Method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil by nanometer zero-valent iron
A nano-zero-valent iron and contaminated soil technology, applied in the field of environmental remediation, can solve the problems of little soil remediation effect, achieve the effect of reducing leaching toxicity and bioavailability, small time and economic cost, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
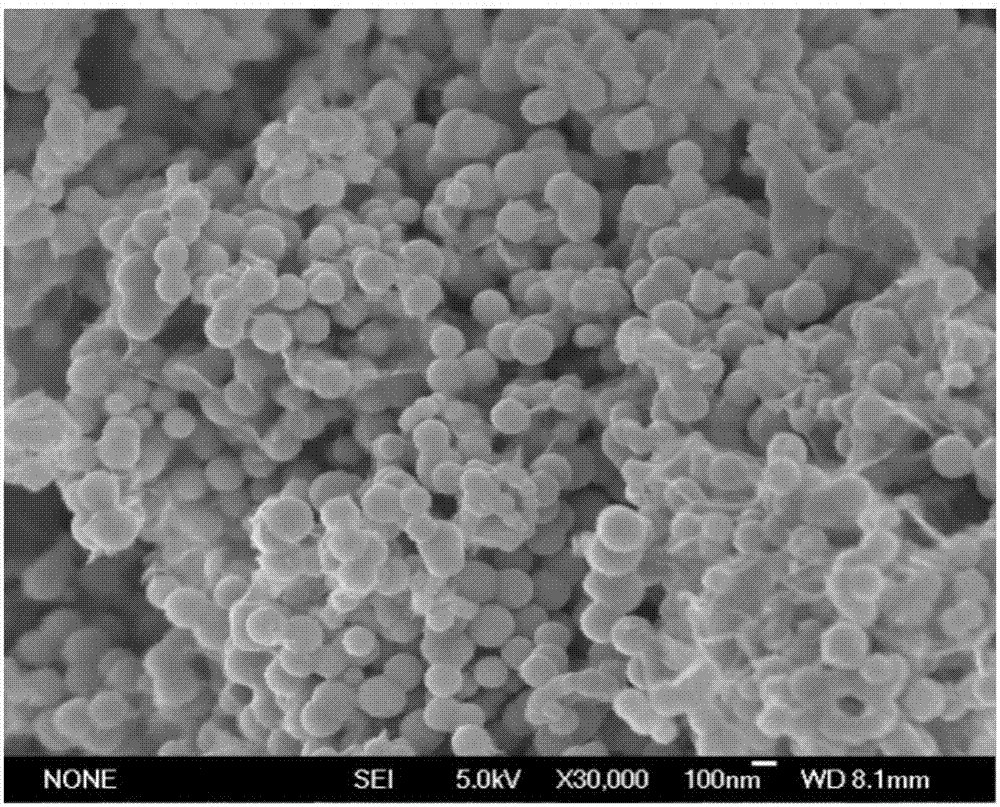
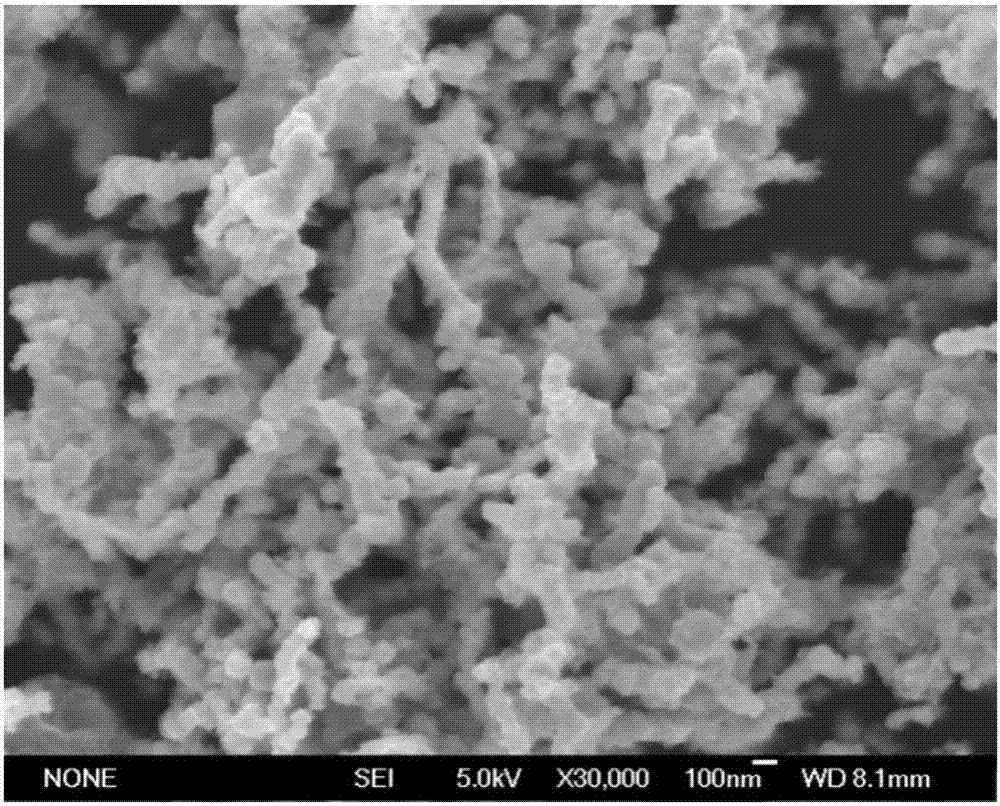
[0035] A nanometer zero-valent iron stabilized by sodium carboxymethylcellulose of the present invention is prepared by the following method:
[0036] (1) Nitrogen gas was passed through ultrapure water for 20 minutes to remove dissolved oxygen as a solvent for preparing the solution.
