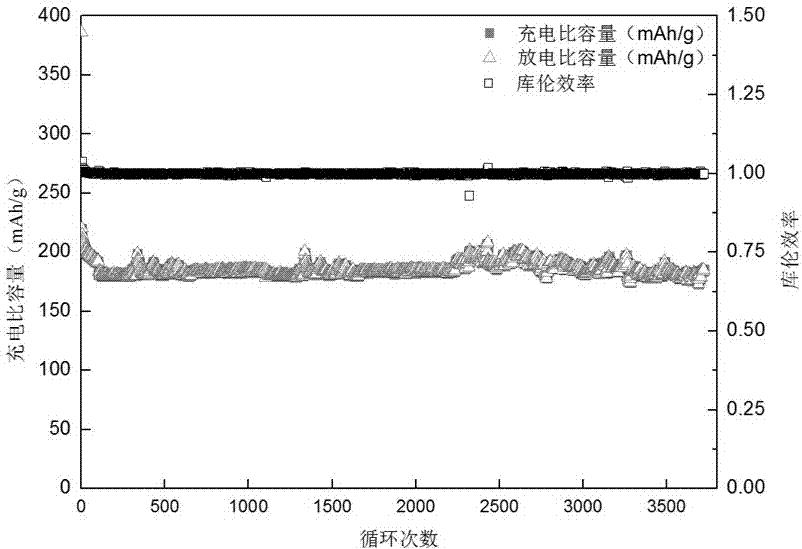
[0021] Scanning electron microscope characterization results showed that the product was a sphere with a diameter between 3-10 μm. The product was used as a working electrode, and a high-purity sodium block was used as a counter electrode to assemble a simulated battery. The electrolyte is 1MNaClO 4 +EC / DEC (the volume ratio of EC to DEC is 1 / 1), and the battery assembly is carried out in an argon-filled dry box. The charging and discharging of the battery is carried out on the Land battery test syste...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Pour 40 mL of 0.5 mol / L sucrose solution into a 50 mL hydrothermal kettle and keep it at 190°C for 3 h to obtain the product after hydrothermal reaction. The hydrothermal product was washed and dried, and then kept in a tube furnace at 1000 °C for 5 h. After cooling down, the product was evenly mixed with elemental sulfur and elemental phosphorus at a ratio of 4:2:1, and then kept in a tube furnace at 400 °C for 3 h, and the final product was obtained after cooling down.
[0024] Scanning electron microscope characterization results showed that the product was a sphere with a diameter between 3-10 μm. The product was used as the working electrode, and the high-purity sodium block was used as the counter electrode to assemble a simulated battery. The electrolyte is 1M NaClO 4 +EC / DEC (the volume ratio of EC to DEC is 1 / 1), and the battery assembly is carried out in an argon-filled dry box. The charging and discharging of the battery is carried out on the Land battery ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Pour 37mL of 1 mol / L sucrose solution into a 50mL hydrothermal kettle and keep it at 180°C for 5 hours to obtain the product after hydrothermal reaction. The hydrothermal product was washed and dried, and then kept in a tube furnace at 1000 °C for 5 h. After cooling down, the product was uniformly mixed with elemental sulfur and elemental phosphorus at a ratio of 4:1:1, and then kept in a tube furnace at 400 °C for 7 h, and the final product was obtained after cooling down.
[0027] Scanning electron microscope characterization results showed that the product was a sphere with a diameter between 3-10 μm. The product was used as the working electrode, and the high-purity sodium block was used as the counter electrode to assemble a simulated battery. The electrolyte is 1M NaClO 4 +EC / DEC (the volume ratio of EC to DEC is 1 / 1), and the battery assembly is carried out in an argon-filled dry box. The charging and discharging of the battery is carried out on the Land batte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com