[0037] (2) Weigh 0.6g of sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) in 100mL of water, seal and heat it in a water bath at 65°C, shake continuously to dissolve it, and after it cools down, deoxidize it with nitrogen for 20 minutes to obtain carboxymethylcellulose sodium solution.
[0038] (3) Weigh 7.4464g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in 250mL water to obtain 0.107M FeSO 4 solution. Weigh 2.0266gNaBH 4 Dissolve in 250mL water to get 0.214M NaBH 4 solution.
[0039] (4) Take 25mL of FeSO with a concentration of 0.107M 4 The solution was immediately added to a 250mL three-neck flask equipped with 100mL sodium carboxymethylcellulose solution, and stirred while blowing nitrogen to obtain CMC-Fe 2...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A method for repairing heavy metal-contaminated soil through sodium carboxymethylcellulose-stabilized nano zero-valent iron of embodiment 1, comprising the following steps:
[0049] (1) Taken from the surface soil (0-25cm) on the banks of the Xiangjiang River in Changsha City, Hunan Province, and carried out pretreatment: remove impurities such as stones, branches and leaves, and pass through a 2mm sieve. The pH of the pretreated surface soil was 7.6, and the local contents of heavy metals Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn in the soil were 22.5mg / kg, 167.10mg / kg, 30.25mg / kg, and 26.17mg / kg, respectively.
[0050] In order to make the experimental effect more obvious, four kinds of soil samples were designed by adding standard in heavy metal soil. The specific steps are as follows:
[0051] Cd-contaminated soil: Add heavy metal cadmium to the surface soil after the above pretreatment, so that the content of cadmium reaches 500mg / kg.
[0052] Pb-contaminated soil: Add heavy metal lead ...
Embodiment 3
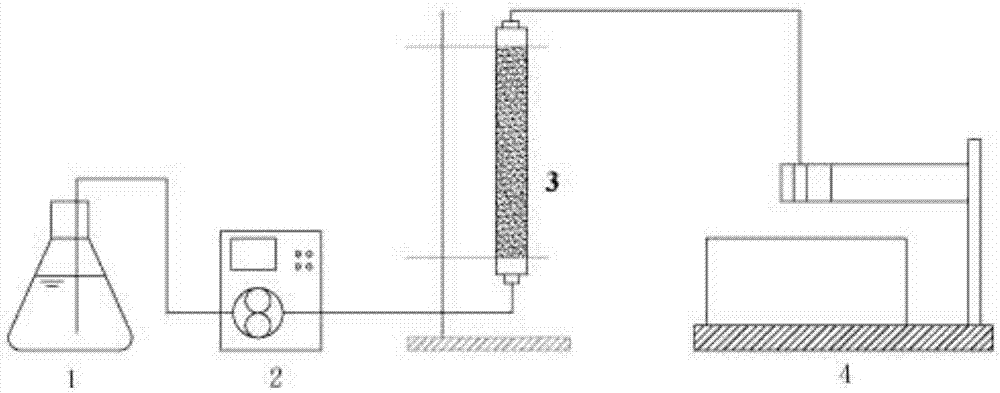
[0072] A method adopting the stable nanometer zero-valent iron of embodiment 1 to remediate heavy metal-contaminated soil, the stable nanometer zerovalent iron made in embodiment 1 is passed into the soil contaminated with cadmium with a migration velocity of 0.0009cm / s respectively (Cadmium-contaminated soil composition is the same as embodiment 2) in the glass fiber reinforced plastic column (glass fiber reinforced plastic column specification and soil filling amount are identical with embodiment 2), pass into volume and be 6~10PV, collect effluent with part collector. The remediation effect is evaluated by the leaching toxicity test and bioavailability test of heavy metals in the soil after remediation, and the specific steps are the same as in Example 2. For inspection results, see Figure 4 .
[0073] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that with the increase of the volume of the stable nano-zero-valent iron suspension, the leaching toxicity and bioavailability treatment...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com